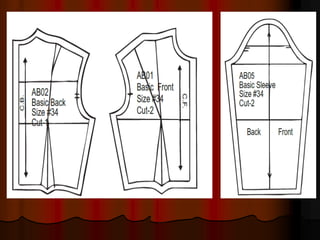
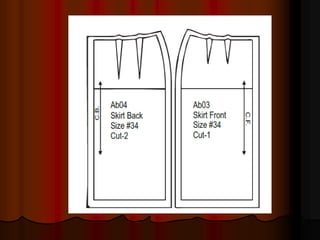
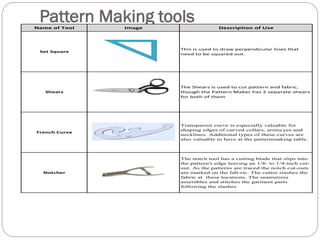
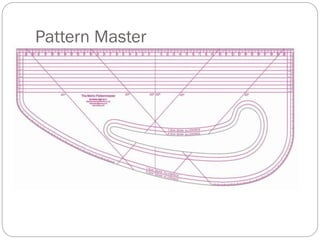
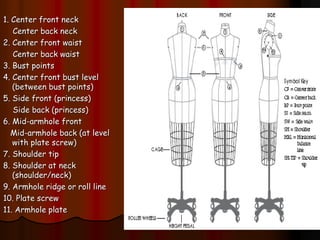
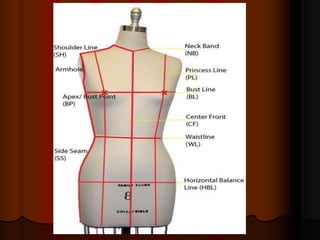
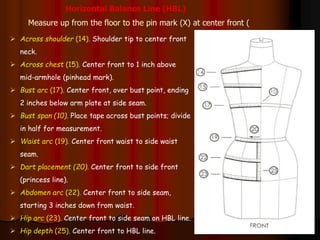
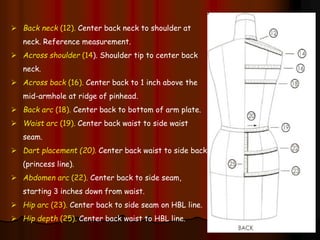
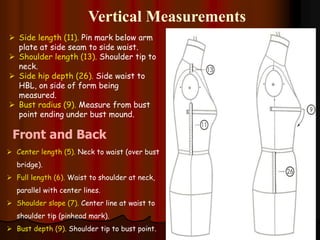
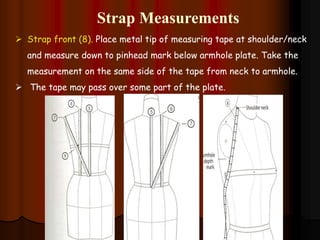
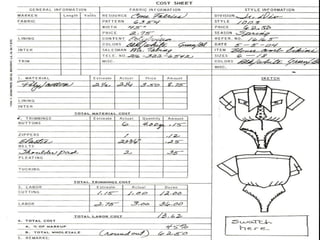
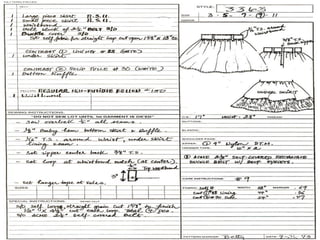
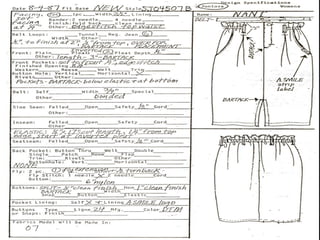
The document provides information about pattern making for men's clothing. It discusses what pattern making is, the purpose of pattern making, and common pattern making tools. It also describes different pattern making methods like direct drafting, flat pattern, and draping. Measurement is a key part of pattern making to accurately create patterns for garments. The document outlines important body measurement landmarks and techniques for properly measuring the body or a form. It also discusses other important pattern making documents like cost sheets, pattern charts, design specification sheets, and technical packs which provide production details for patterns and garments. Accurate measurement and documentation are essential for successful pattern making.