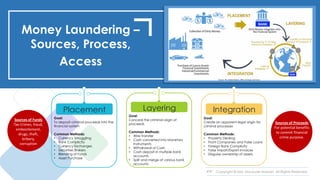
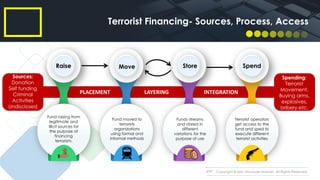
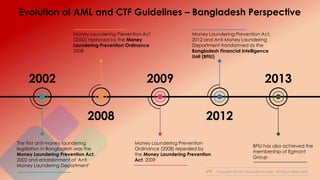
Money laundering and terrorist financing guidelines have evolved over time through various international conventions and organizations seeking to combat these financial crimes (1). Key events included the 1988 UN Drug Trafficking Convention and the 1989 Financial Action Task Force on money laundering (2). Guidelines also evolved at the national level, such as Bangladesh's first anti-money laundering law passed in 2002 (3). Proper policies, procedures and programs are needed by financial institutions to comply with regulations and mitigate risks, starting with an overarching AML/CTF policy endorsed at the highest levels.





![Copyright © Md. Moulude Hossain. All Rights Reserved.
01
STRUCTURING
Often known as smurfing,
whereby cash is broken into
smaller deposits of money,
used to defeat suspicion of
money laundering.
02
BULK CASH SMUGGLING
Pysically smuggling cash to
another jurisdiction and
depositing it in a financial
institution, such as an
offshore bank
03
CASH-INTENSIVE BUSINESSES
Business typically expected to
receive a large proportion of its
revenue as cash uses its
accounts to deposit criminally
derived cash
04
TRADE-BASED LAUNDERING
Under- or over-valuing
invoices to disguise the
movement of money.
Money Laundering - Methods
05
SHELL COMPANIES & TRUSTS
Trusts and shell companies
disguise the true owners of
money. Trusts and corporate
vehicles, depending on the
jurisdiction, need not disclose
their true owner.
06
ROUND-TRIPPING
Money deposited in a
controlled foreign corporation
offshore, preferably in a tax
haven where minimal records
are kept, and then shipped
back as a foreign direct
investment.
07
BANK CAPTURE
Money launderers or
criminals buy a controlling
interest in a bank, preferably
in a jurisdiction with weak
money laundering controls,
and then move money
through the bank without
scrutiny.
08
CASINOS
An individual walks into a
casino and buys chips with
illicit cash. The individual will
then play for a relatively
short time.
09
OTHER GAMBLING
Money is spent on gambling,
preferably on high odds
games. One way to minimize
risk with this method is to bet
on every possible outcome
of some event that has many
possible outcomes,
10
BLACK SALARIES
A company may have
unregistered employees
without written contracts
and pay them cash salaries.
Dirty money might be used
to pay them.
11
TAX AMNESTIES
Those that legalize
unreported assets and cash
in tax havens.
12
TRANSACTION LAUNDERING
Merchant unknowingly
processes illicit credit card
transactions for another
business[19]. It is a growing
problem[20][21] and
recognized as distinct from
traditional money laundering](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/moneylaunderingandterroristfinancinginanutshell-chapterone-190328164914/85/Money-Laundering-and-Terrorist-Financing-in-a-Nutshell-Chapter-One-6-320.jpg)