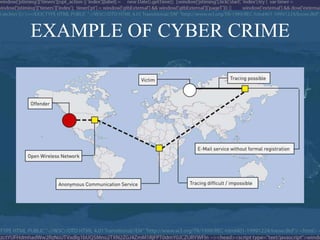
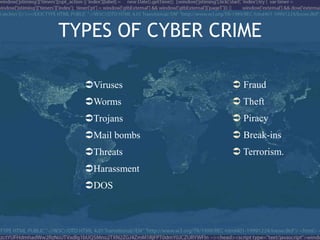
This document discusses cyber crime and cyber law. It defines cybercrime as any illegal act committed using a computer network, and provides examples such as child pornography, threatening emails, identity theft, and software piracy. The document classifies cybercrimes as offenses against data/systems, content-related offenses, and copyright offenses. It also discusses the need for cyber law to address challenges in applying traditional law to computer-related crimes and technologies.