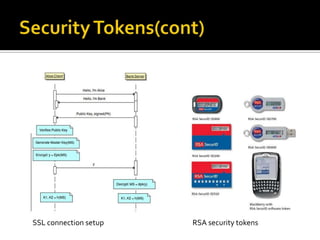
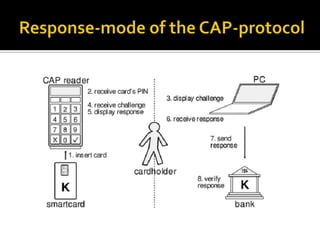
The document discusses security trends in e-banking, including common attacks such as phishing and trojans, security measures implemented by banks like two-factor authentication and secured applications, and emerging technologies like transaction signing using mobile phones or security tokens. It also covers security protocols like SSL and implementations of security standards like EMV's chip authentication program. The outlook presented suggests users and banks will both need different solutions to manage evolving security risks in e-banking.