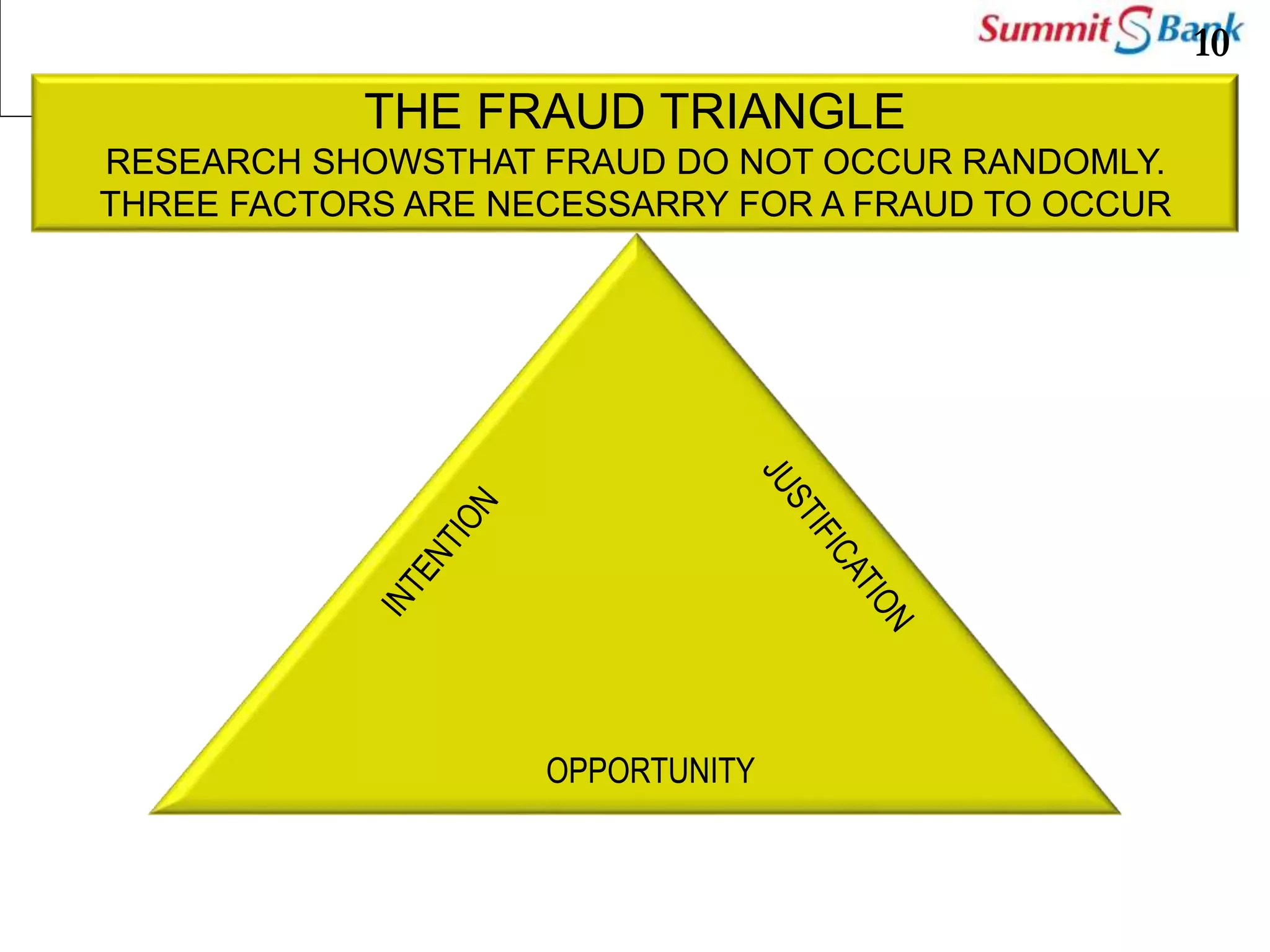
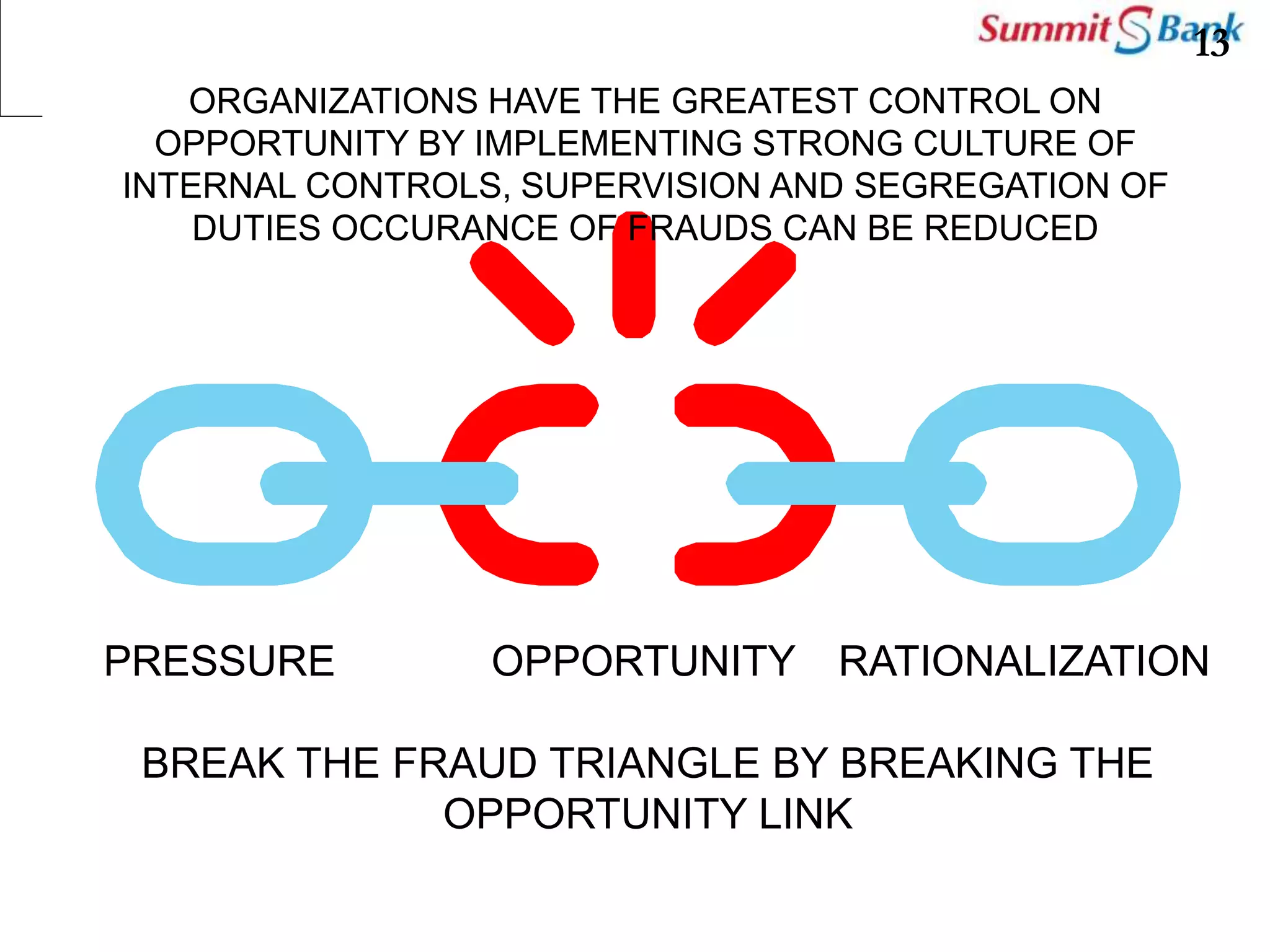
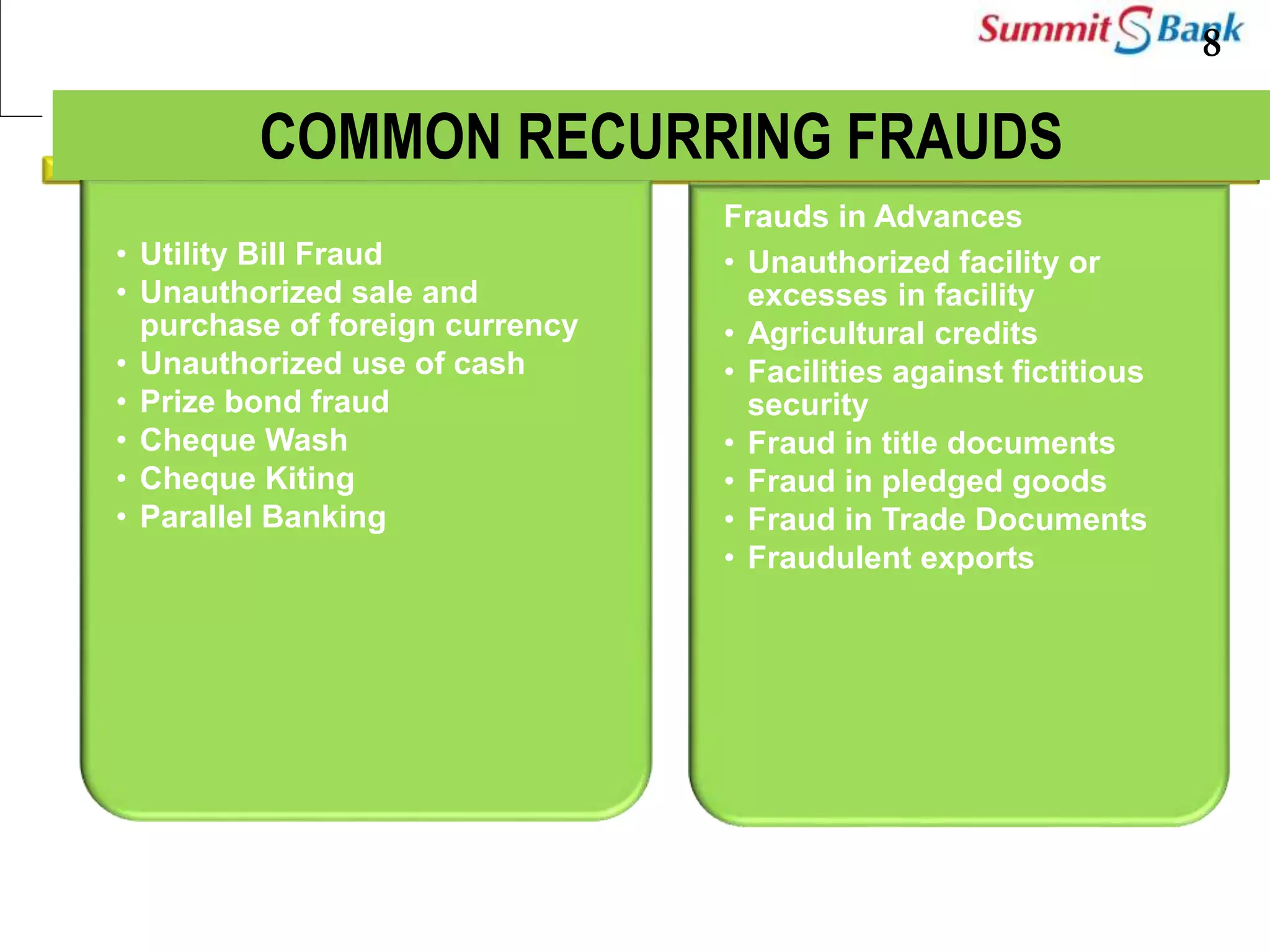
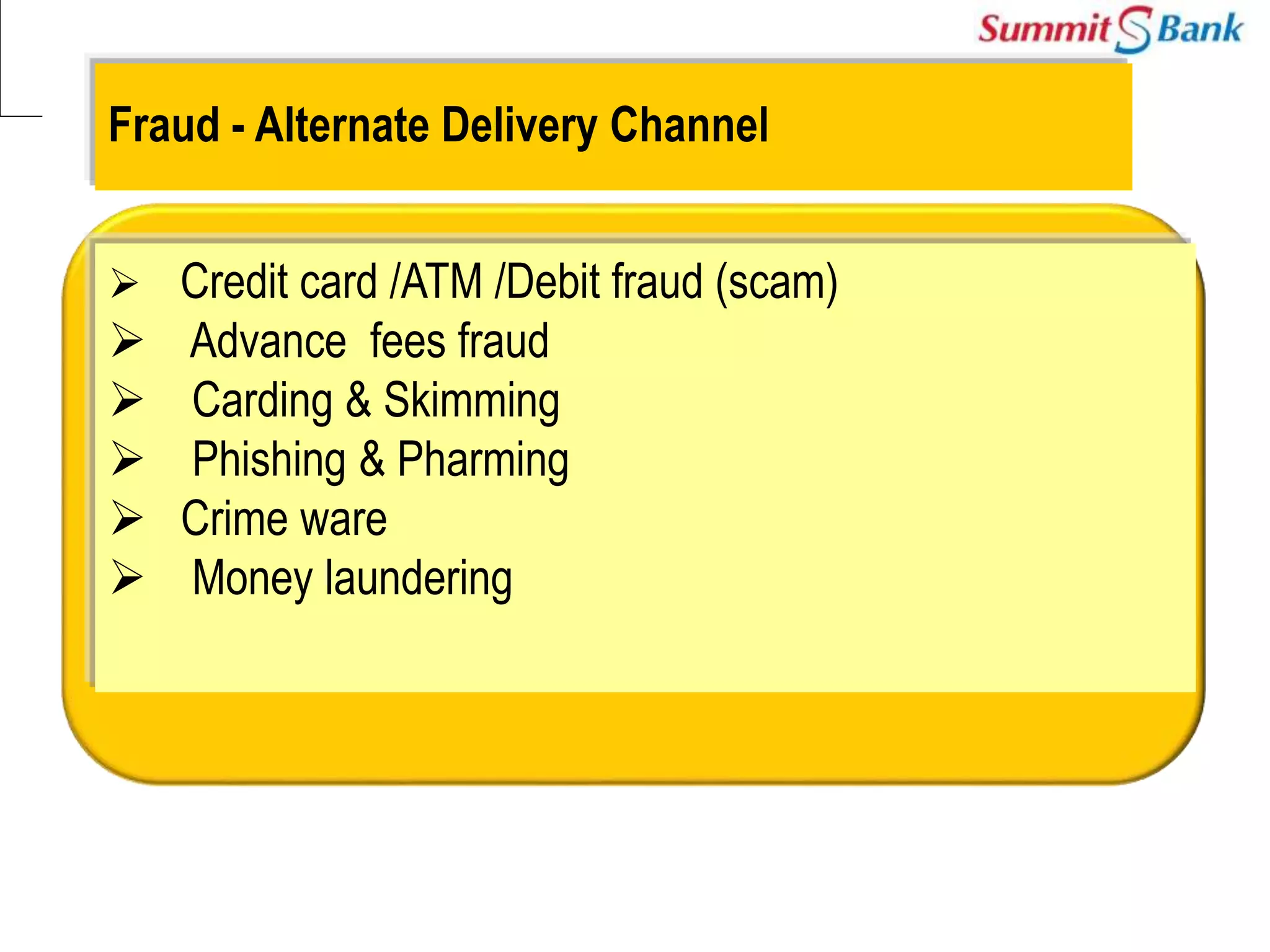
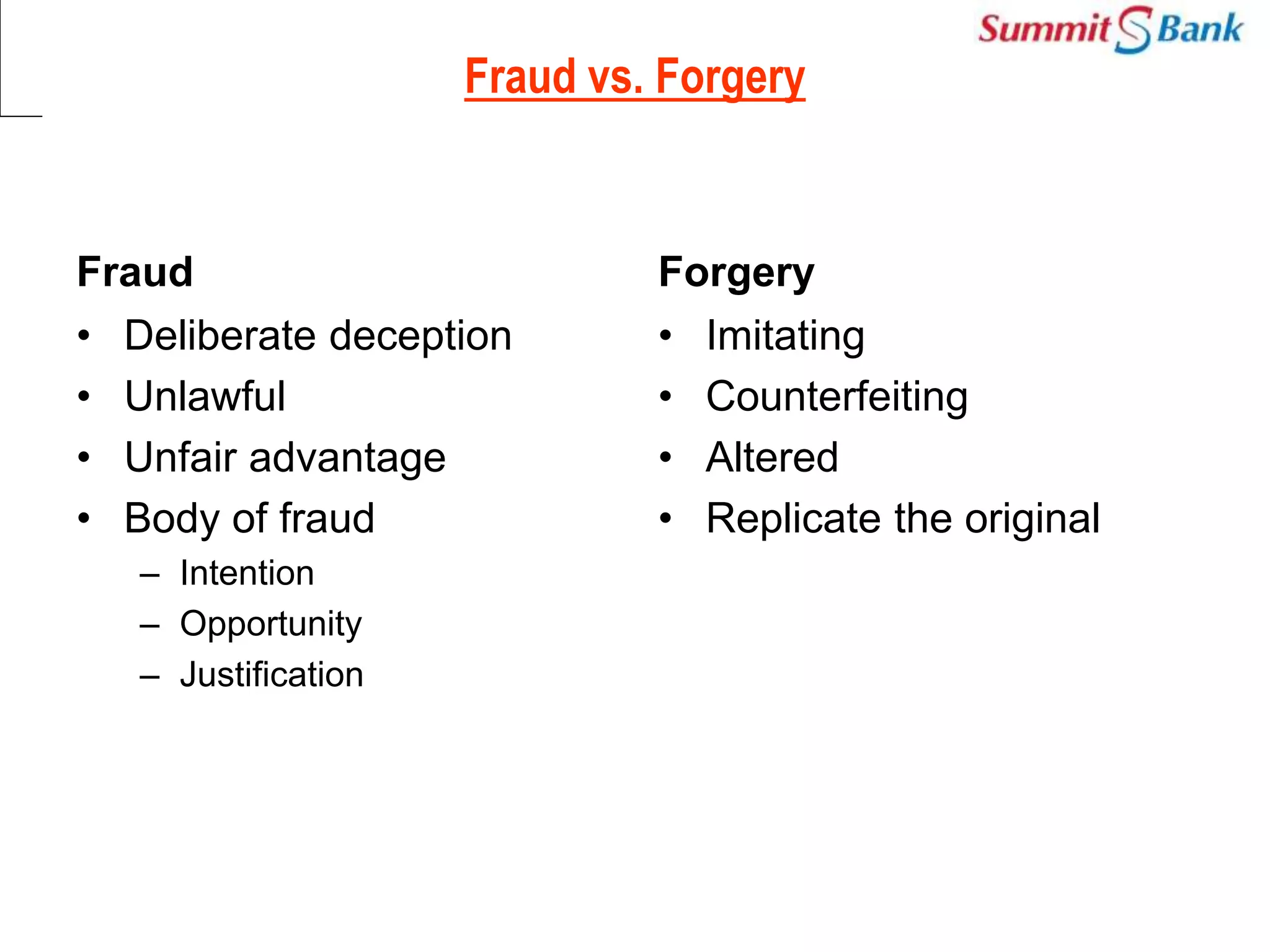
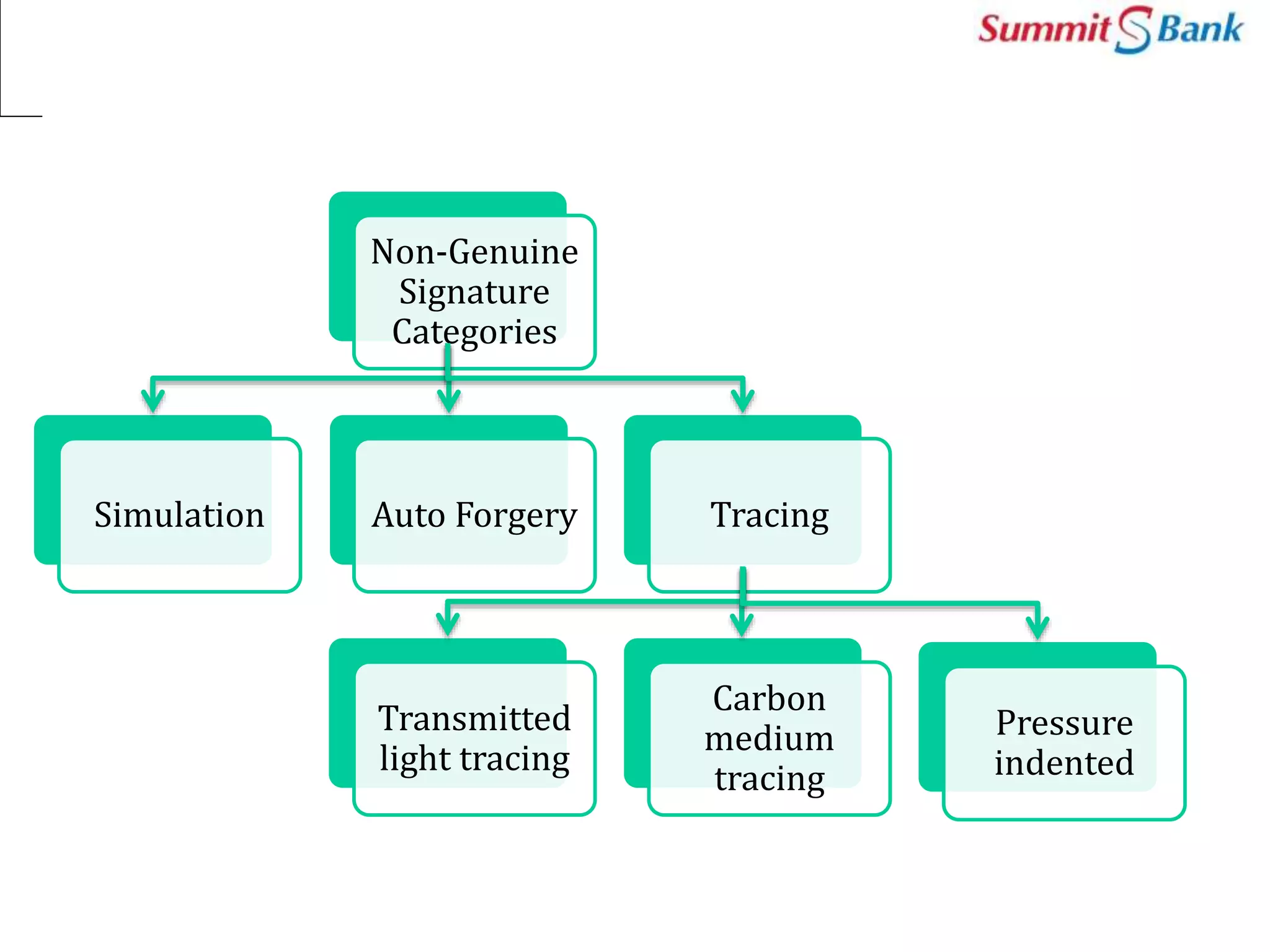
This document discusses fraud prevention at Summit Bank Limited. It defines fraud and notes that banks are susceptible to both internal and external fraud due to their operations. All employees are responsible for preventing fraud by complying with laws, rules and procedures. The key elements of an effective anti-fraud program are a strong control environment, risk assessment, control activities, information and communication, and ongoing monitoring. Common types of bank fraud include fake instruments, unauthorized transactions, and cybercrimes. Red flags that could indicate fraud include changes in an employee's lifestyle and behavior. Thoroughly knowing banking operations, employees, risks, and investigating anomalies are important for mitigating fraud risk.