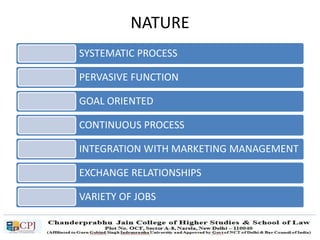
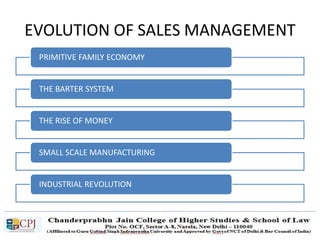
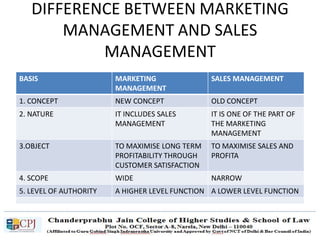
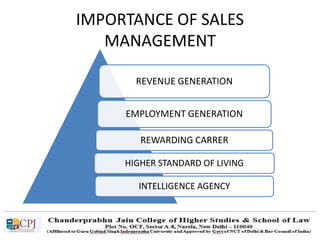
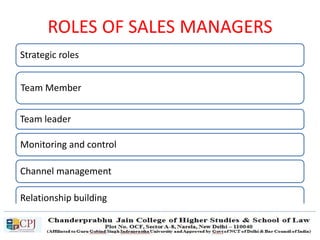
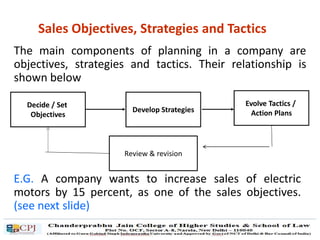
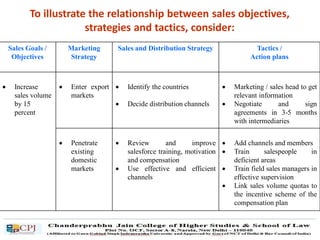
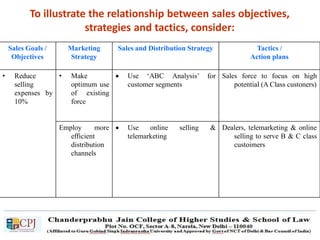
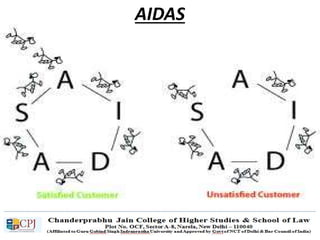
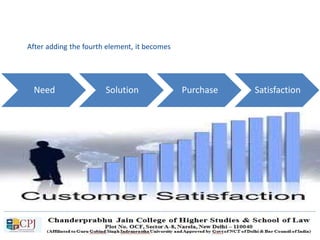
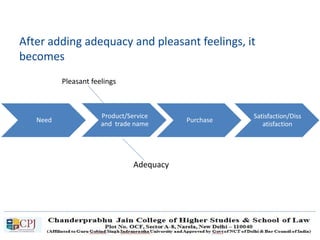
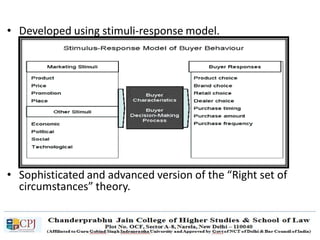
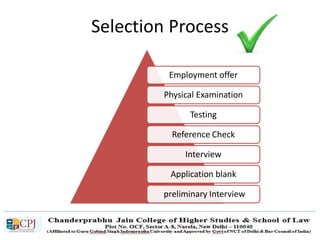
The document discusses key concepts in sales management including the meaning and nature of sales management, the scope and objectives of sales management, theories of selling such as AIDAS and the buying formula theory, and strategies for recruiting and selecting successful salespeople by determining job requirements and desirable qualities.