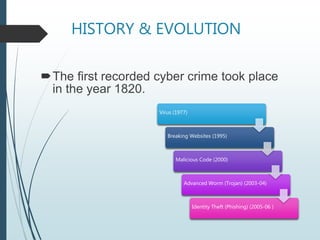
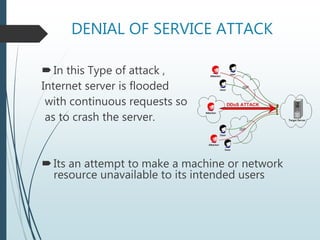
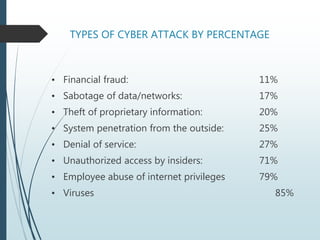
This document discusses cyber crime, including its definition, history, categories, and types. It defines cyber crime as any criminal activity involving computers and networks. The first recorded cyber crime took place in 1820. Common types of cyber crimes include hacking, virus dissemination, denial of service attacks, computer vandalism, cyber terrorism, and software piracy. The document provides statistics on types of cyber attacks and recommends safety tips to prevent cyber crime, such as using antivirus software and firewalls.