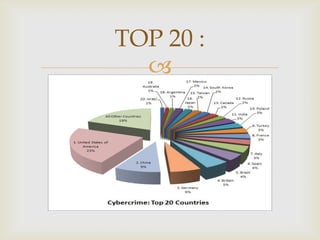
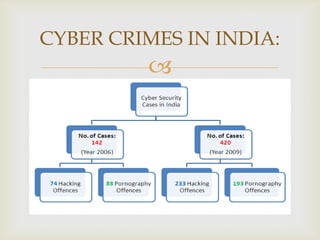
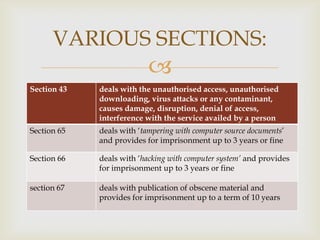
The document discusses cyber crime and the legal provisions around it in India. It begins by defining cyber crime and noting that the term was first coined in the 1980s. Cyber criminals can include children, organized hackers, professional hackers, and discontent employees. Common cyber crimes include hacking, theft of electronic information, email bombing, and denial of service attacks. The Information Technology Act of 2000 is the primary legislation dealing with cyber crimes in India. It identifies offenses such as unauthorized access, publishing obscene material, and tampering with computer source documents. Notable cyber crime cases in India include the DPS mms case and the Air Force school mms case. Prevention involves using antivirus software, backups, and being wary of personal information