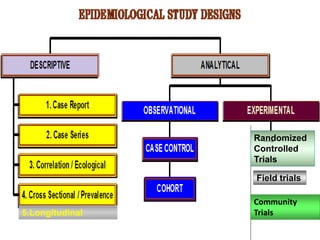
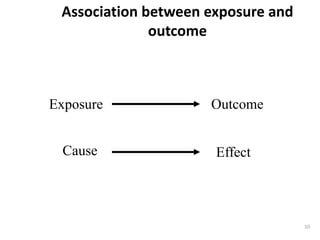
This document discusses various epidemiological study designs. It begins by defining descriptive studies, which involve systematically collecting and presenting data to describe a situation, and analytical studies, which attempt to establish causes or risk factors by comparing exposed and unexposed groups. The main types of descriptive studies covered are cross-sectional (examining a population at a single point in time), longitudinal (following a population over time), and ecological (examining population-level associations between exposures and outcomes). Advantages and disadvantages of each design are provided.