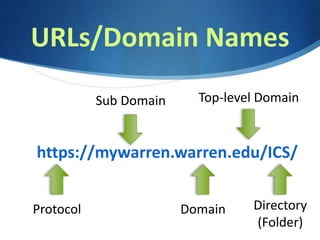
This document provides an overview of the history and components of the Internet. It discusses how ARPAnet in 1969 connected 4 computers and led to the development of the World Wide Web by Tim Berners-Lee in 1989. It describes the growth of Internet users from 1% of the world population in 1995 to over 40% today. Key components covered include browsers, URLs, IP addresses, protocols, and HTML. The document concludes with a discussion of content management systems used to create websites.