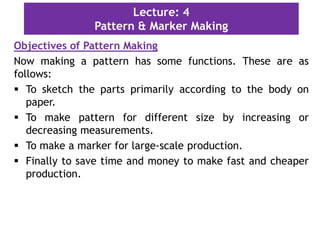
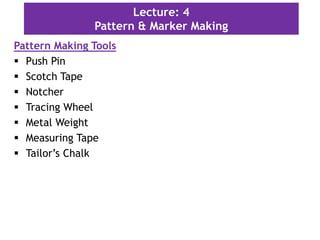
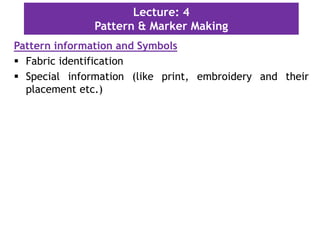
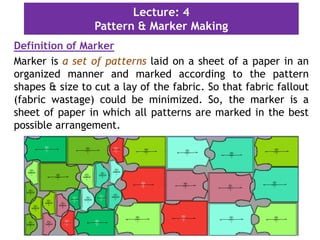
This document discusses pattern making and marker making in garment production. It defines a pattern as a paper template used to cut fabric for garment parts. Markers are arrangements of patterns on paper that minimize fabric waste when cutting multiple sizes. The document outlines tools and methods for pattern making, important information to include on patterns like size and grain lines, and how to grade patterns for different sizes. It defines different types of markers based on garment style and fabric characteristics. The goal of markers is to efficiently arrange patterns to reduce fabric usage and costs during bulk production.