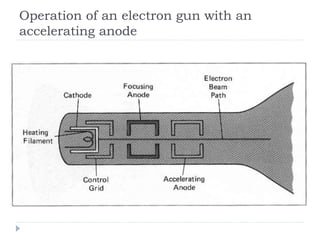
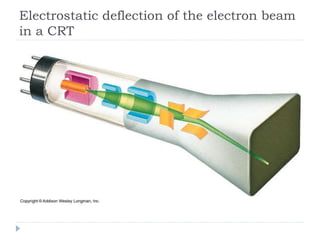
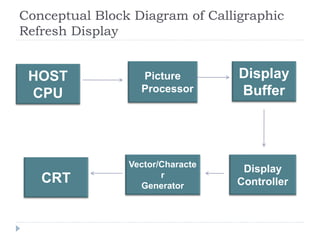
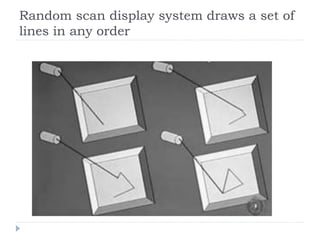
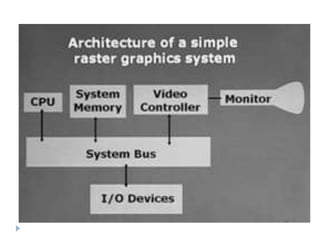
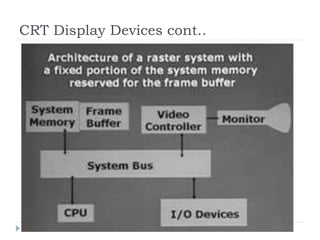
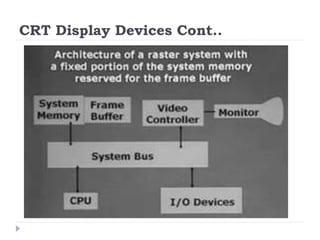
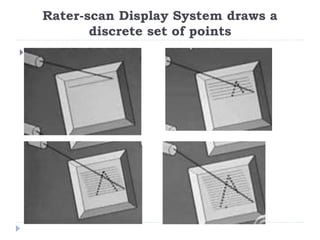
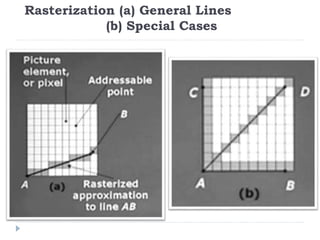
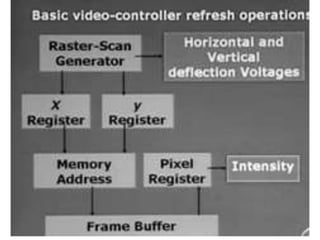
This document discusses different types of CRT display systems. It describes Direct View Storage Tubes (DVST) which store images using a long persistence phosphor but cannot be updated quickly. Random scan/calligraphic displays draw lines in arbitrary order but must be refreshed at 30 Hz. Raster scan displays store images as a matrix of pixels in a refresh buffer and draw the entire screen sequentially one line at a time, allowing for animation and faster updating than DVST systems.