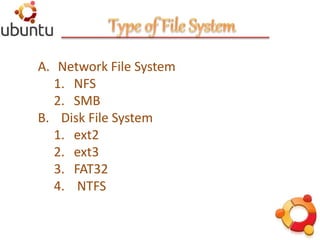
This document discusses Ubuntu file systems. It begins with an overview of Ubuntu's history and pros and cons. It then covers the basics of file systems, including what they are, common types (e.g. ext2, ext3), and how they are structured and mounted. It also discusses commands used to create, modify, and manage file systems.