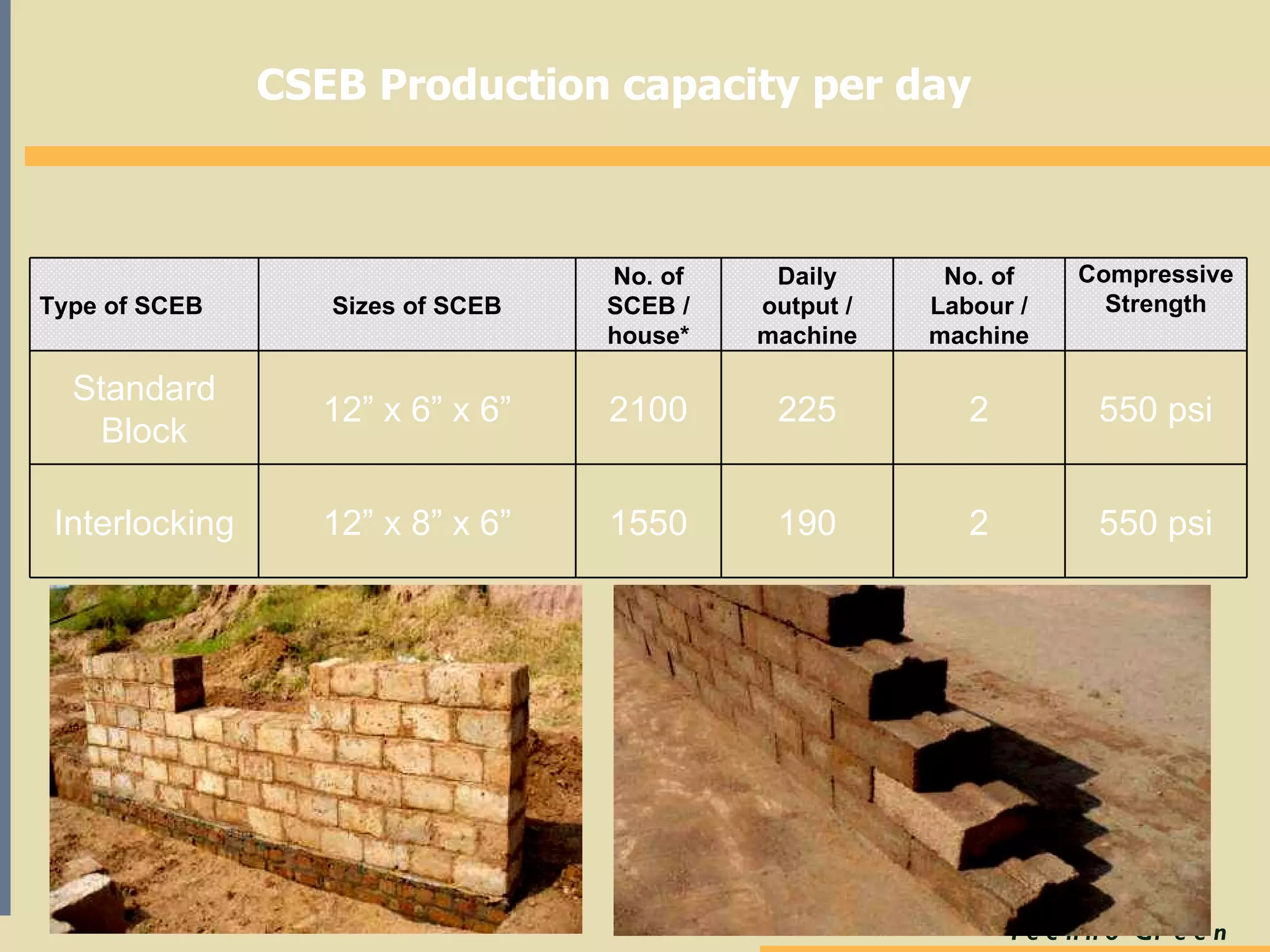
The document discusses the impact of the traditional brick production industry in Pakistan, highlighting environmental, economic, and social issues such as deforestation, CO2 emissions, and child labor. It presents Compressed Stabilized Earth Blocks (CSEB) as a sustainable alternative, detailing their production process, benefits, and community-driven implementation in various regions. Training initiatives and pilot projects are proposed to foster local production and enhance disaster resilience in housing.

















![Follow up & More Info Technical working group possible Online wiki-site under development Focal Point: Tahir Dar Tel: 0333 515 9090 Email: [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csebpresentation2ndmarch2011compressed-111212120613-phpapp01/75/Cseb-presentation-2nd-march-2011-compressed-23-2048.jpg)