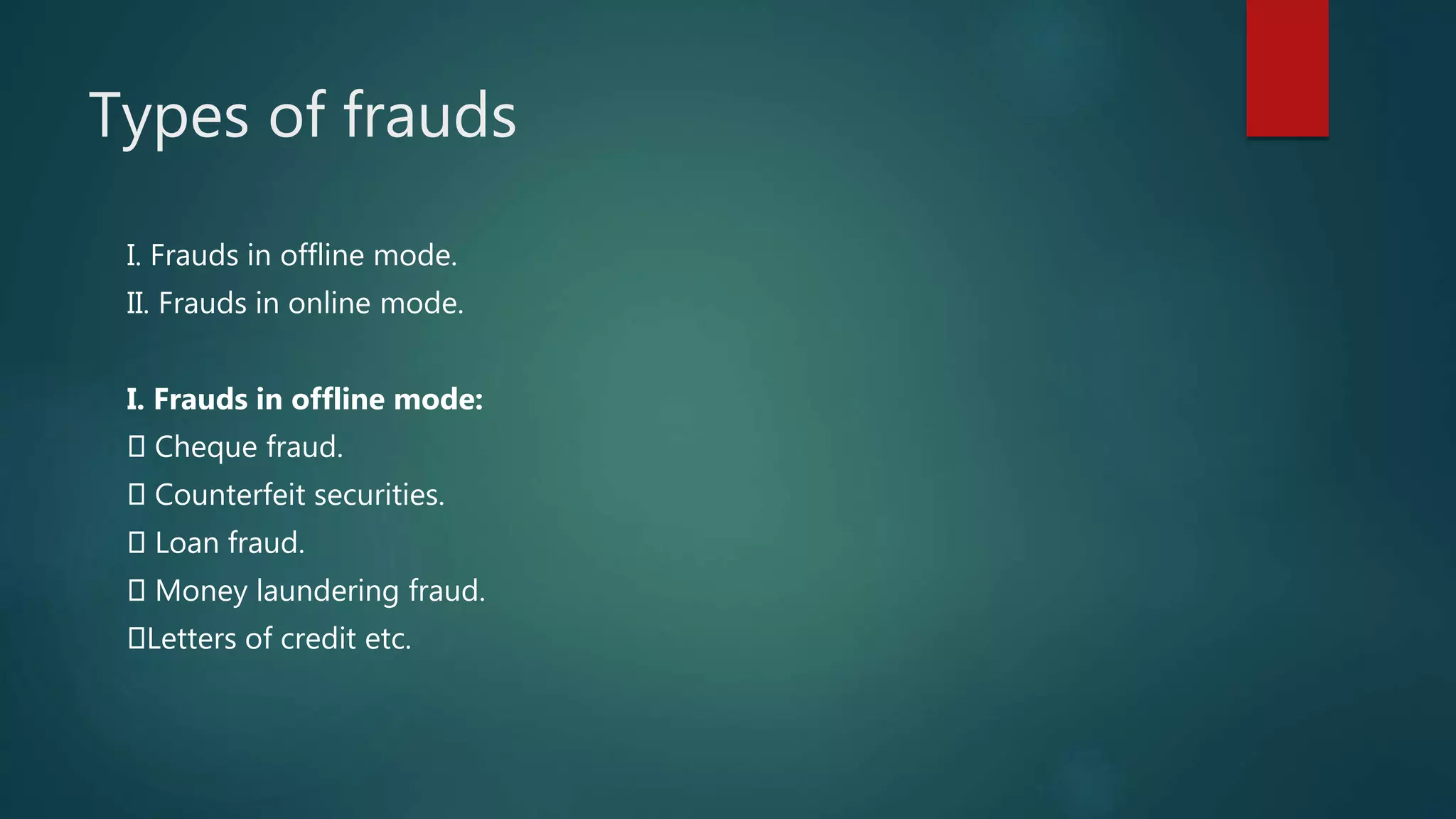
The document discusses bank frauds in India. It defines bank fraud and outlines some common types of offline and online bank frauds such as cheque fraud, payment card fraud, forgery, money laundering, and phishing. It provides tips for preventing fraud and recent examples of reported bank fraud cases in India totaling hundreds of crores. The conclusion states that fraud undermines trust in banks and the economy, so prevention through education and technology is important.