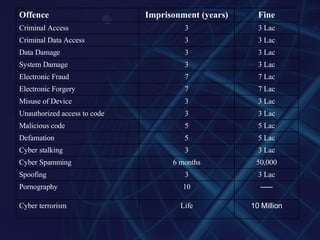
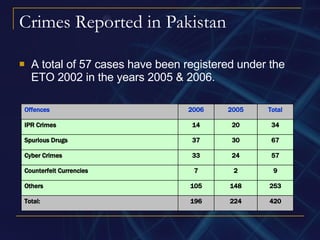
The document discusses cyber laws in Pakistan. It provides an overview of two key pieces of legislation: the Electronic Transaction Ordinance of 2002, which recognized electronic documentation and established rules around digital signatures; and the Electronic/Cyber Crime Bill of 2007, which defined 17 types of cyber crimes and assigned punishments including imprisonment and fines. It also presents some statistics on cyber crimes reported in Pakistan and globally.