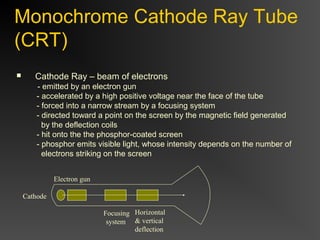
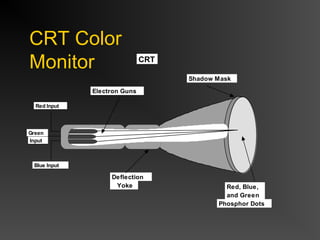
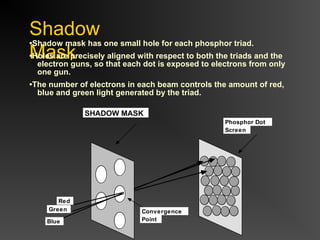
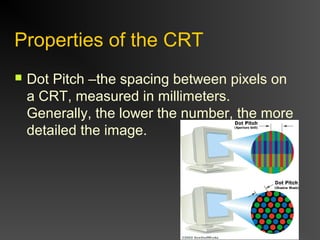
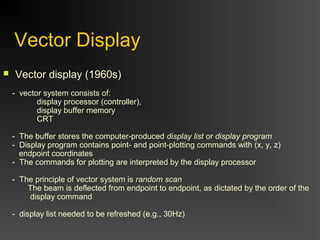
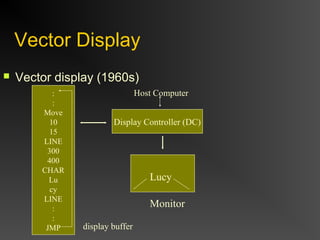
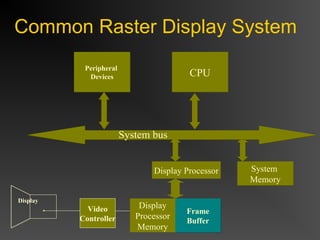
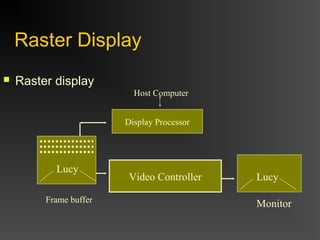
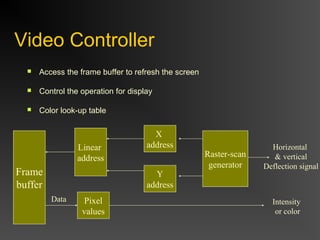
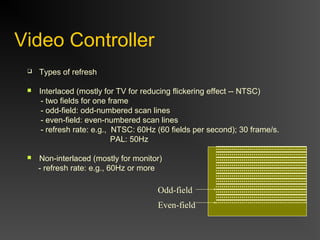
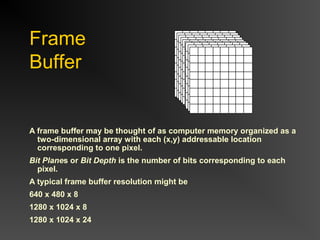
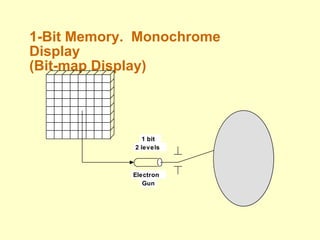
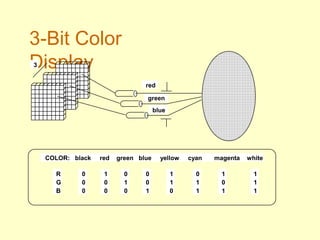
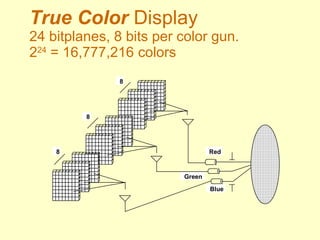
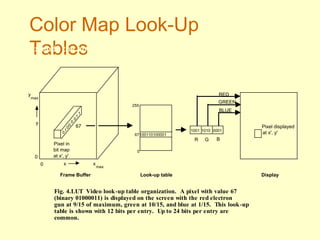
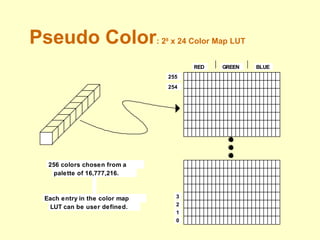
The document discusses different types of displays including emissive displays like CRTs and non-emissive displays like LCDs. It then provides details on how CRTs work including the electron gun, deflection coils, and phosphor screen. Key properties of CRTs are described such as resolution, refresh rate, and color reproduction using an electron gun and shadow mask arrangement. Raster scanning is introduced as the process of drawing the image line by line using a frame buffer and video controller. Color mapping with a lookup table is also summarized.