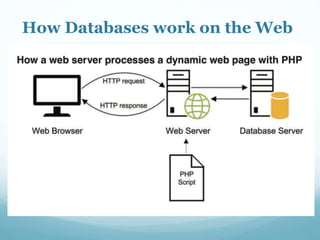
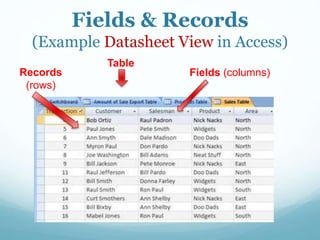
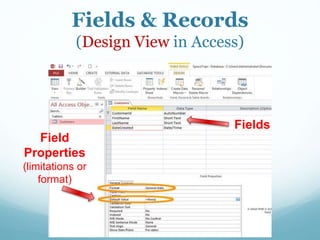
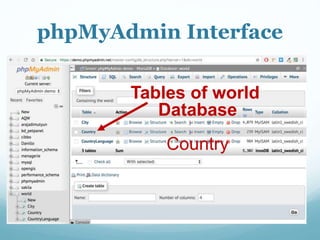
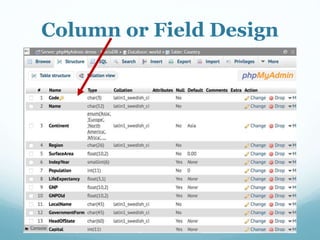
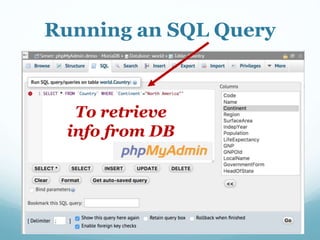
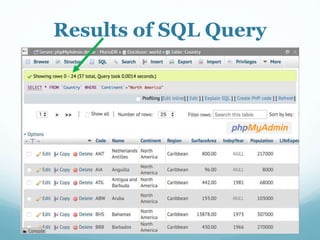
This document discusses databases and how they are used to organize collections of information. A database consists of records and fields that can be easily accessed, managed and updated. Common databases include customer profiles, employee information, and product inventories. Information in databases is organized into tables with rows and columns. Popular database software includes Microsoft Access, which allows users to create, read, update and delete records. Databases are stored on servers and can be accessed via query languages like SQL.