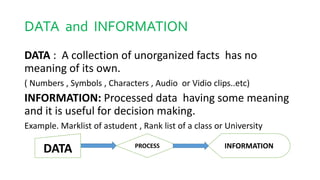
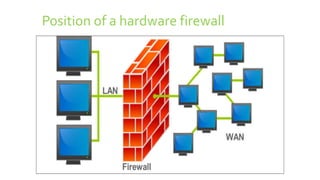
Data protection and security involves safeguarding data from corruption, compromise or loss. This includes data encryption, backups, and disaster recovery systems. Data security refers specifically to protecting data from unauthorized access through its entire lifecycle. Common threats include cyberattacks, malware, data breaches from theft or human error. Malware like viruses, worms and ransomware can damage systems, while hacking aims to gain unauthorized access through password cracking. Firewalls act as barriers, filtering network traffic to block malicious software and attacks based on security rules.