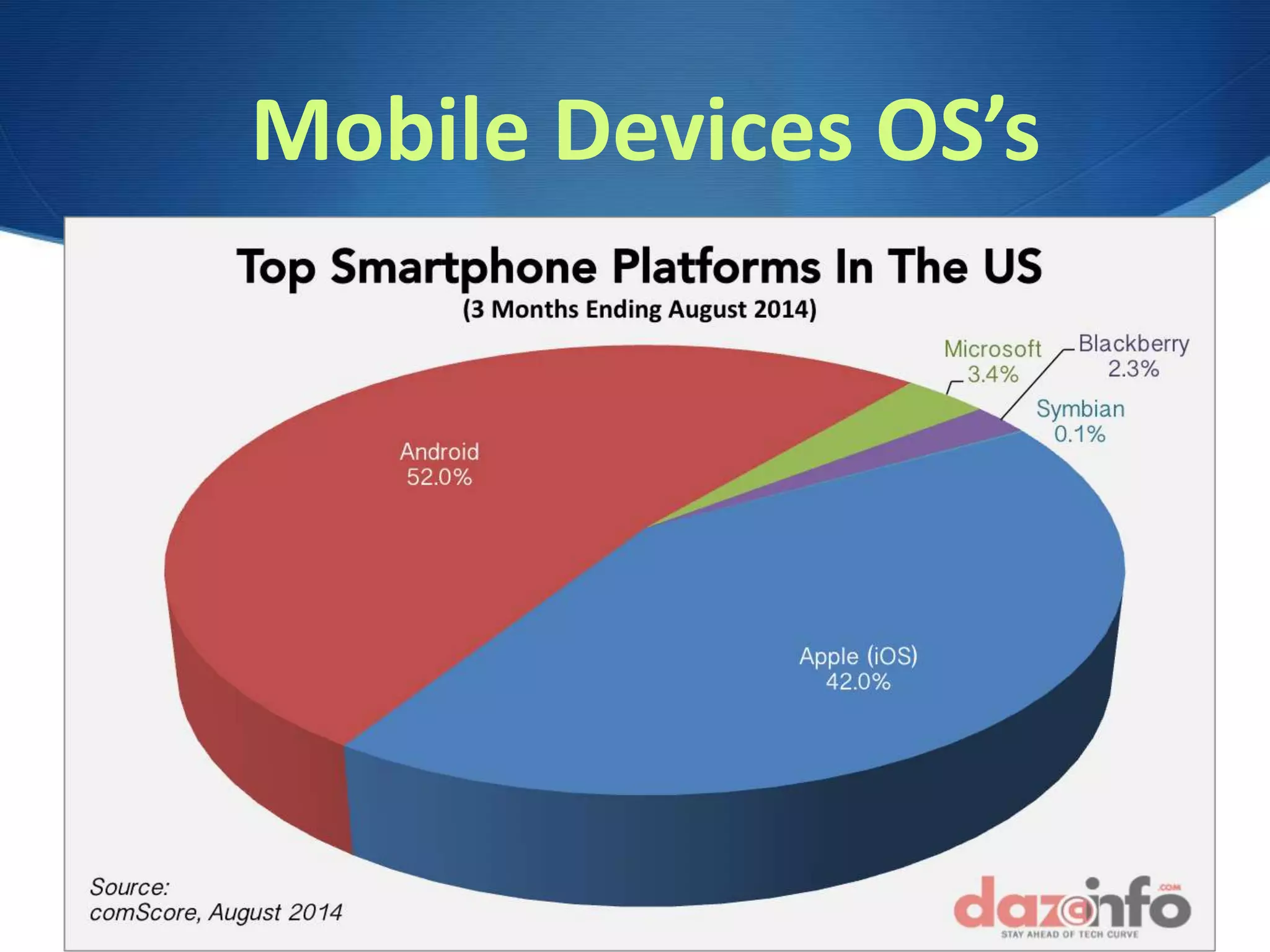
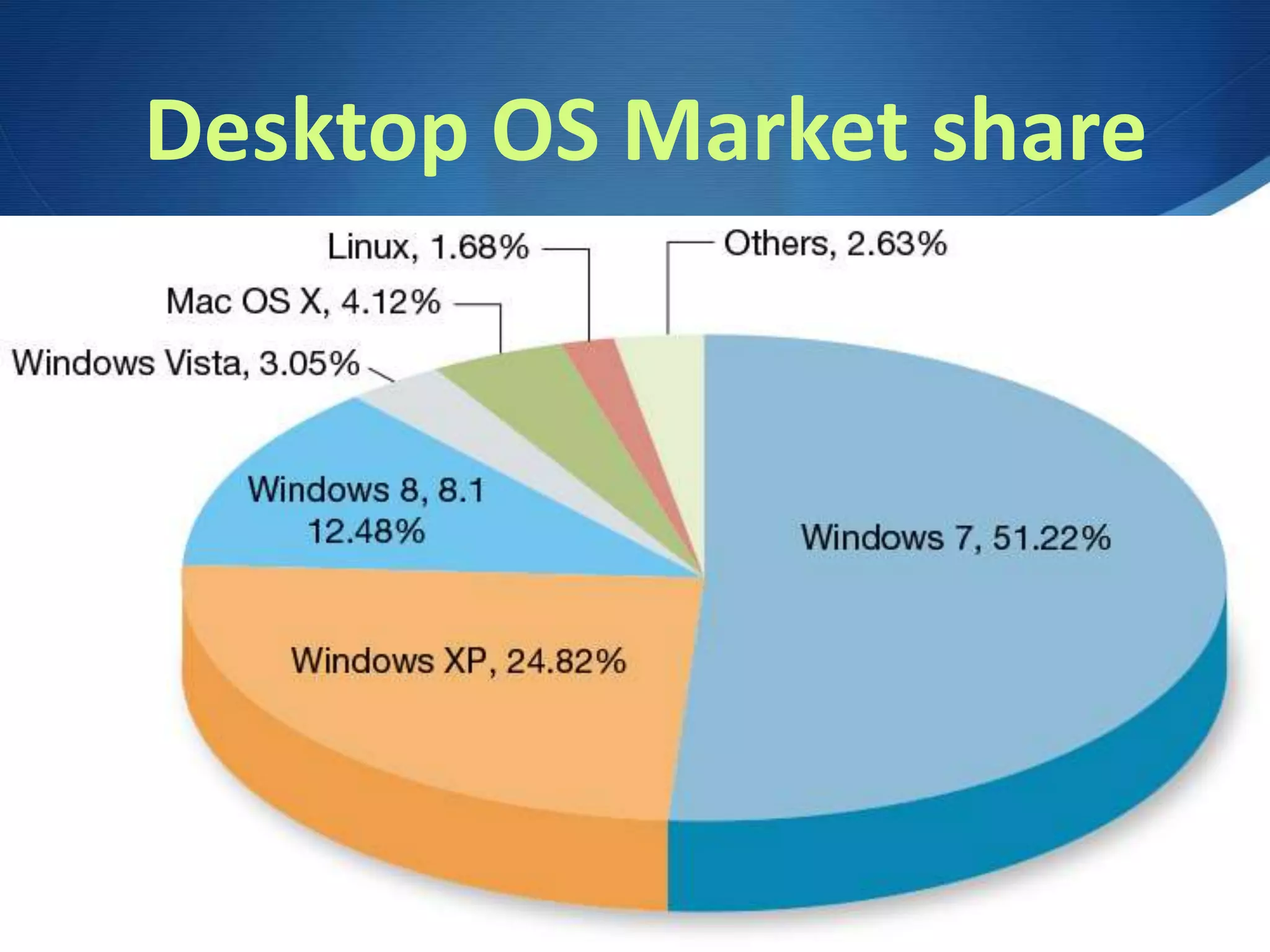
This document discusses system software and operating systems. It defines system software as programs that help run the computer by coordinating between applications and hardware. It notes the main components are the operating system and utility programs. The operating system manages processing, memory, storage, devices, and tasks. Common operating systems include Windows, Mac OSX, Linux, iOS, and Android. The operating system provides a graphical user interface, manages CPU instructions and devices, and prioritizes multitasking. It discusses the boot process and roles of the BIOS, POST, kernel, and system files.