- CSS3 is made up of modular components at different stages of development rather than a single specification. These include selectors, properties, and other modules.
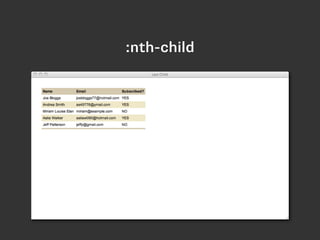
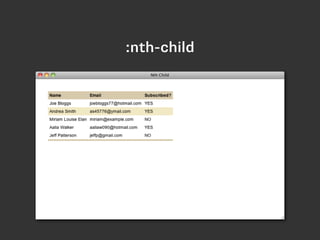
- CSS selector capabilities were expanded in CSS3 with things like attribute selectors that select elements based on attributes, pseudo-classes for dynamic states like hover and active, and structural pseudo-classes for things like first-child.
- CSS4 is extending selector functionality further with things like the :matches pseudo-class to apply rules to groups of selectors, pseudo-classes for time-based states, and grid selector features. Support for CSS4 selectors is starting to appear in modern browsers.












![form input[type="text"] {
}
form input[type="submit"] {
}
Attribute
Selectors](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/css3-selectorsconfoo-150219065746-conversion-gate02/85/CSS-Selectors-13-320.jpg)

![label[for="fContact"] {
float: none;
width: auto;
}
Attribute
Selectors](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/css3-selectorsconfoo-150219065746-conversion-gate02/85/CSS-Selectors-15-320.jpg)
![a[href ^="mailto:"] {
padding-right: 20px;
background-
image:url(email.png);
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-position: right
center;
}
Attribute
Selectors](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/css3-selectorsconfoo-150219065746-conversion-gate02/85/CSS-Selectors-16-320.jpg)








































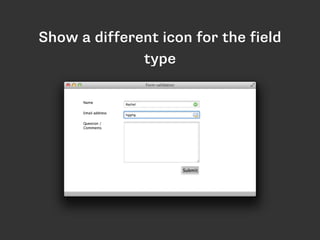
![input[type="email"]:focus:required:invalid
{
background-image: url(email_error.png);
}
Show a different
icon for the field
type](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/css3-selectorsconfoo-150219065746-conversion-gate02/85/CSS-Selectors-60-320.jpg)