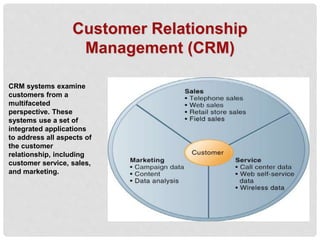
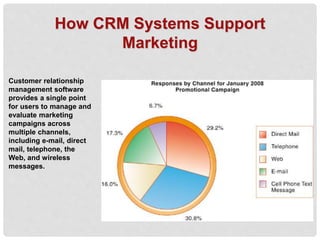
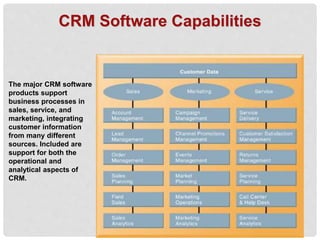
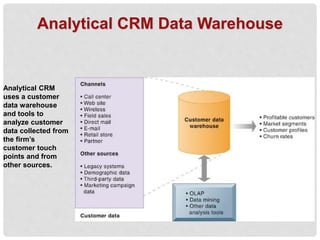
Customer relationship management (CRM) systems capture, integrate, and analyze customer data from across an organization to provide a single view of customers. CRM systems examine customers from many perspectives to address all aspects of customer relationships, including customer service, sales, and marketing. CRM software packages provide tools to support operational CRM like sales force automation and customer service, as well as analytical CRM to analyze customer data and assess things like customer lifetime value. Implementing CRM systems can provide business benefits such as increased customer satisfaction, reduced marketing costs, more effective marketing, and increased sales revenue.