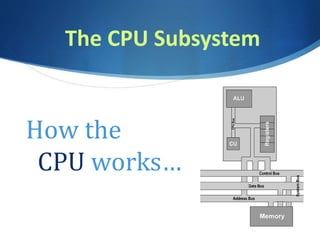
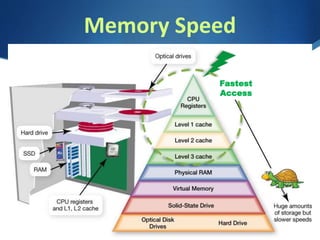
This document discusses digital devices and their processing and memory components. It describes how the CPU works with a control unit and ALU to fetch, decode, and execute instructions. The CPU has factors like clock speed, number of cores, and cache memory. Memory is volatile RAM for short-term use and non-volatile ROM and hard drives for long-term storage. Storage needs depend on the operating system, applications, data, photos, music and video. Larger storage options include cloud, SSD, multiple hard drives, and external drives.