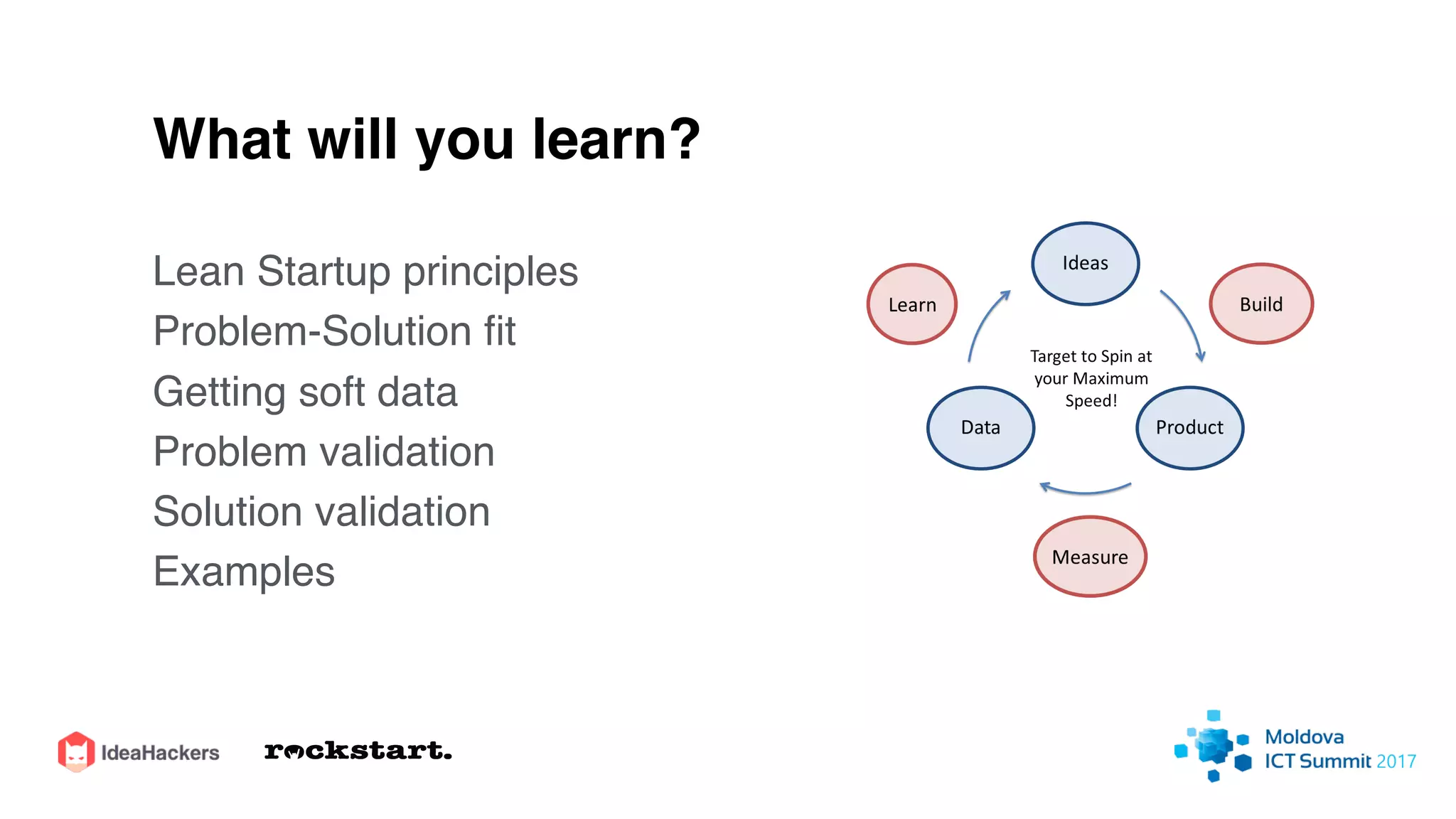
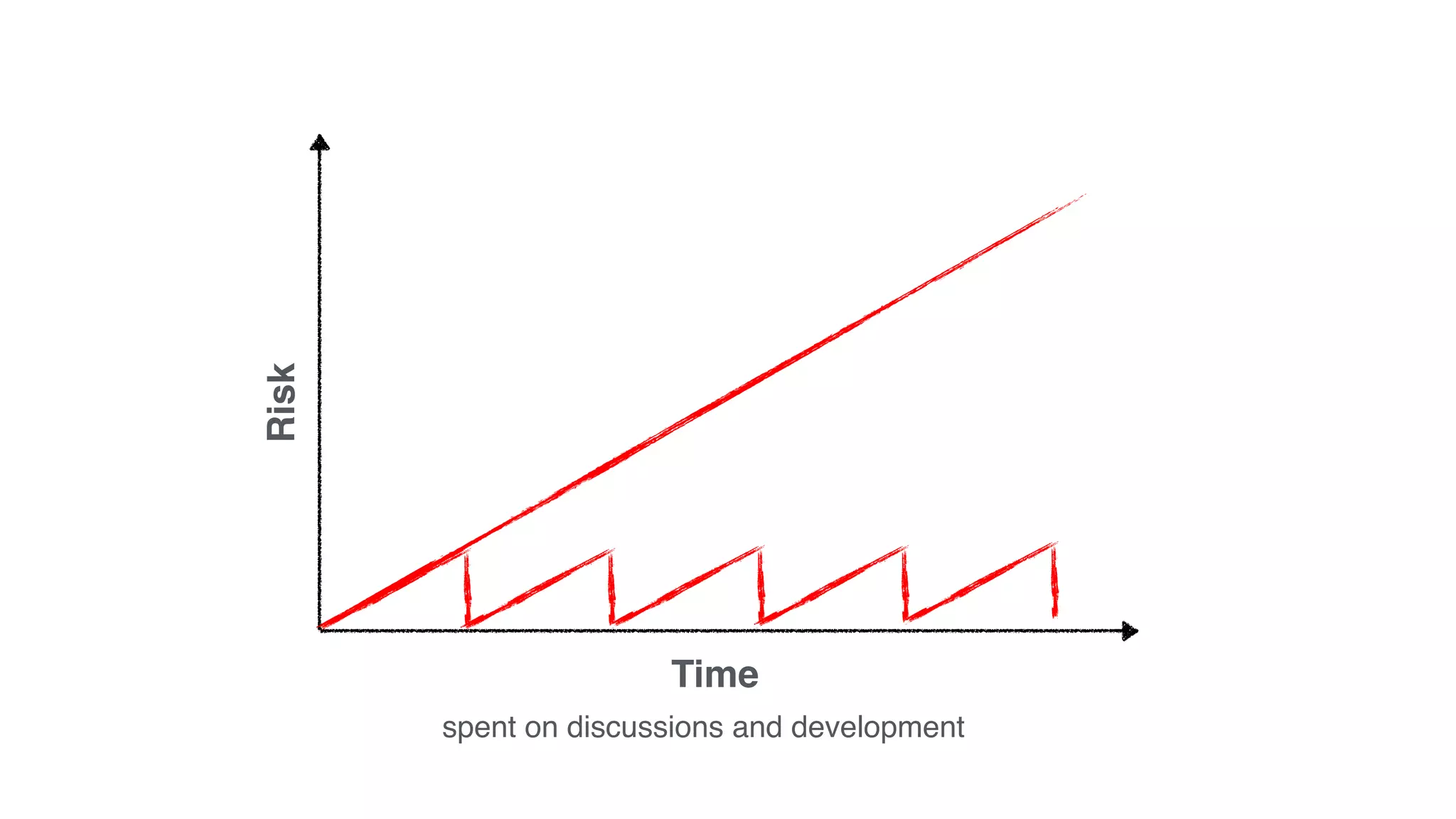
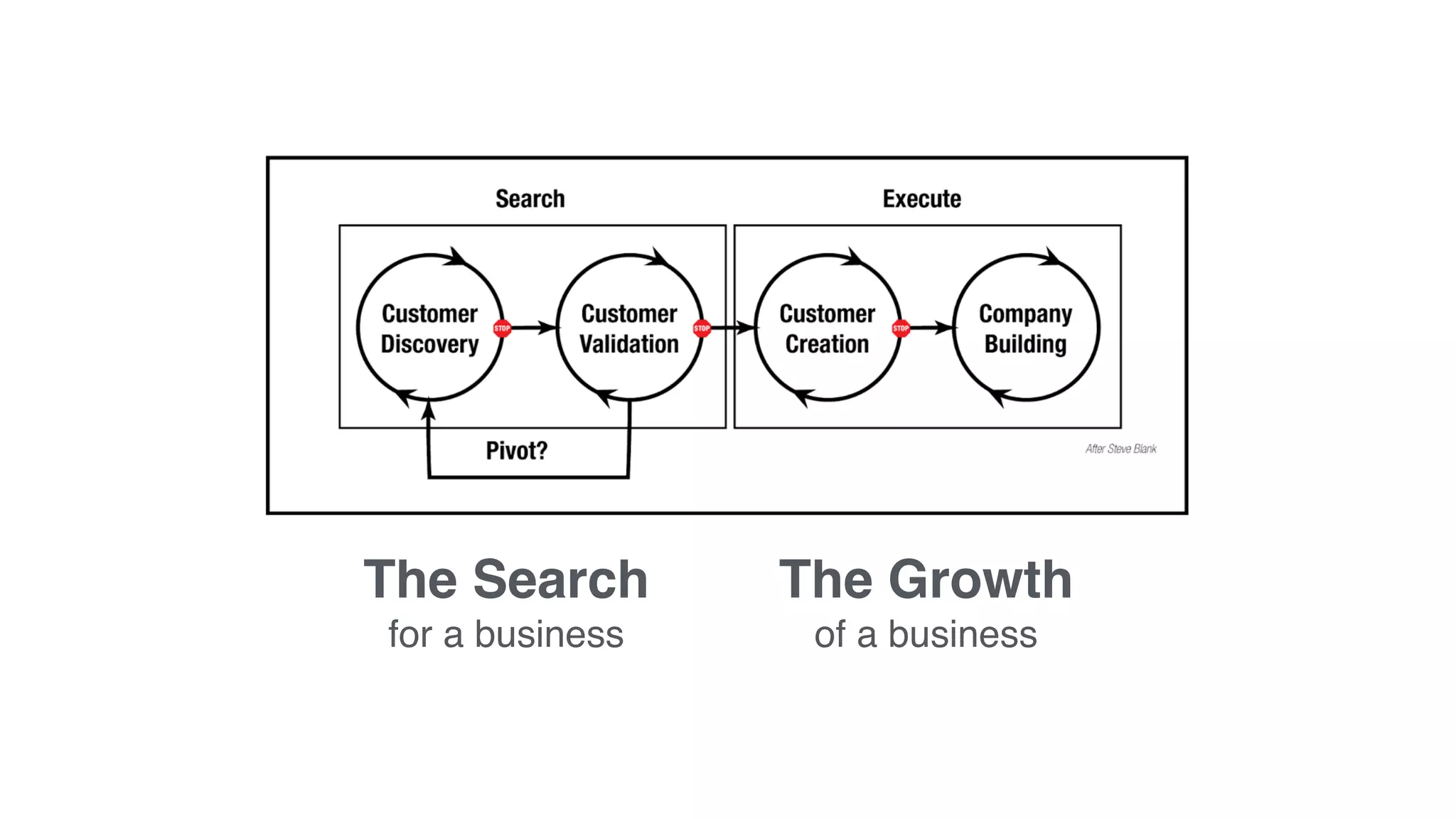
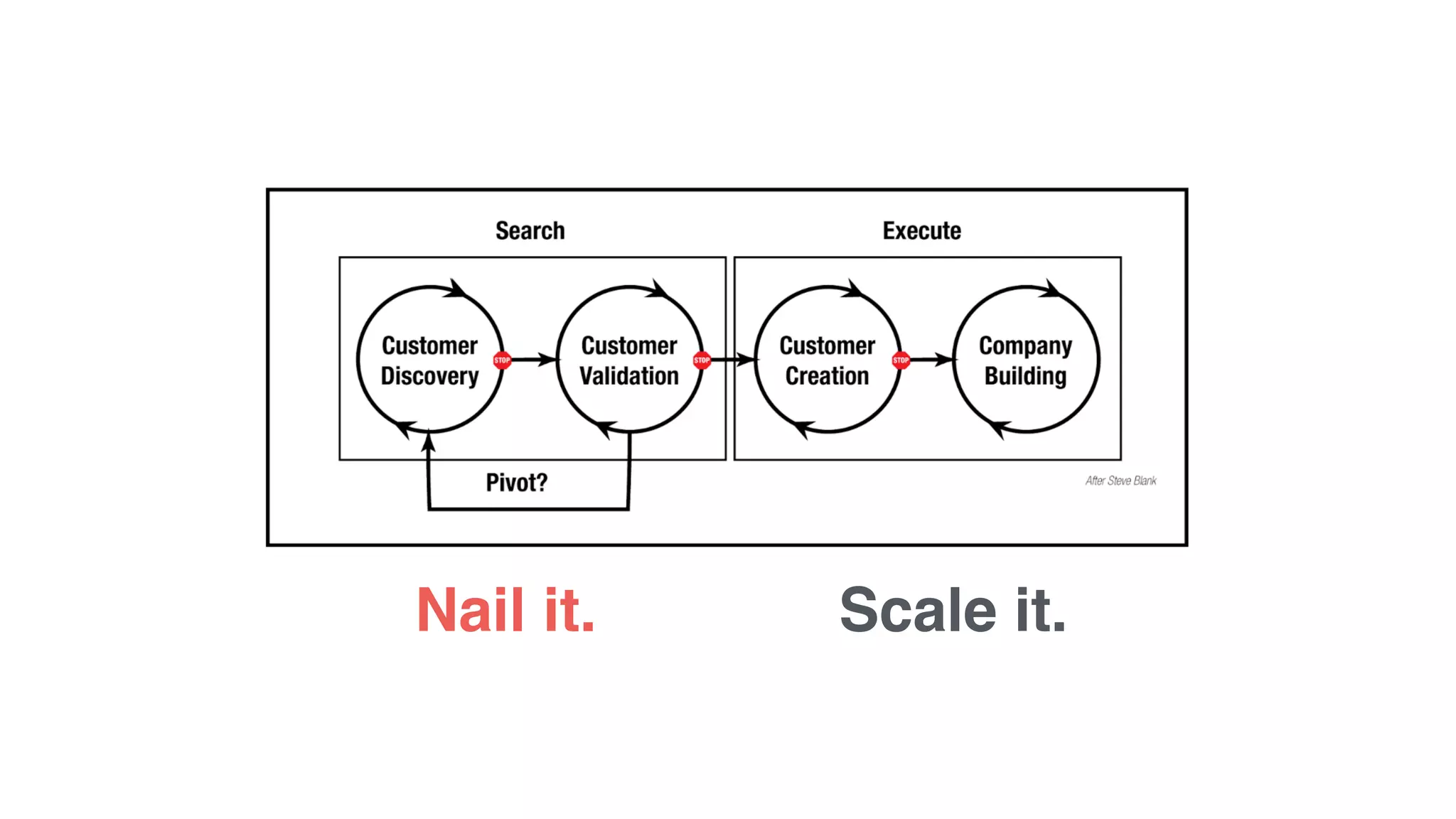
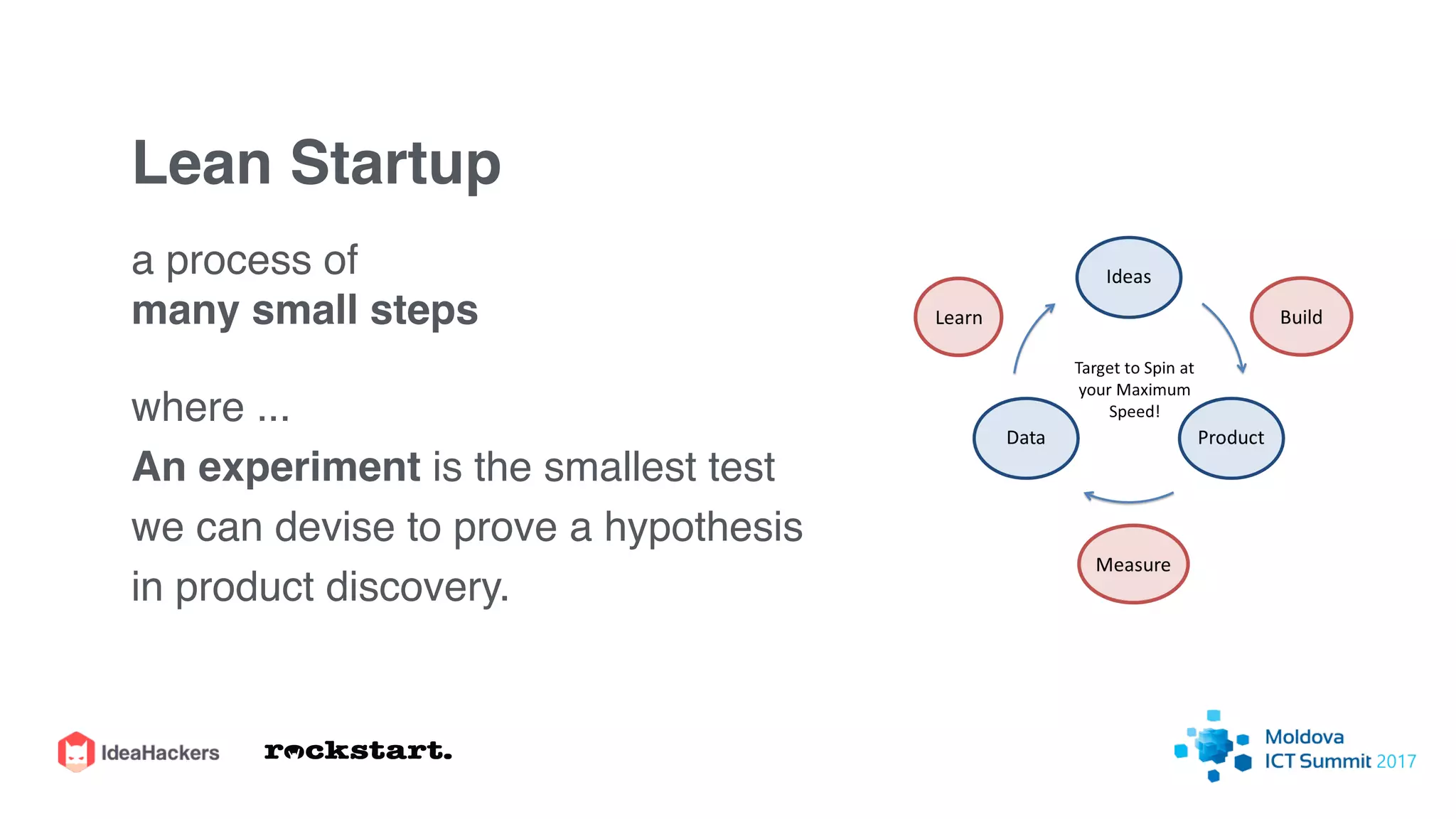
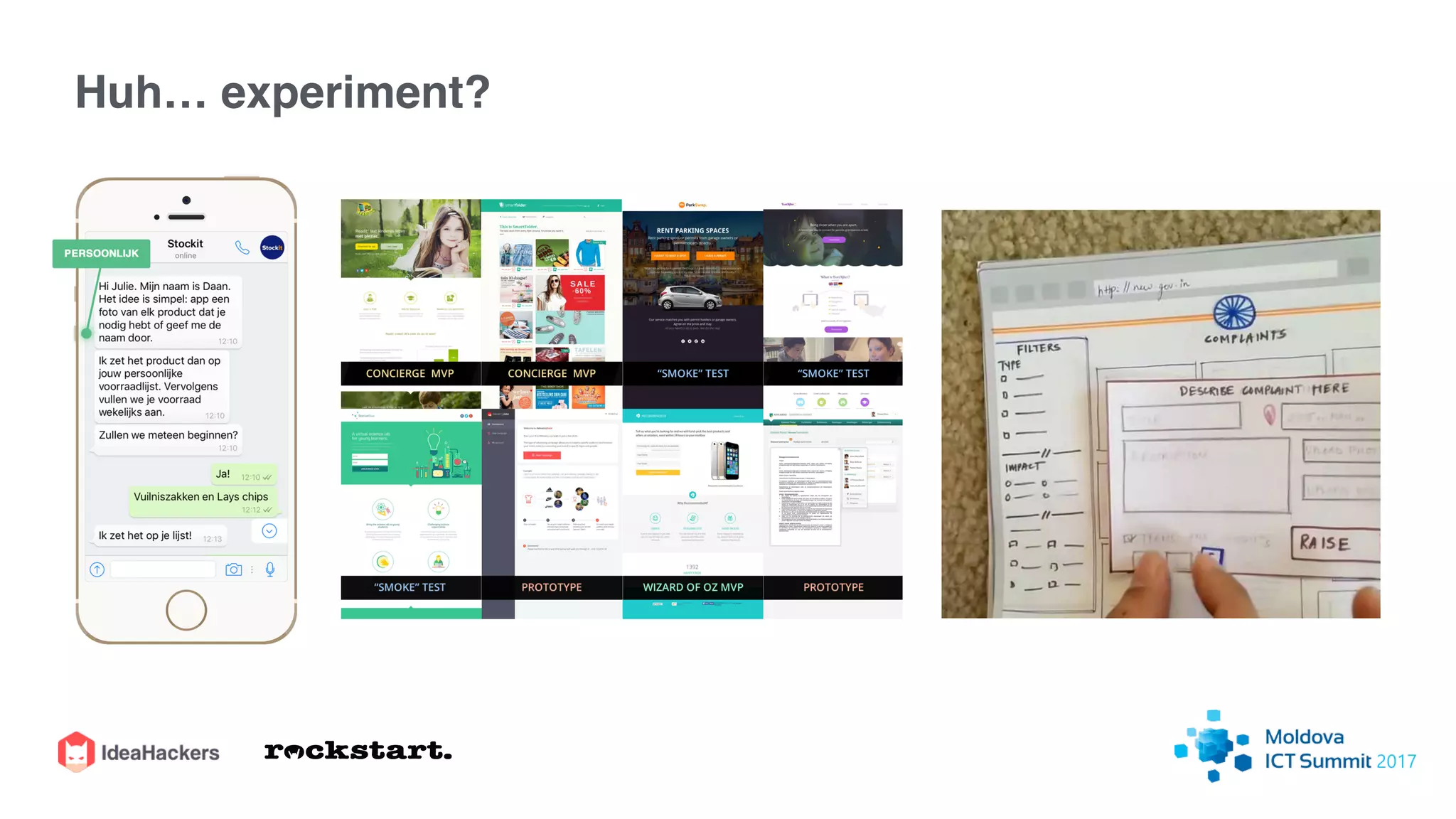
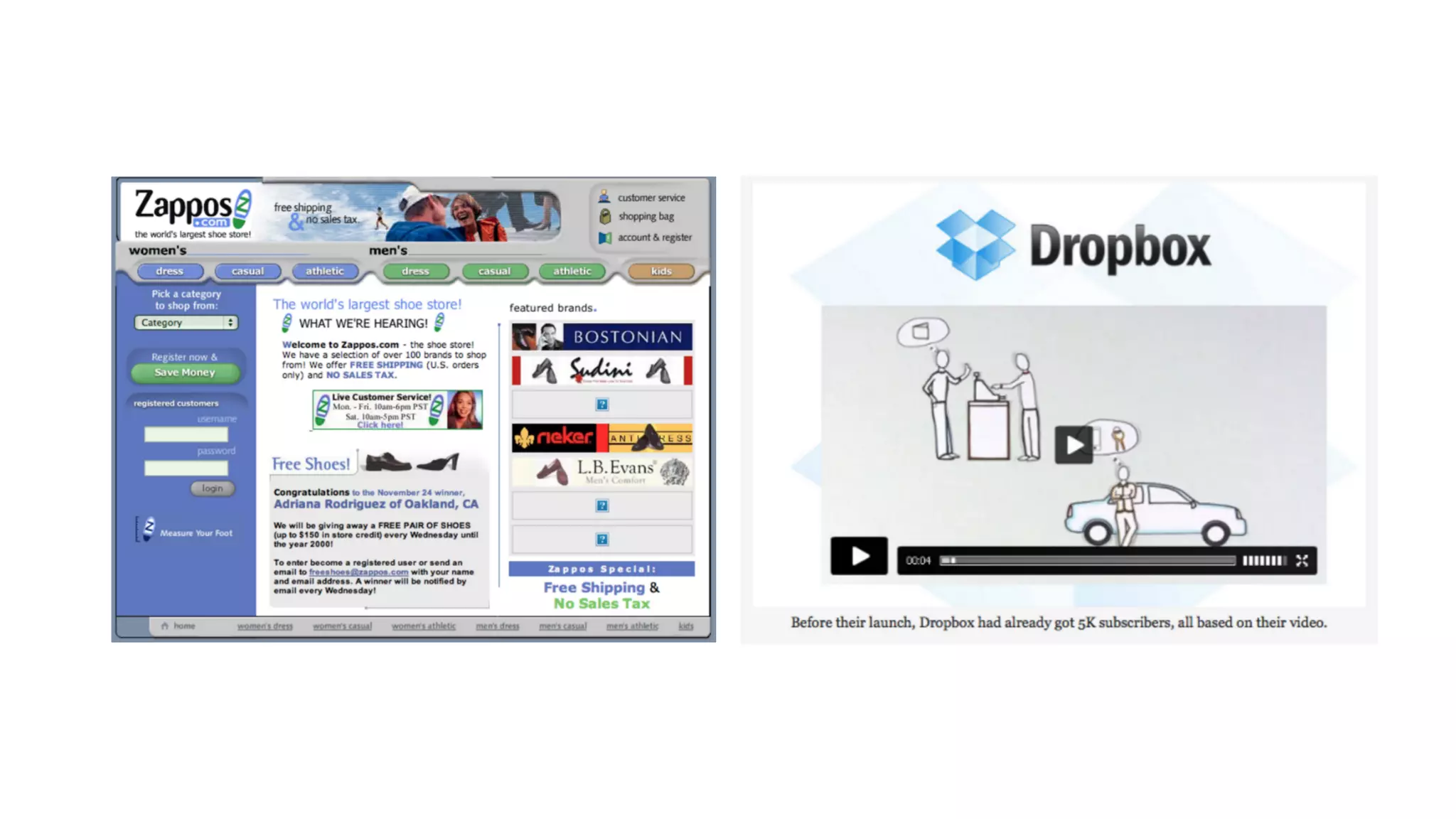
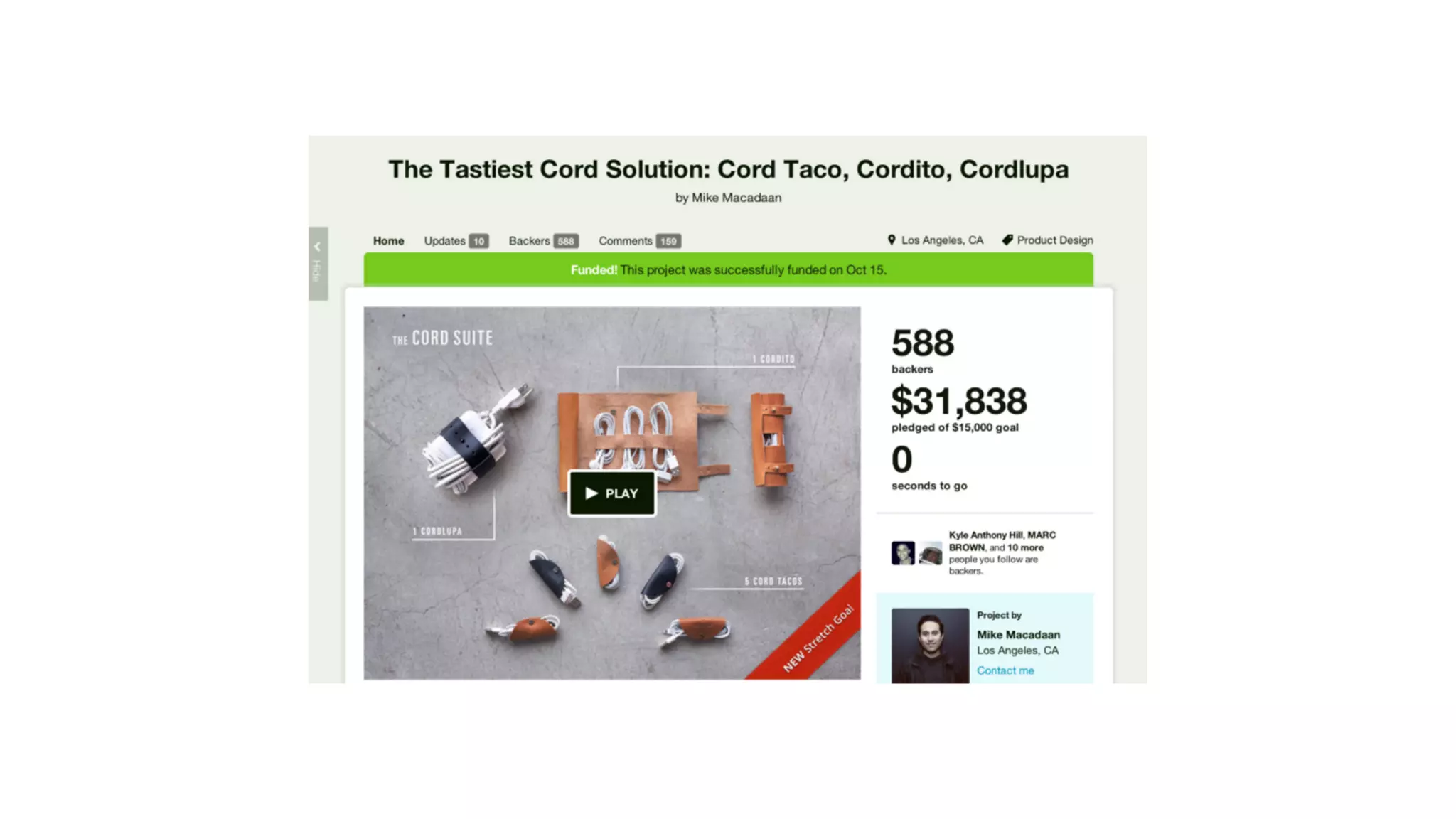
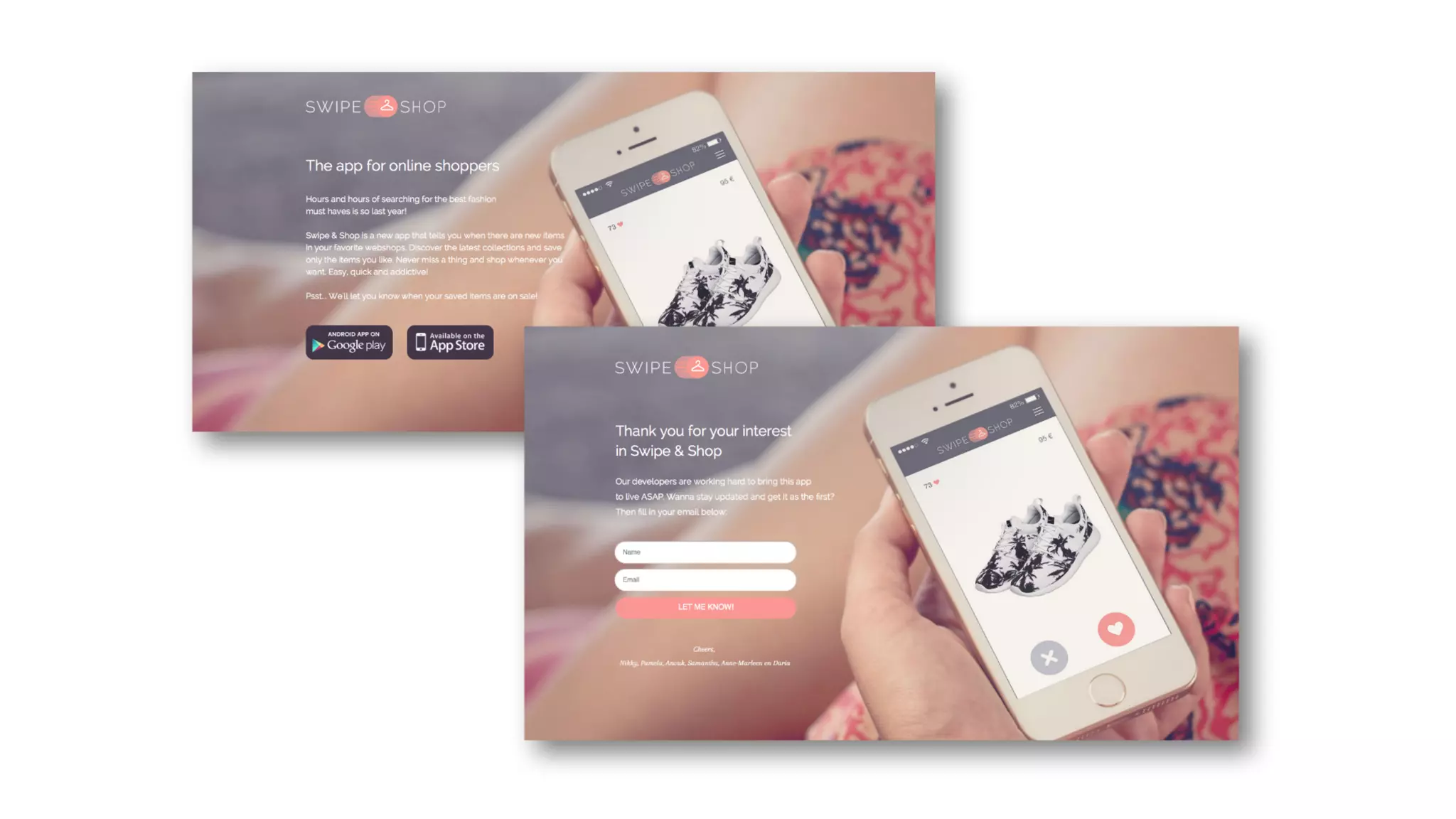
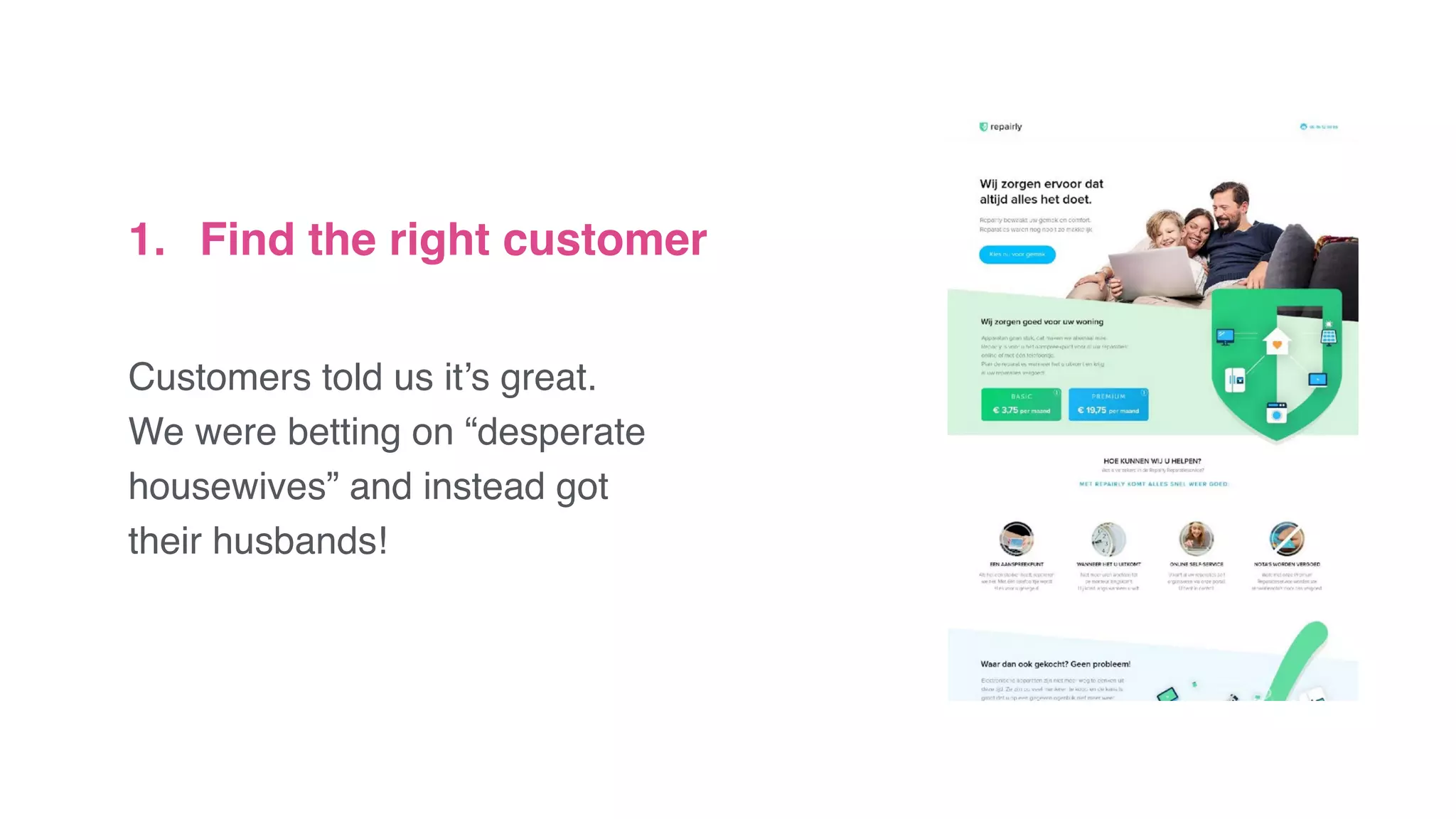
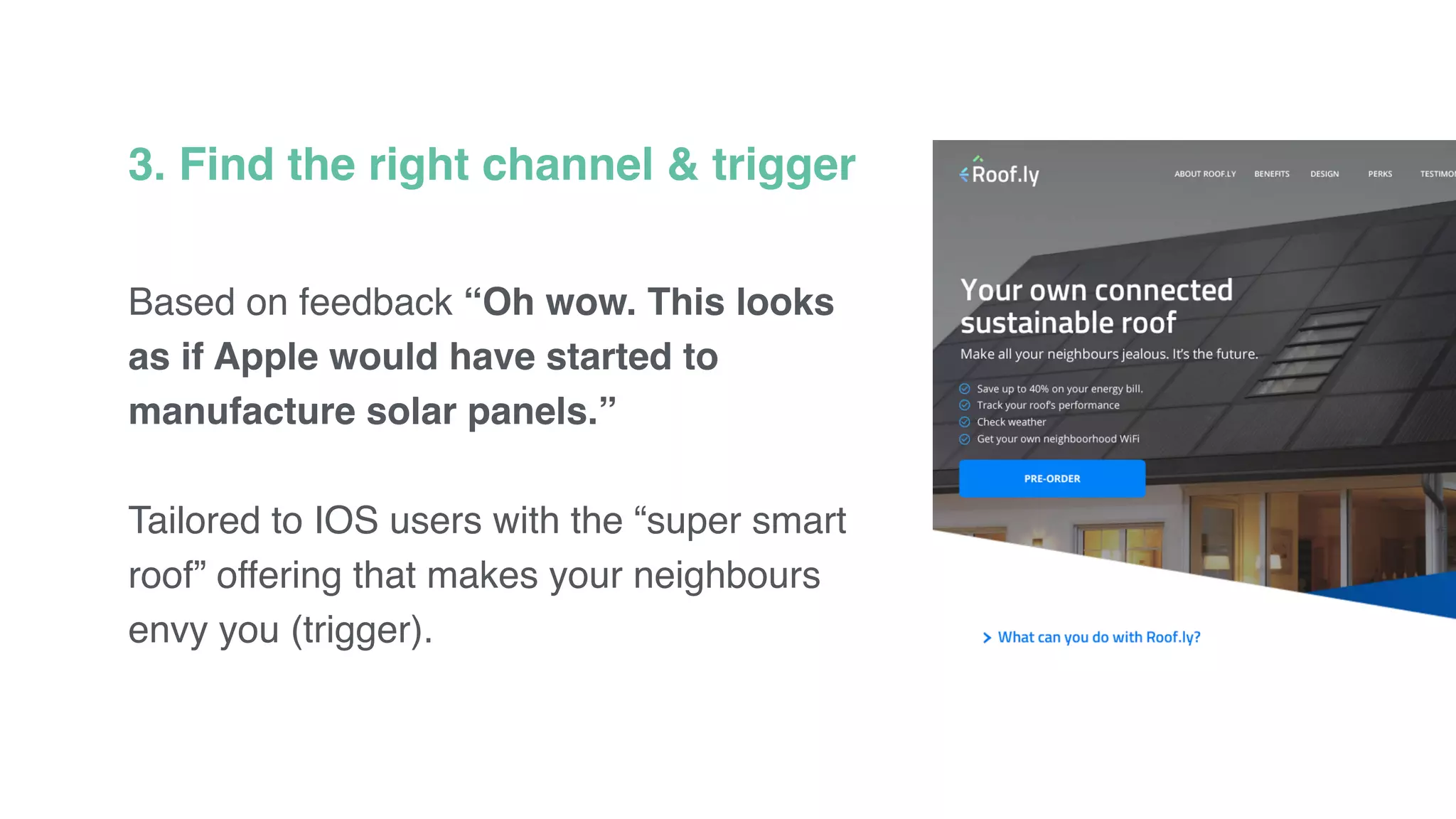
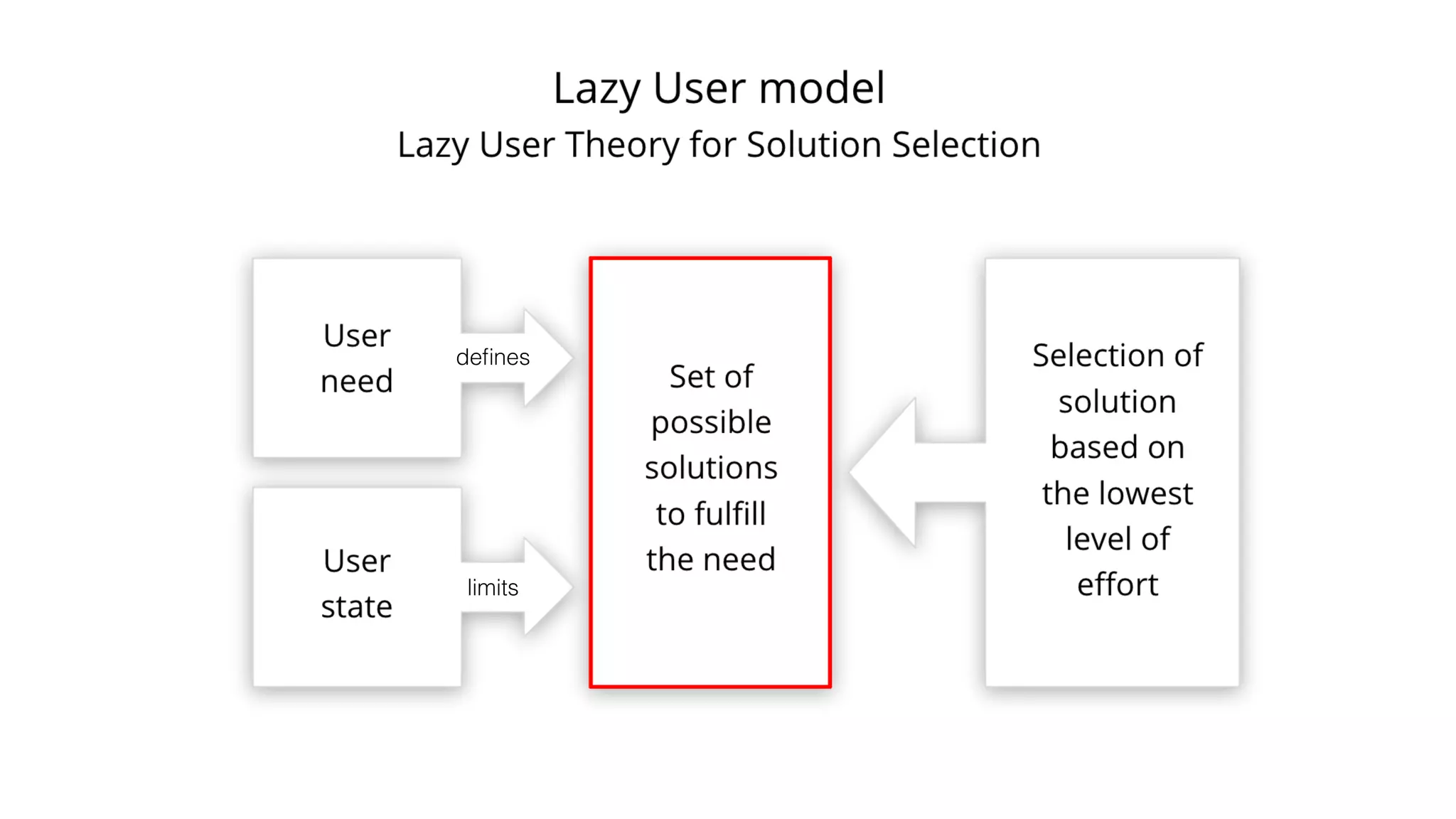
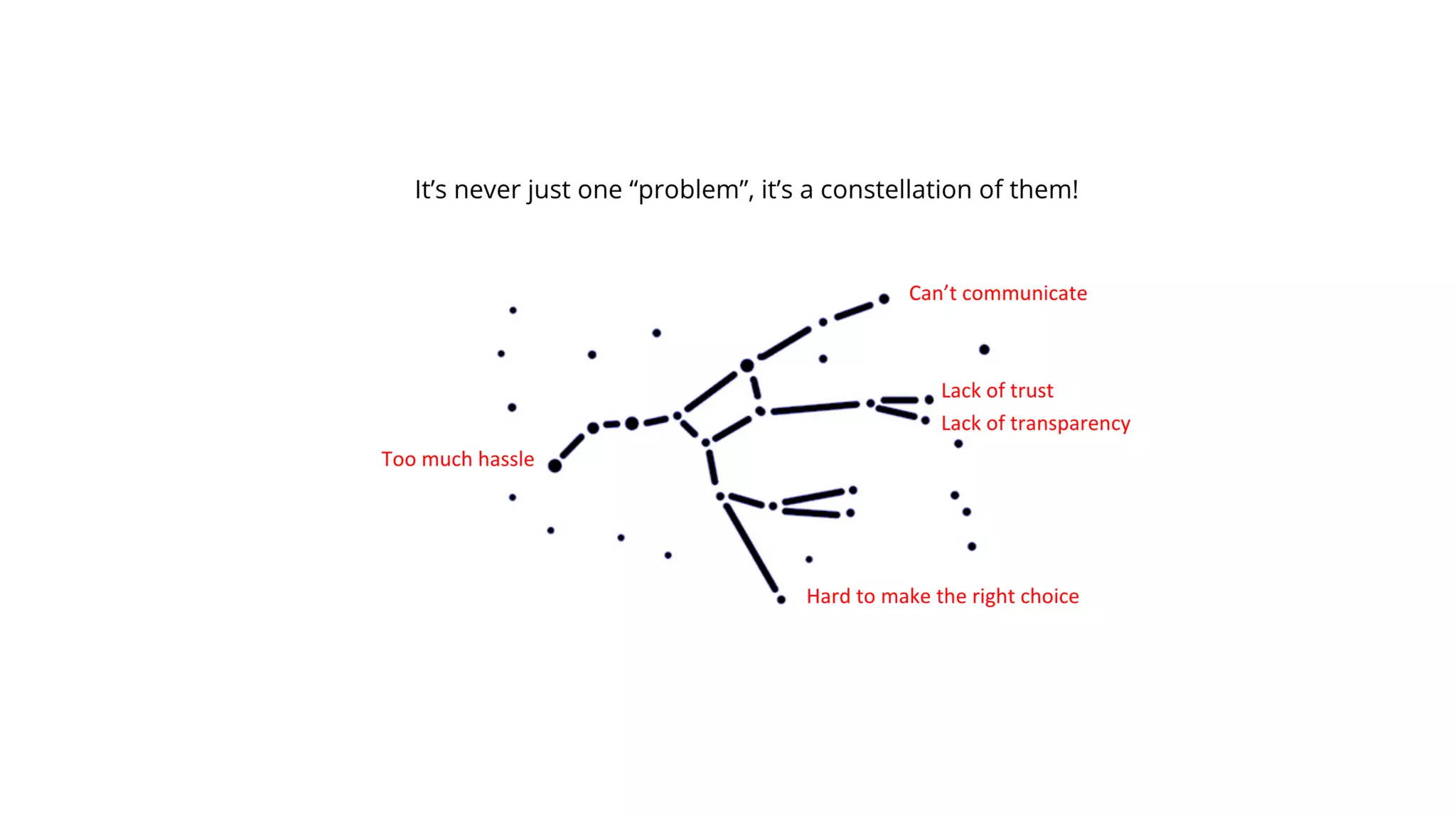
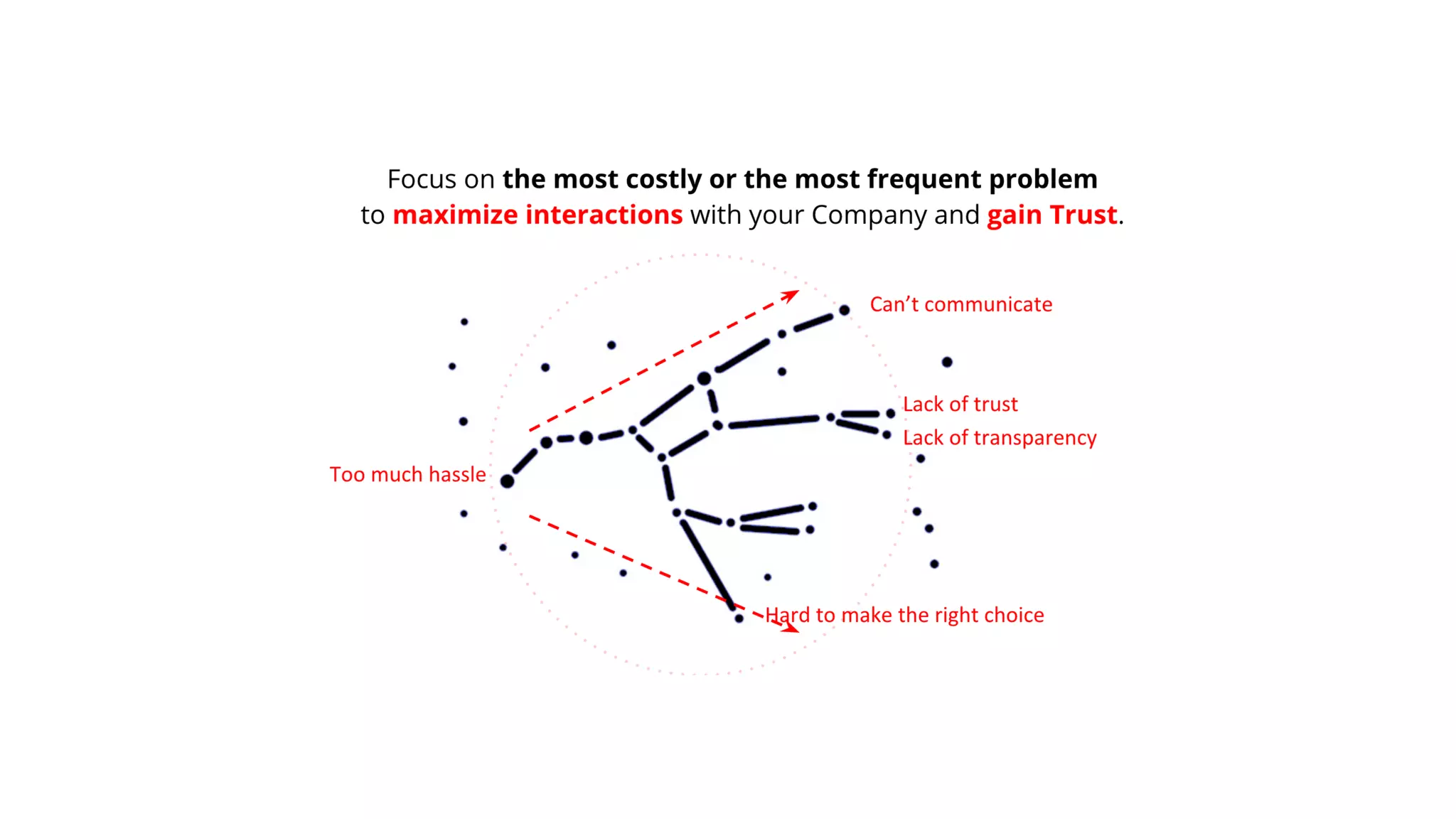
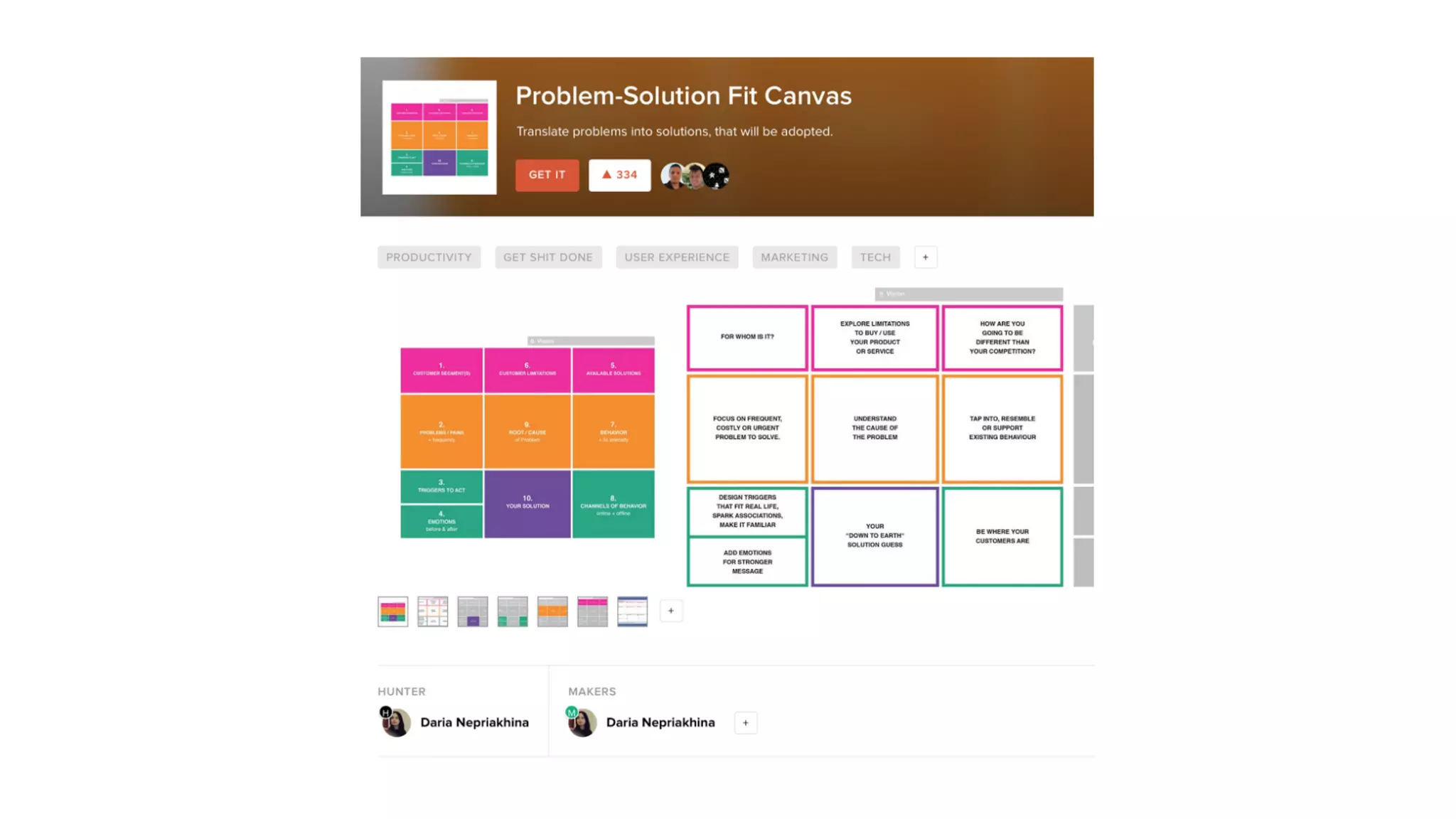
The document discusses the Lean Startup methodology for developing solutions that customers will adopt. It emphasizes validating assumptions with experiments and customer feedback rather than discussions. The key aspects are:
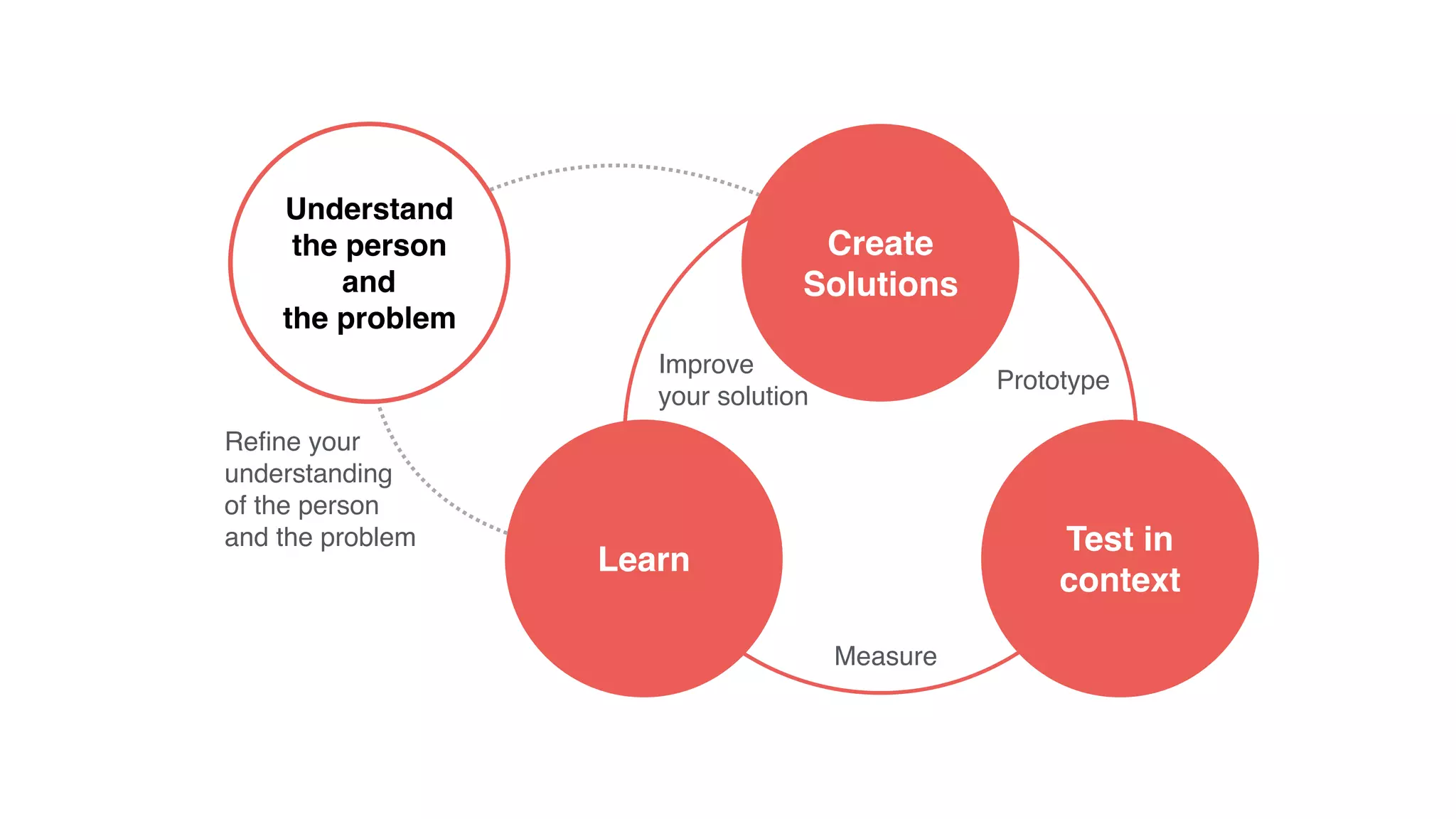
1) Understanding customer problems, limitations, and existing solutions through interviews and observation of behavior.
2) Hypothesizing the root causes of problems and designing small experiments to test solutions.
3) Identifying triggers for customer action and channels they use to find solutions and get feedback through iterative testing.
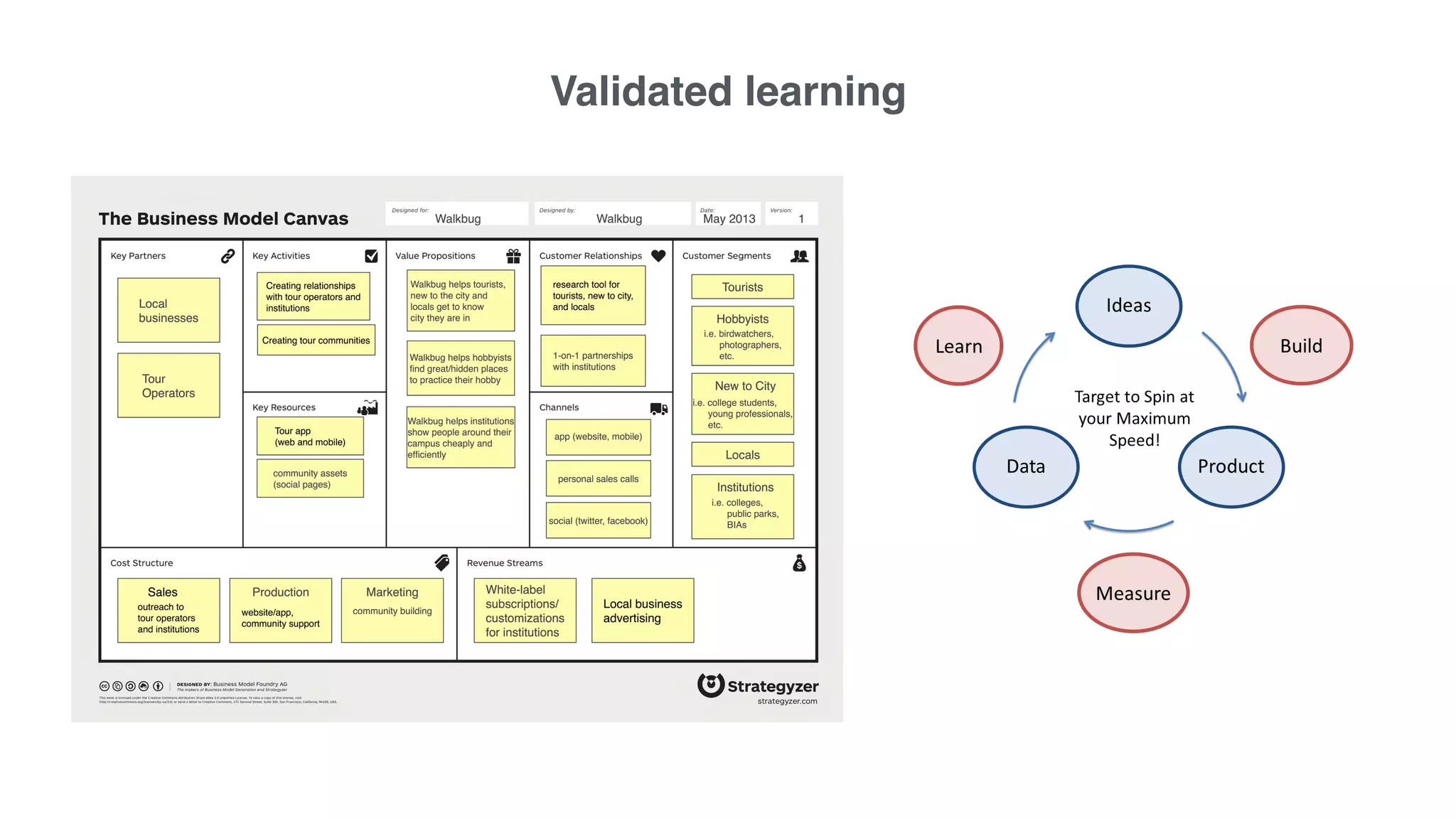
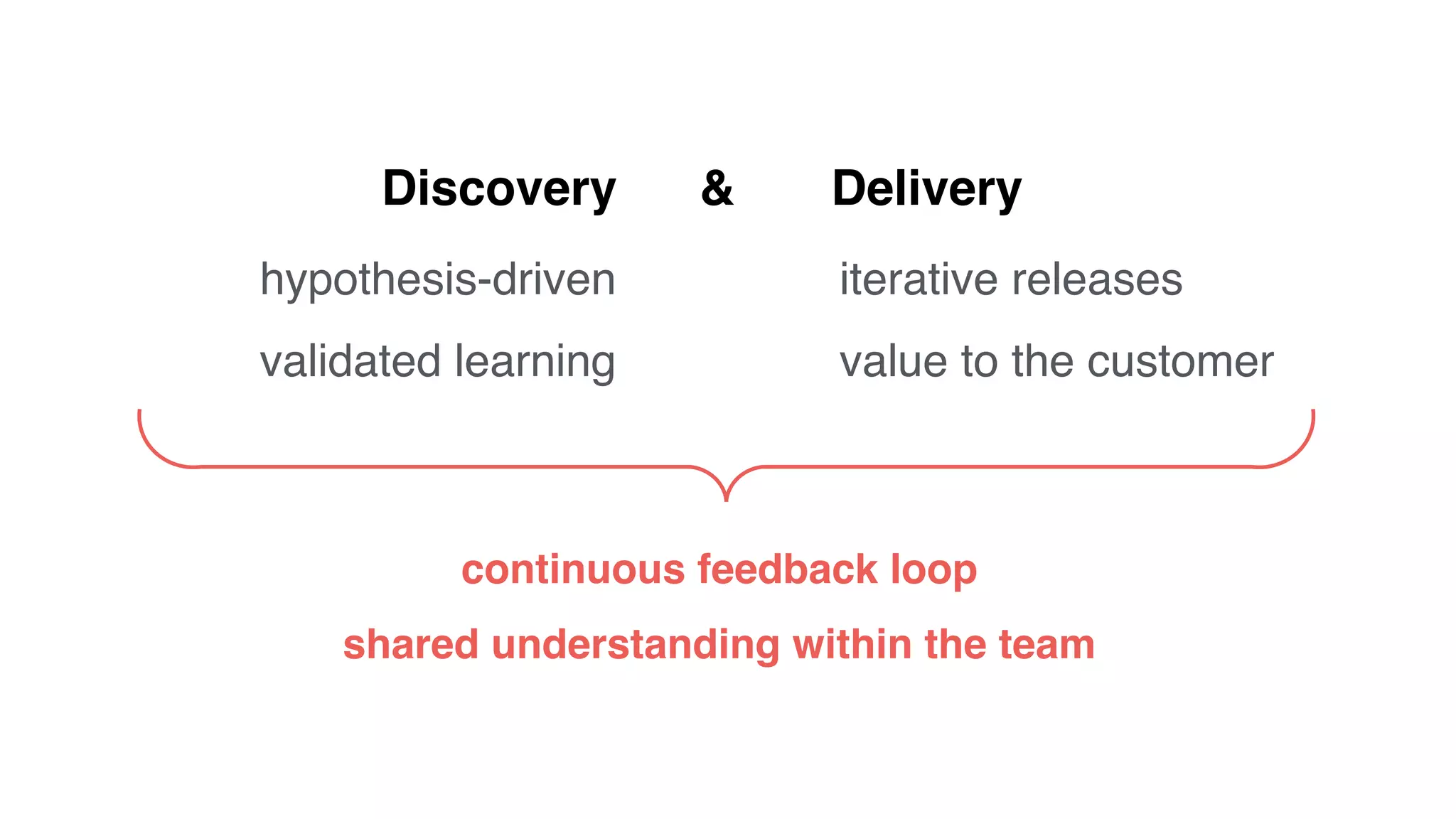
4) Continually learning and improving solutions based on validated data from customers rather than assumptions within discussions.