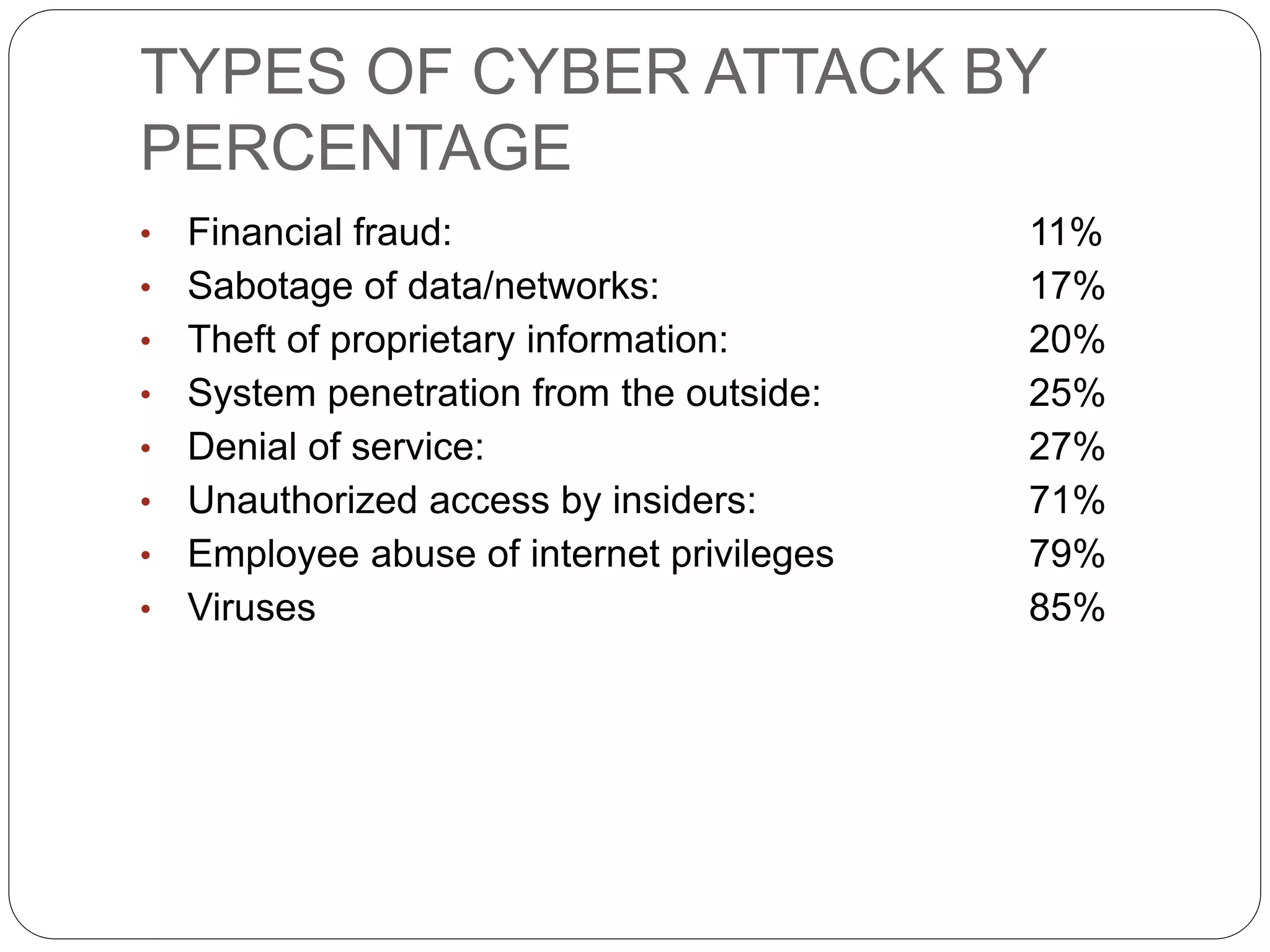
This document discusses cyber crimes and cyber laws in India. It defines cyber crime as criminal activities conducted online or using the internet. It outlines various types of cyber crimes like credit card fraud, software piracy, and cyber terrorism. It also discusses statistics on common types of cyber attacks. The document then examines India's Information Technology Act 2000 which defines cyber crimes and assigns investigation of such crimes to authorized police officers. It analyzes sections 65, 66, and 67 which pertains to tampering with computer source documents, hacking, and publishing obscene content online. It notes challenges faced by law enforcement in dealing with cyber crimes and provides tips to enhance cyber safety.