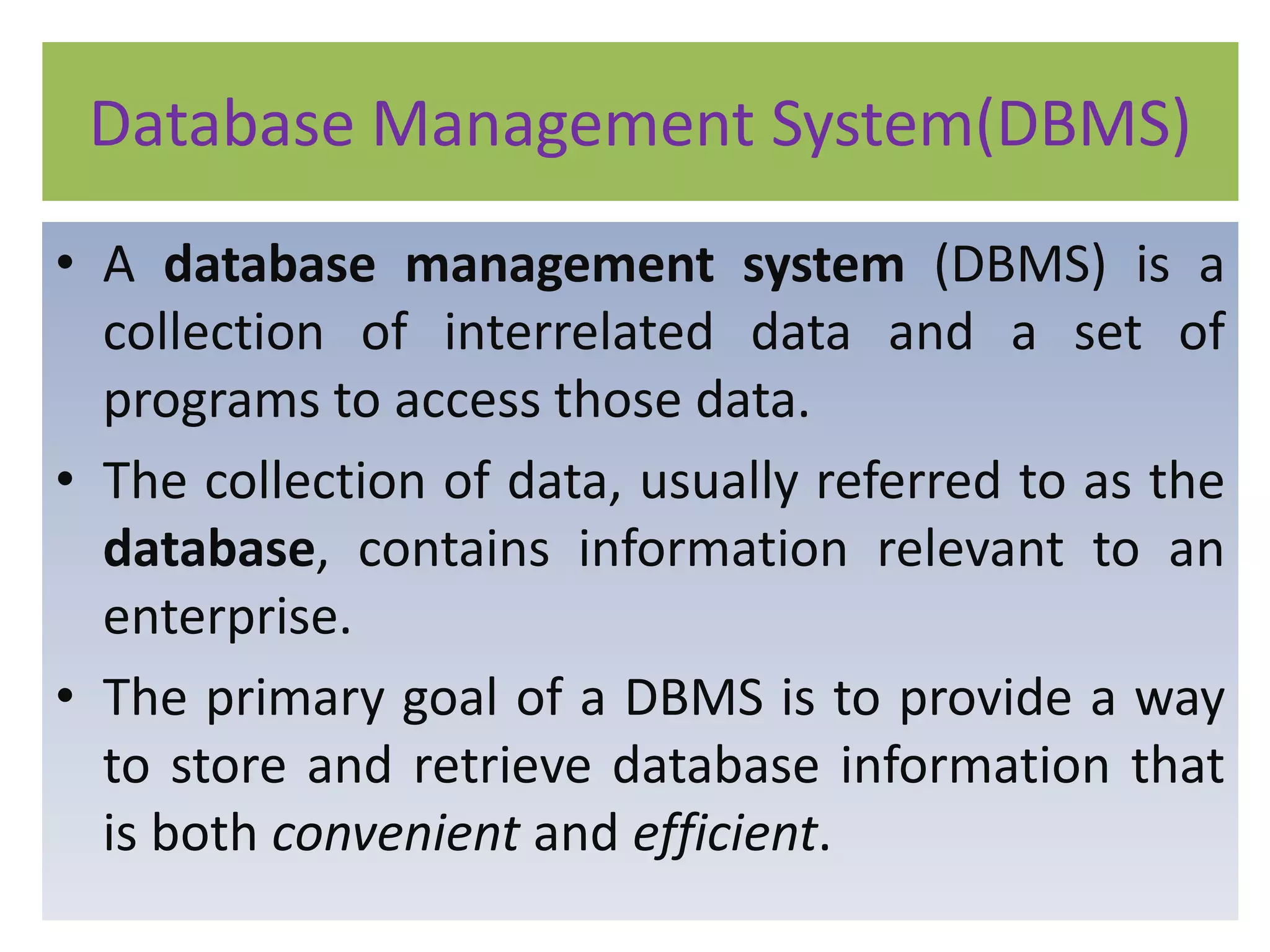
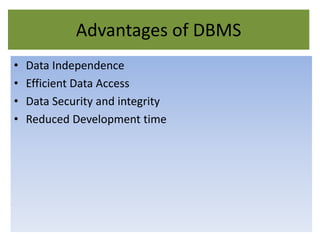
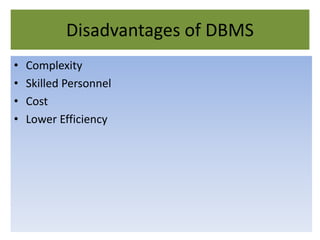
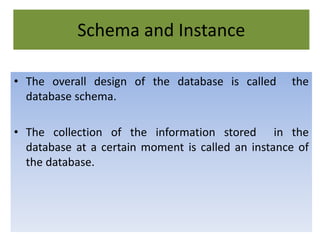
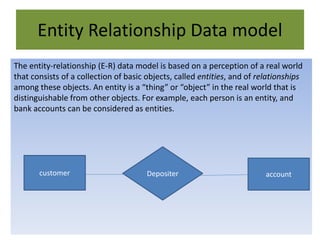
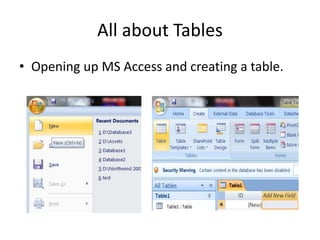
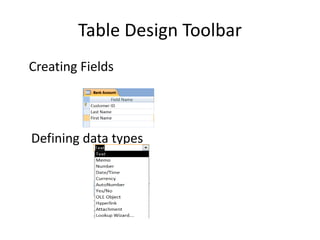
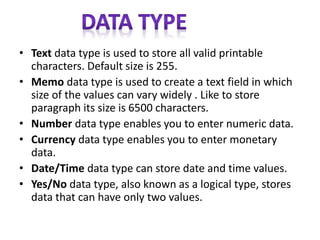
A database management system (DBMS) stores and manages data and provides efficient ways to store, retrieve, and manipulate that data. The primary goals of a DBMS are to provide convenient and efficient ways to store and retrieve database information. It uses tables to represent entities, their relationships, and the data, with each table having multiple columns and rows. Some common DBMSs are Microsoft Access, which is designed for small home or business databases, and SQL Server, which is intended for larger server-based databases accessed remotely.