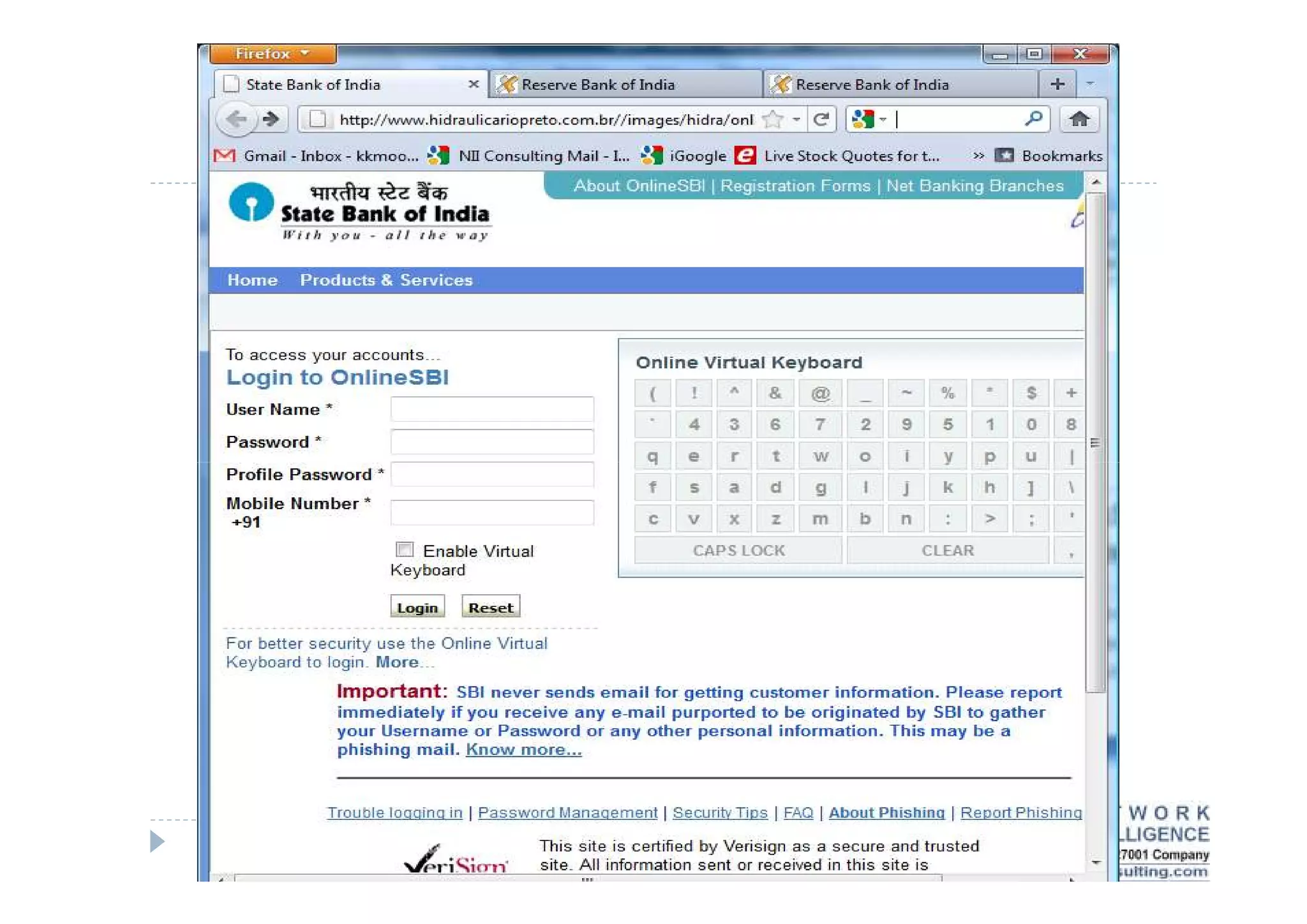
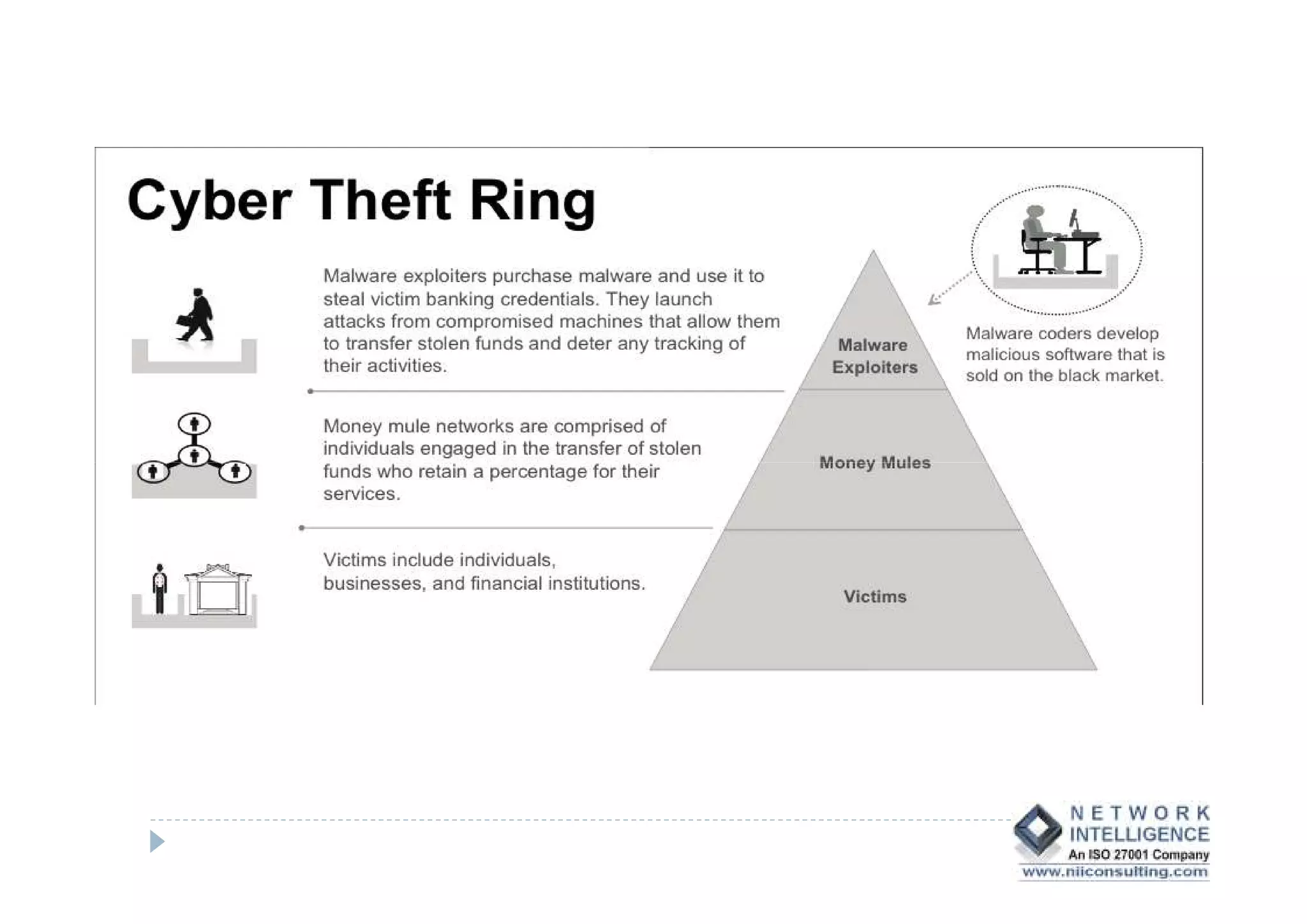
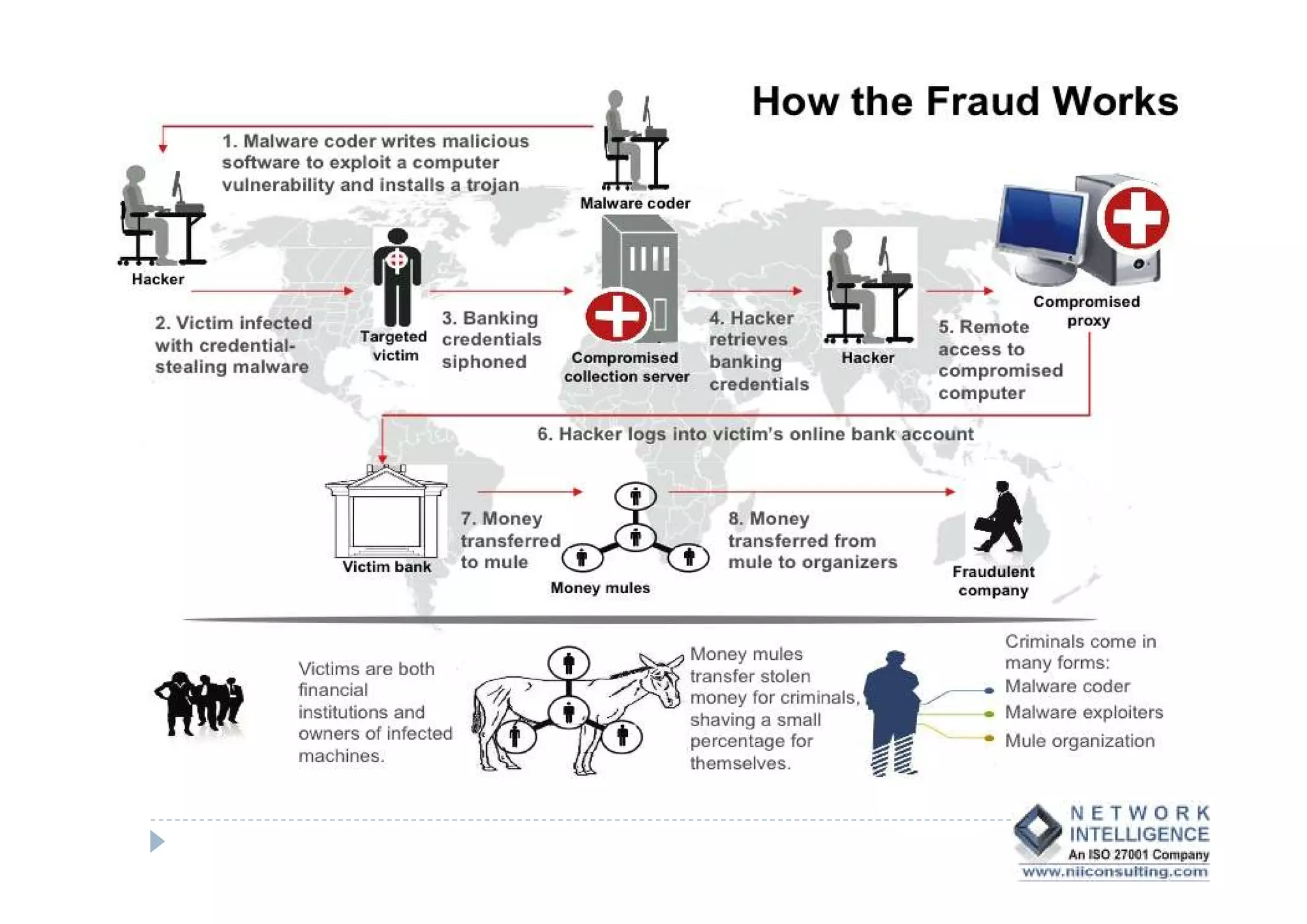
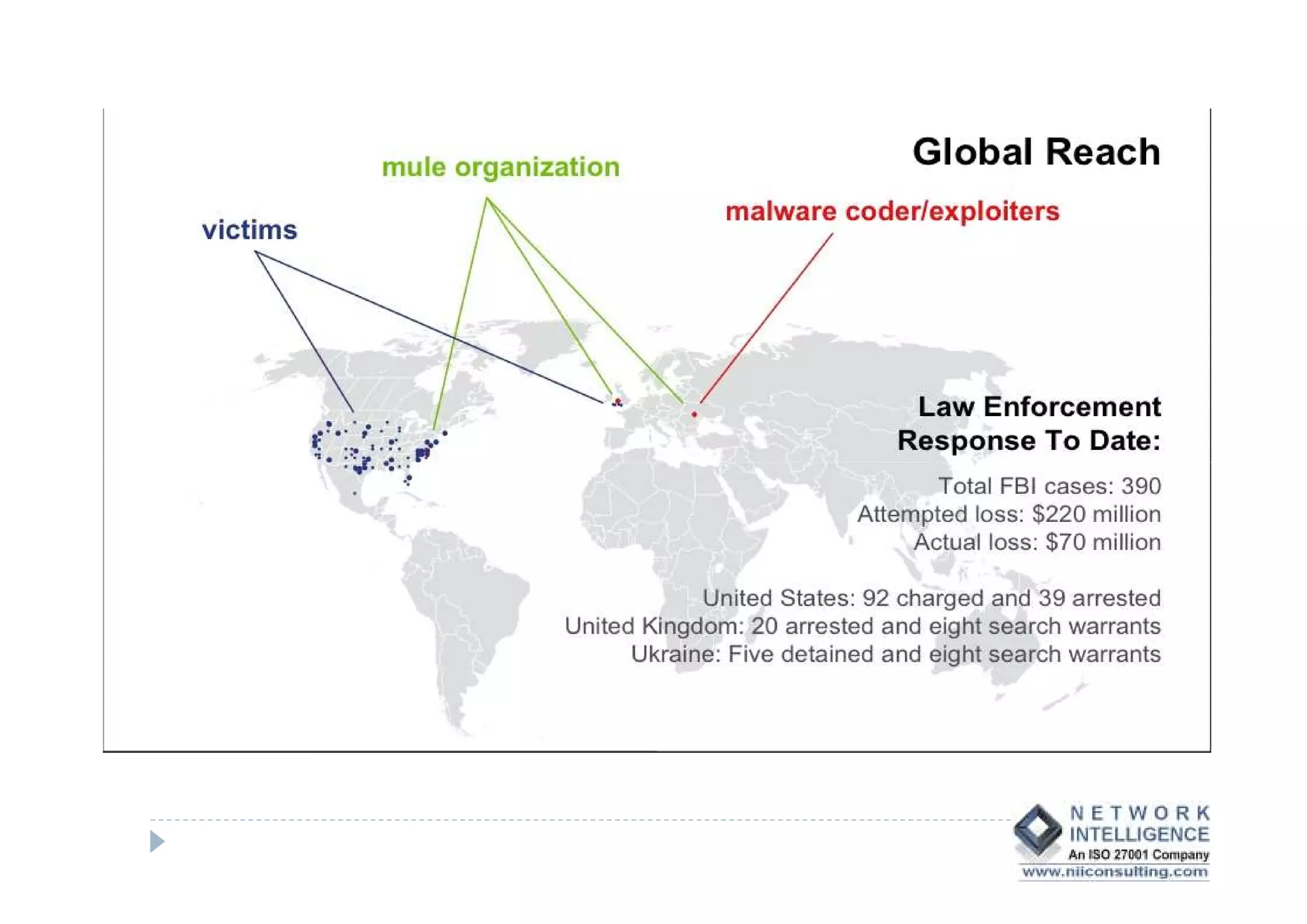
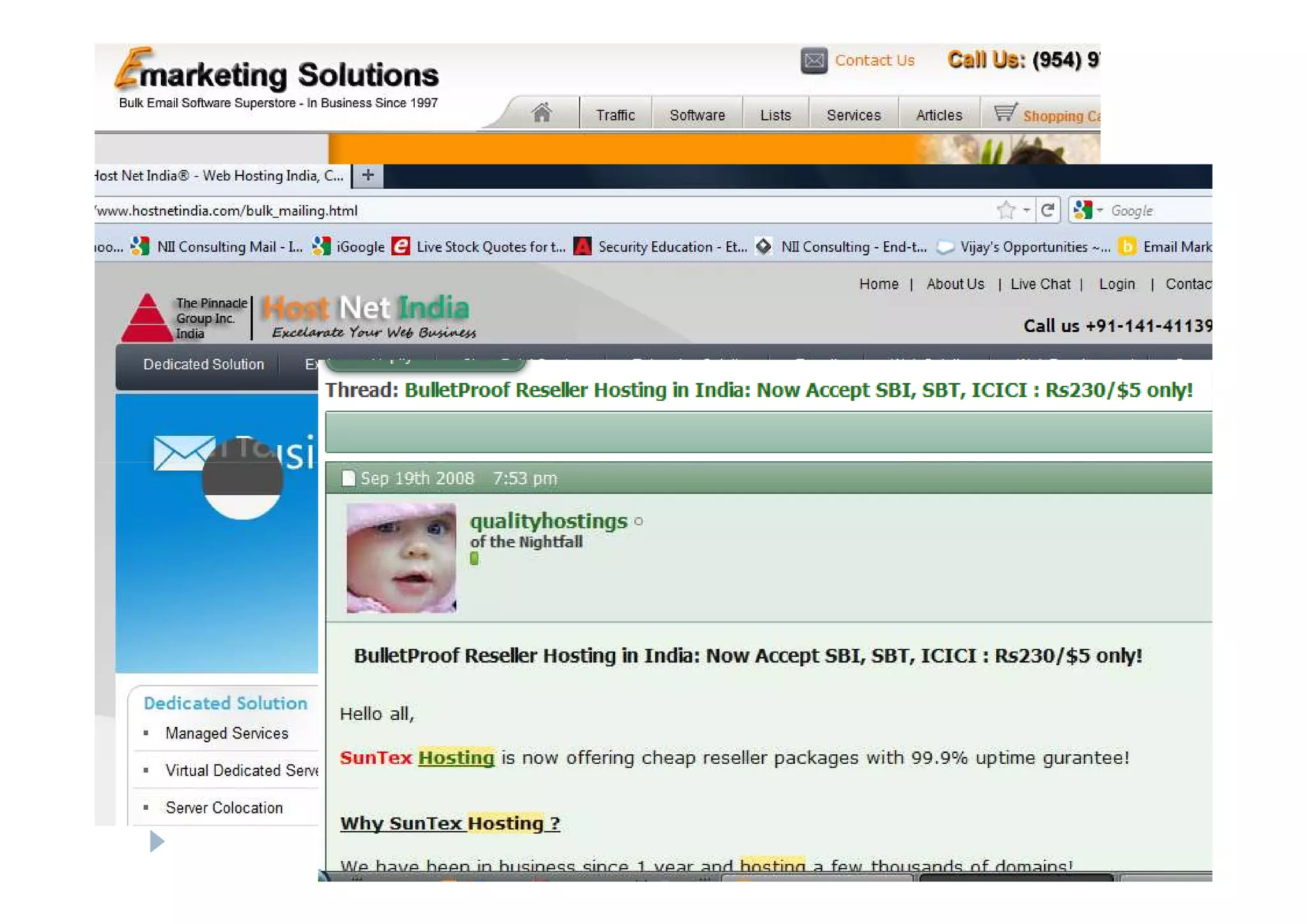
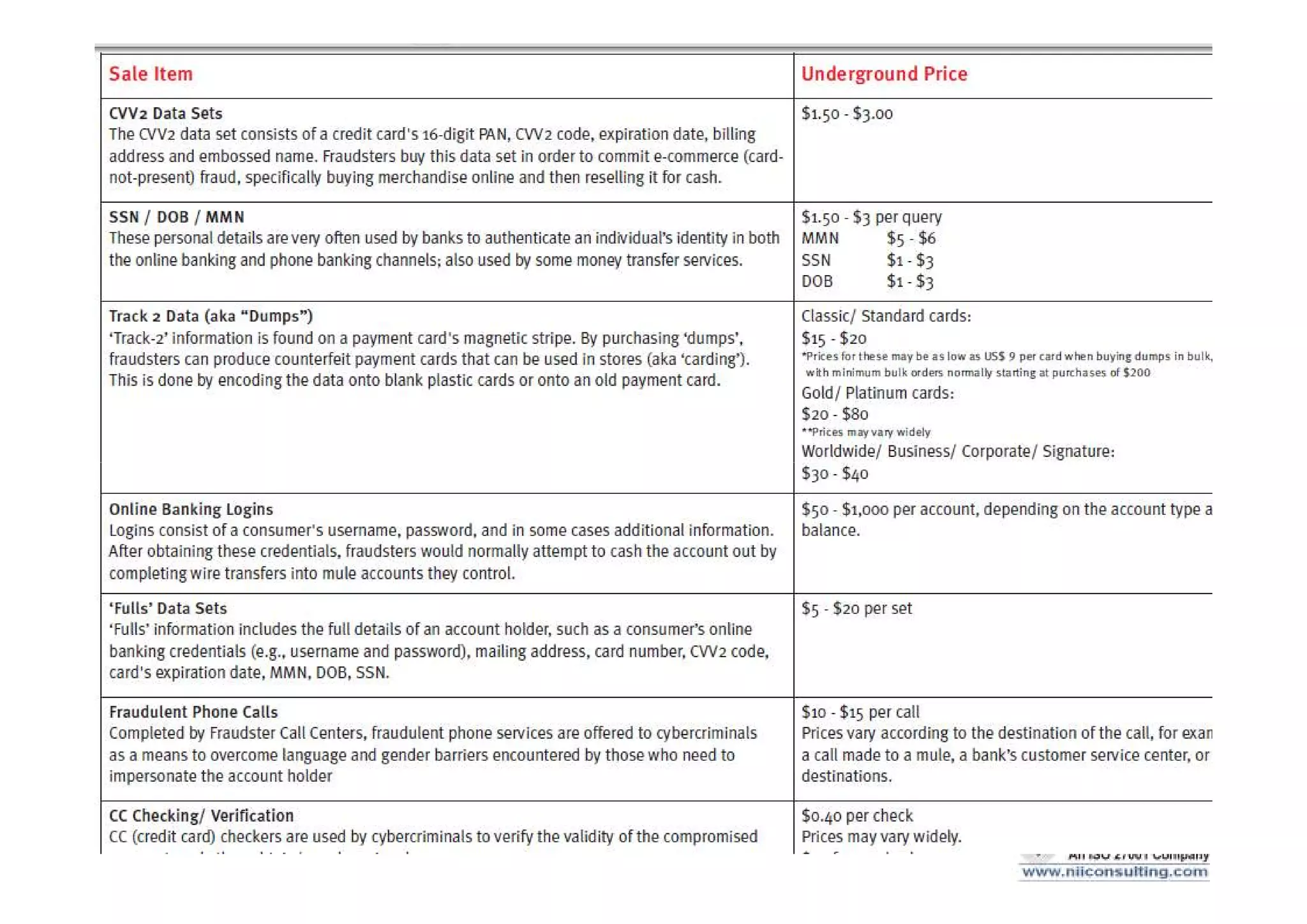
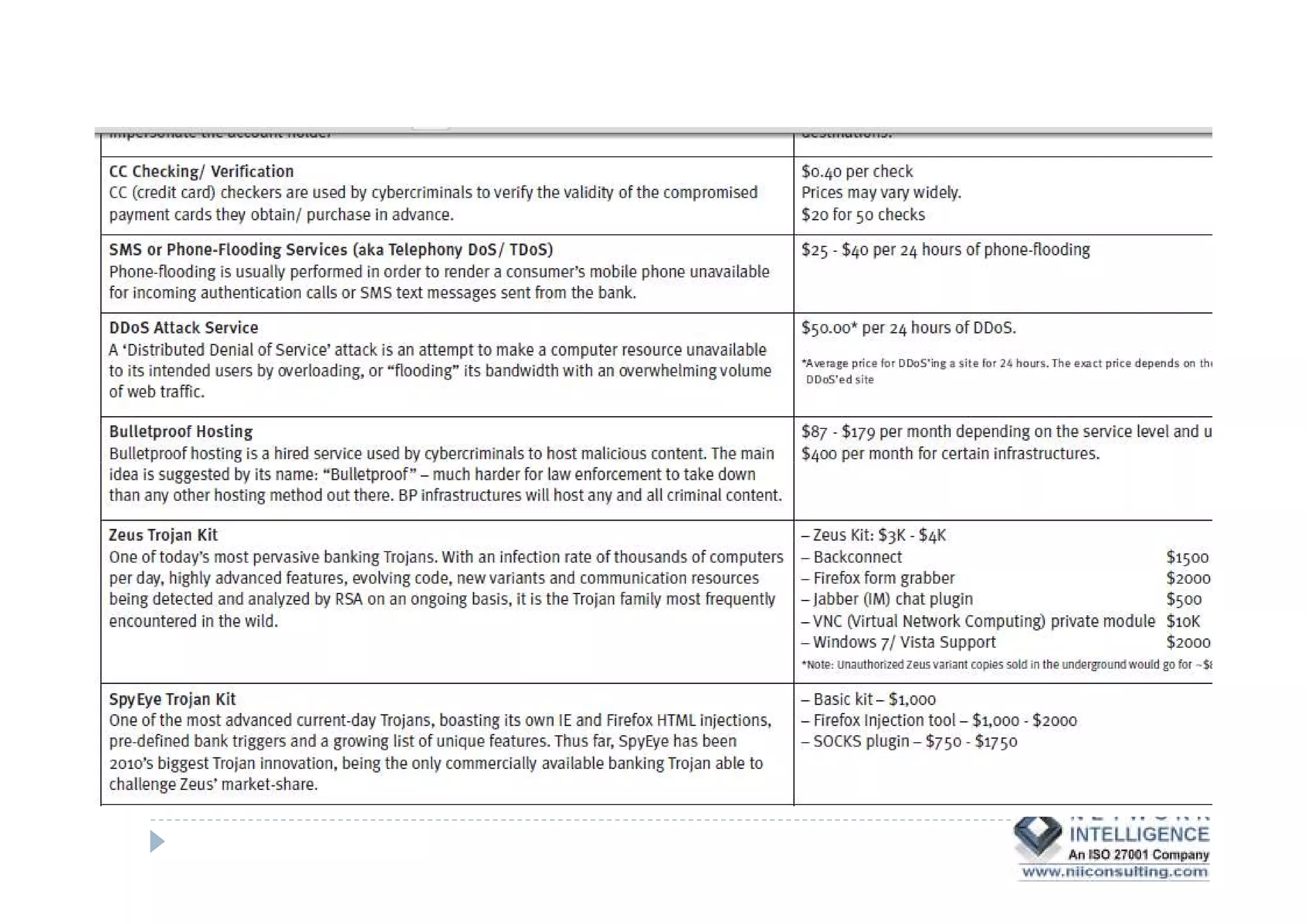
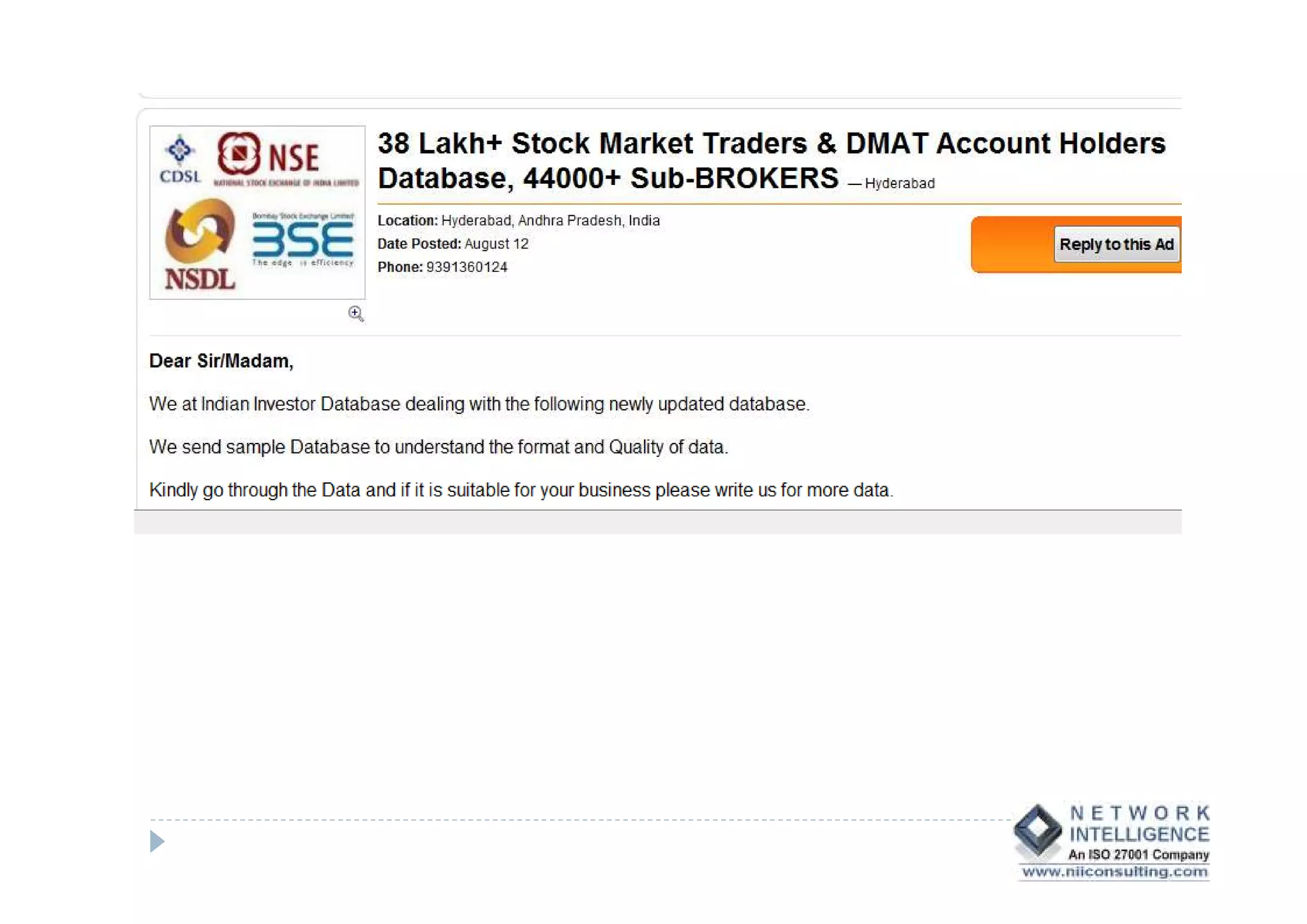
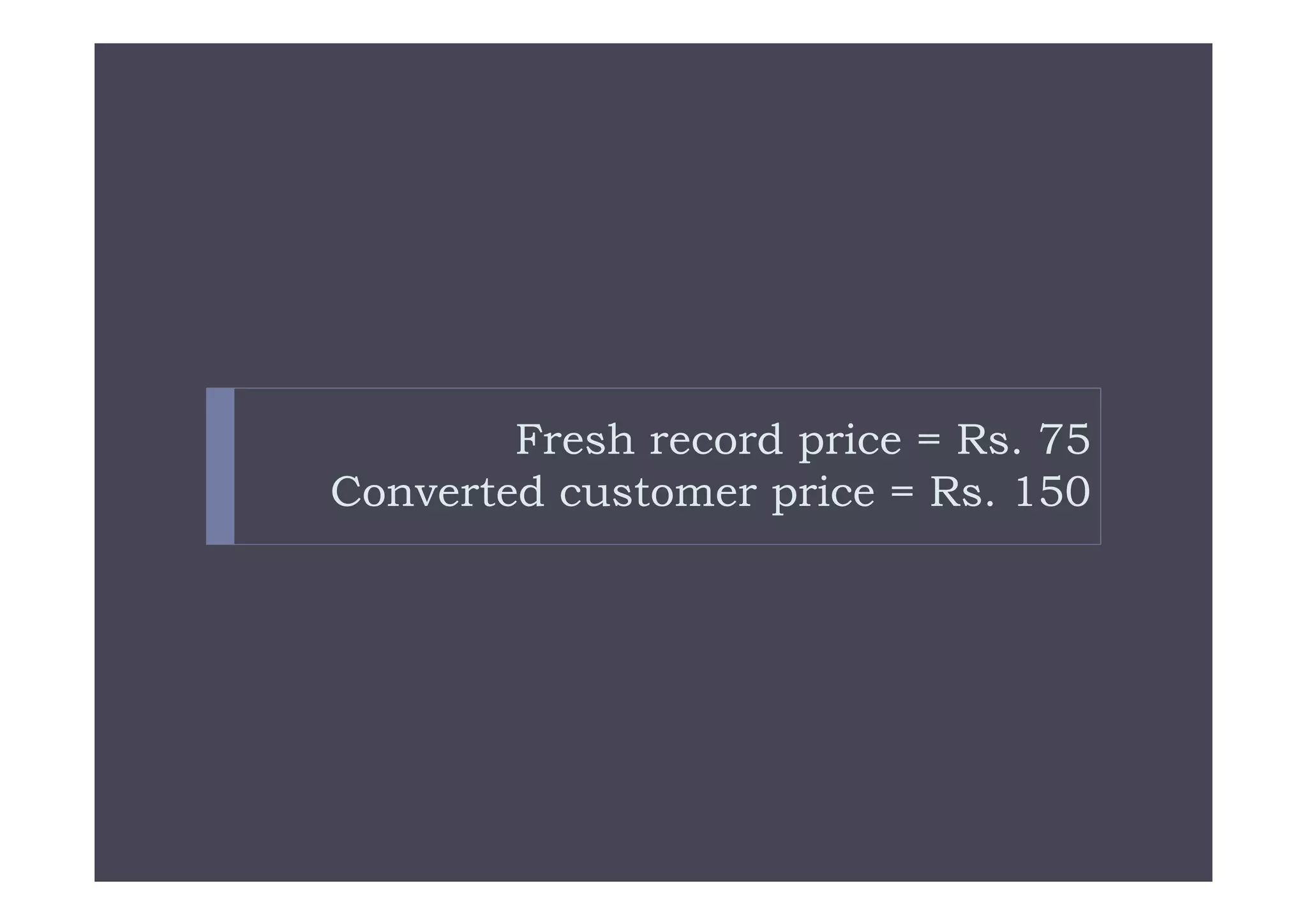
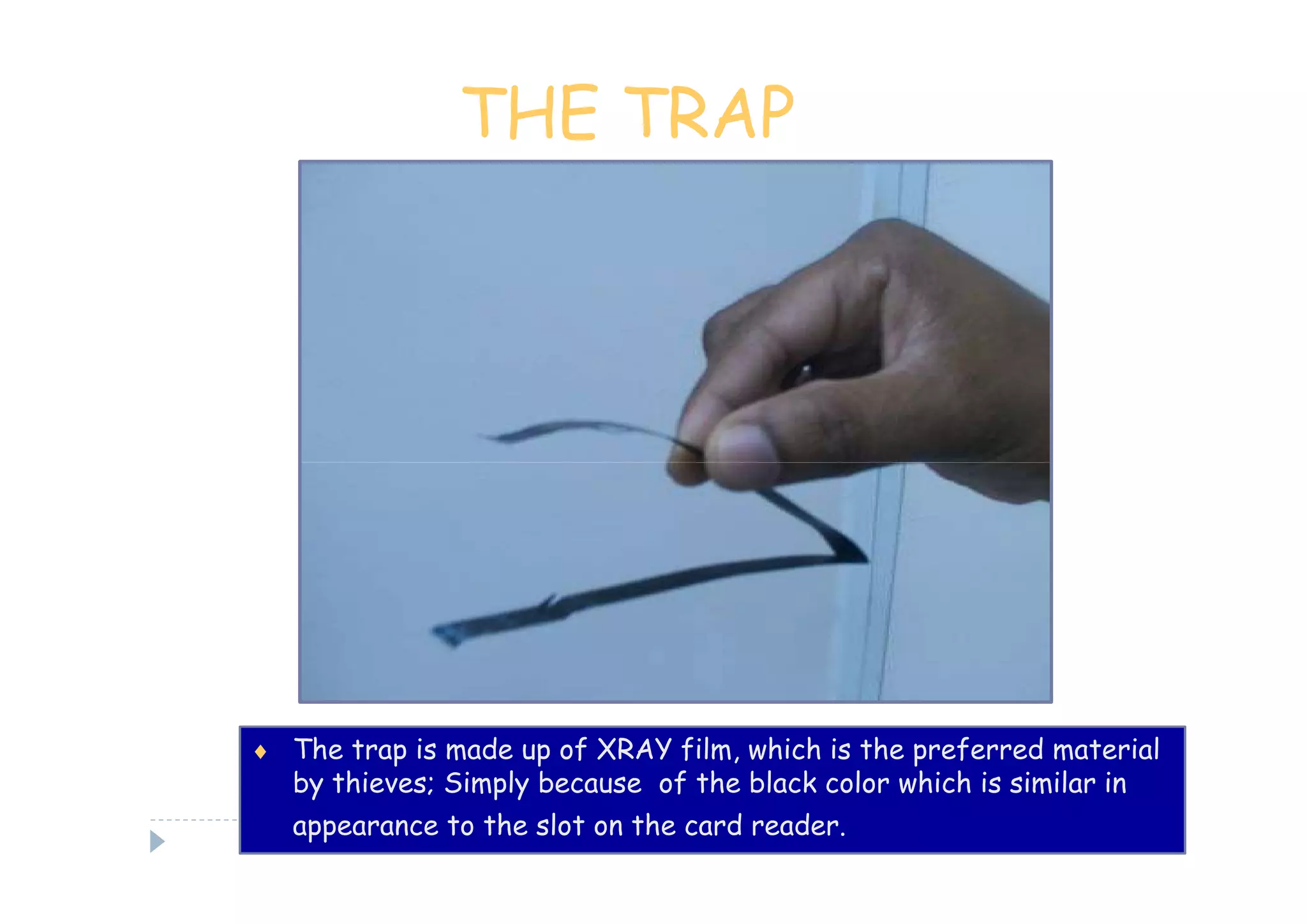
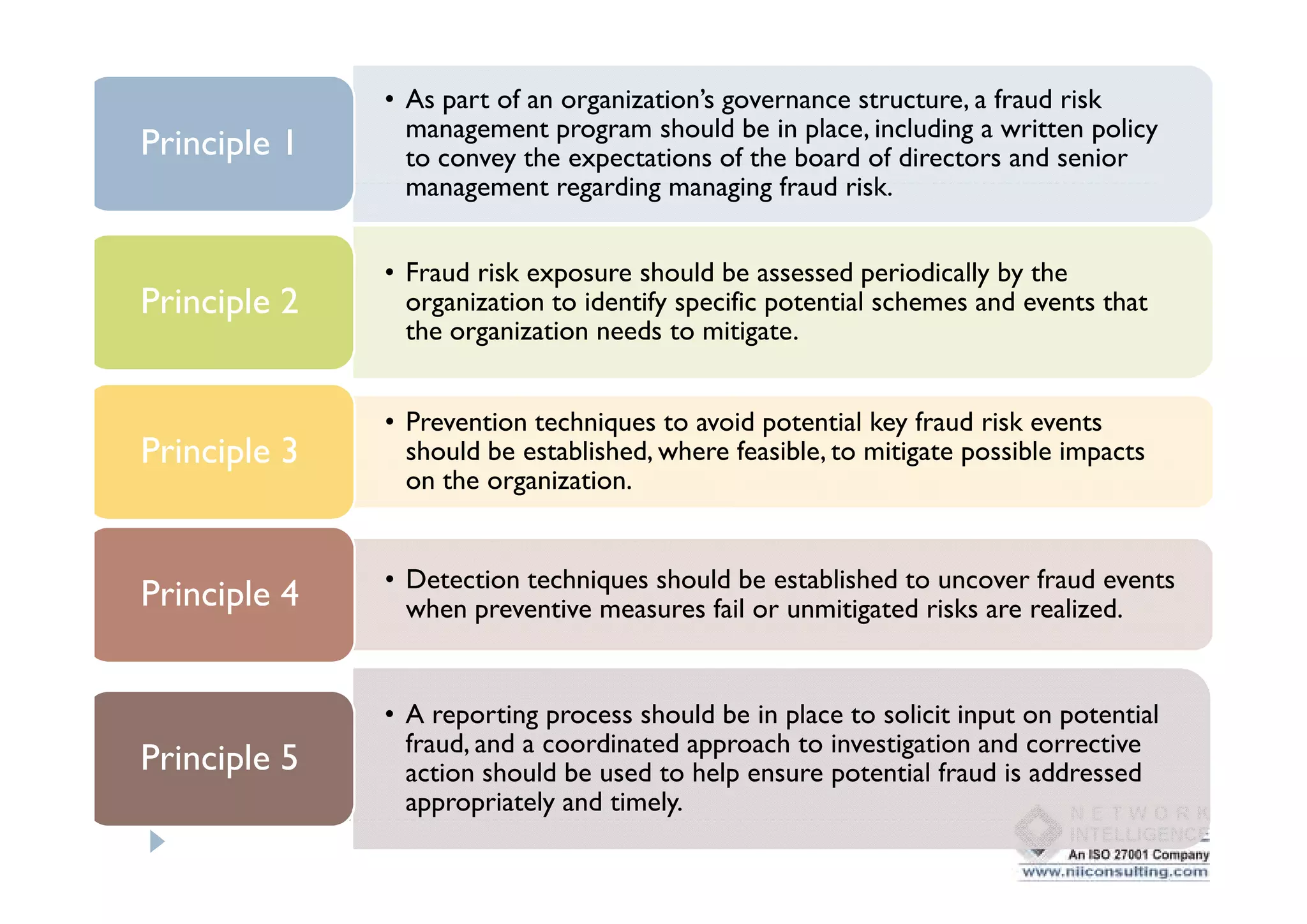
This document discusses various types of cyber fraud and solutions. It covers online banking fraud, data theft, ATM skimming, spear phishing, and technology red flags. It recommends establishing fraud risk management programs with policies, periodic risk assessments, prevention and detection techniques. Technology solutions like data leakage prevention and identity access control are suggested. The document also proposes setting up special committees to review new products and share details of fraudulent employees. It provides resources on fraud risk management systems and prevention in an automated world.