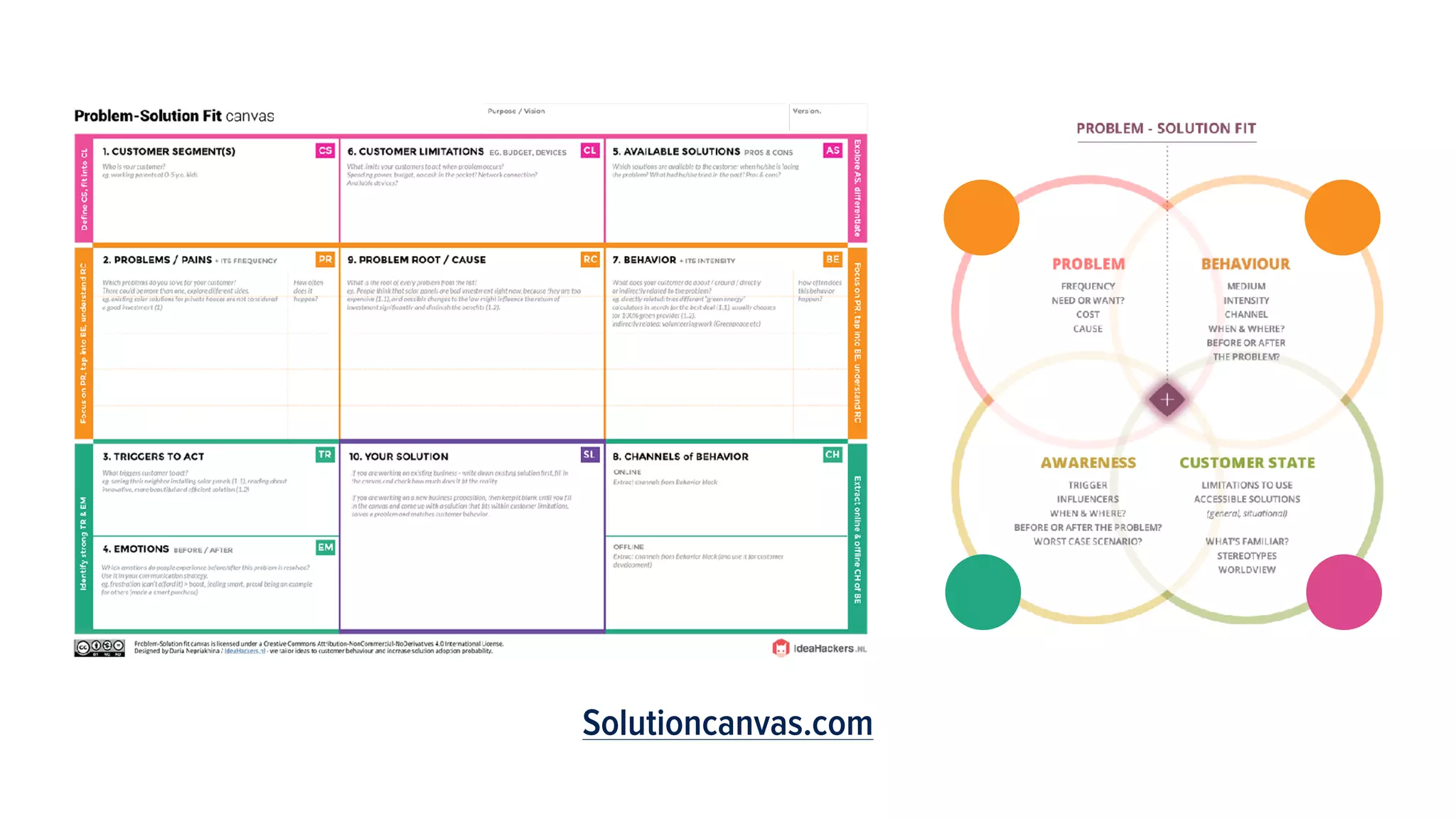
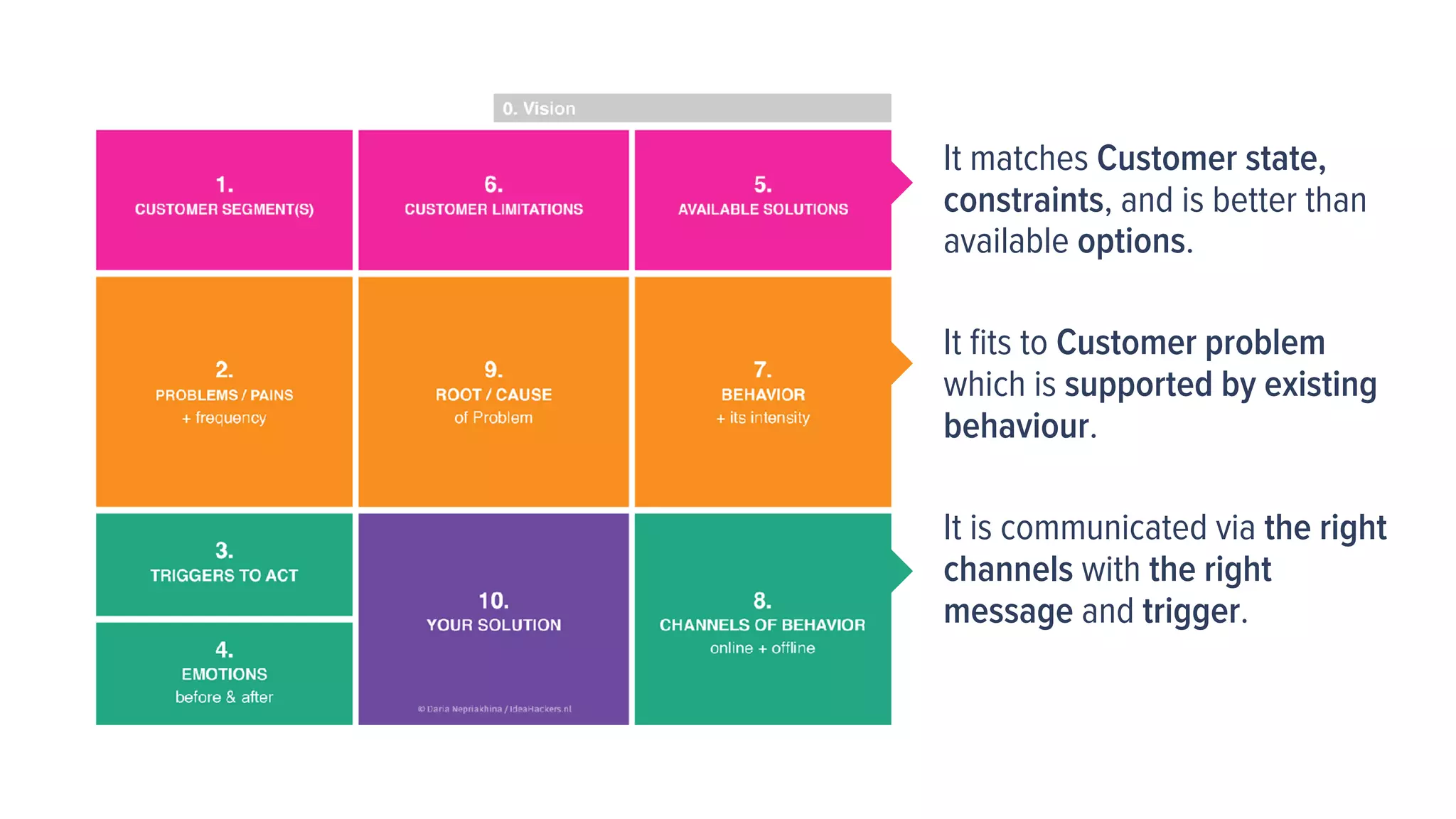
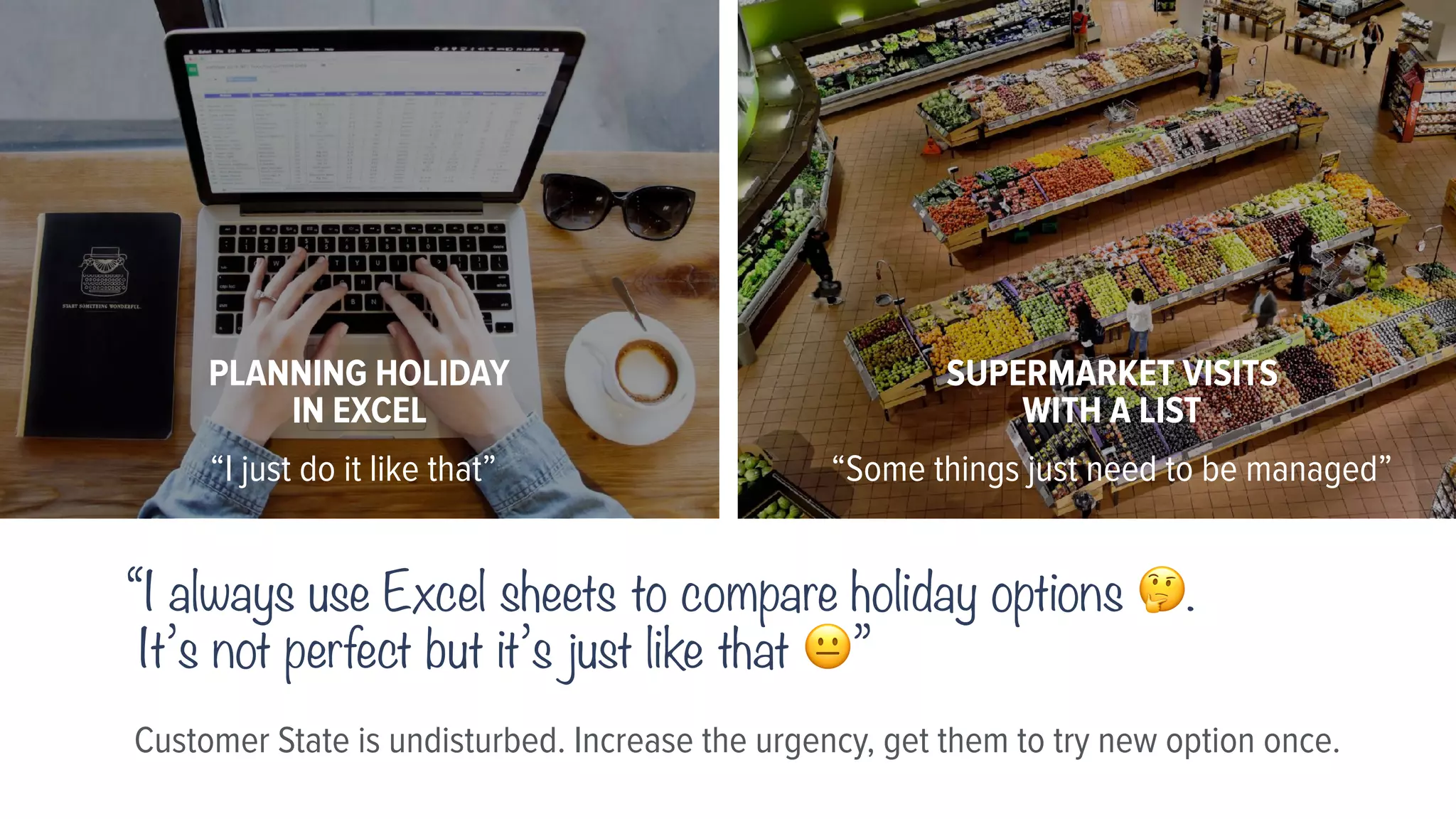
This document provides guidance on understanding customers and their problems. It emphasizes the importance of understanding the customer's perspective and context in order to design effective solutions. It introduces the "lazy user model" which describes how customers select solutions based on the lowest effort. The document also provides a framework to analyze a customer's state, constraints, behaviors, triggers, and problems in order to identify opportunities and strategies to solve problems in a way that fits the customer.