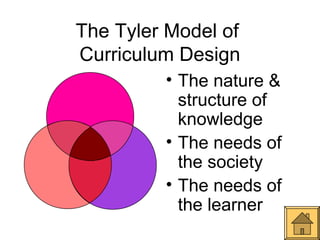
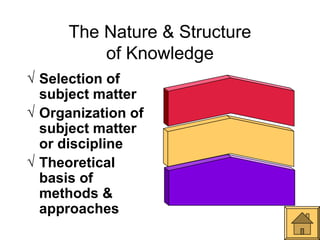
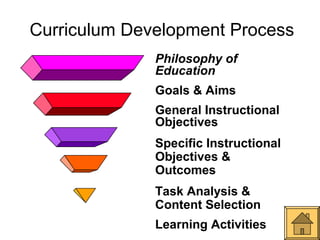
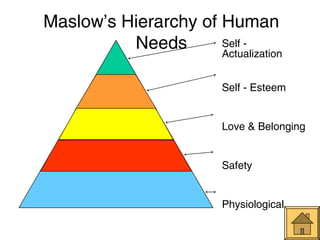
This document outlines Ralph Tyler's model for curriculum design. It begins with a definition of curriculum as the planned learning experiences and outcomes designed to promote students' growth. It then discusses curriculum models as being based on theories of teaching and learning and tailored to specific learners. The core of Tyler's model involves answering 4 fundamental questions: 1) desired educational goals, 2) learning experiences to achieve these goals, 3) effective organization of experiences, and 4) evaluation of goal achievement. The model also considers the nature of knowledge, needs of learners and society to design curriculum.