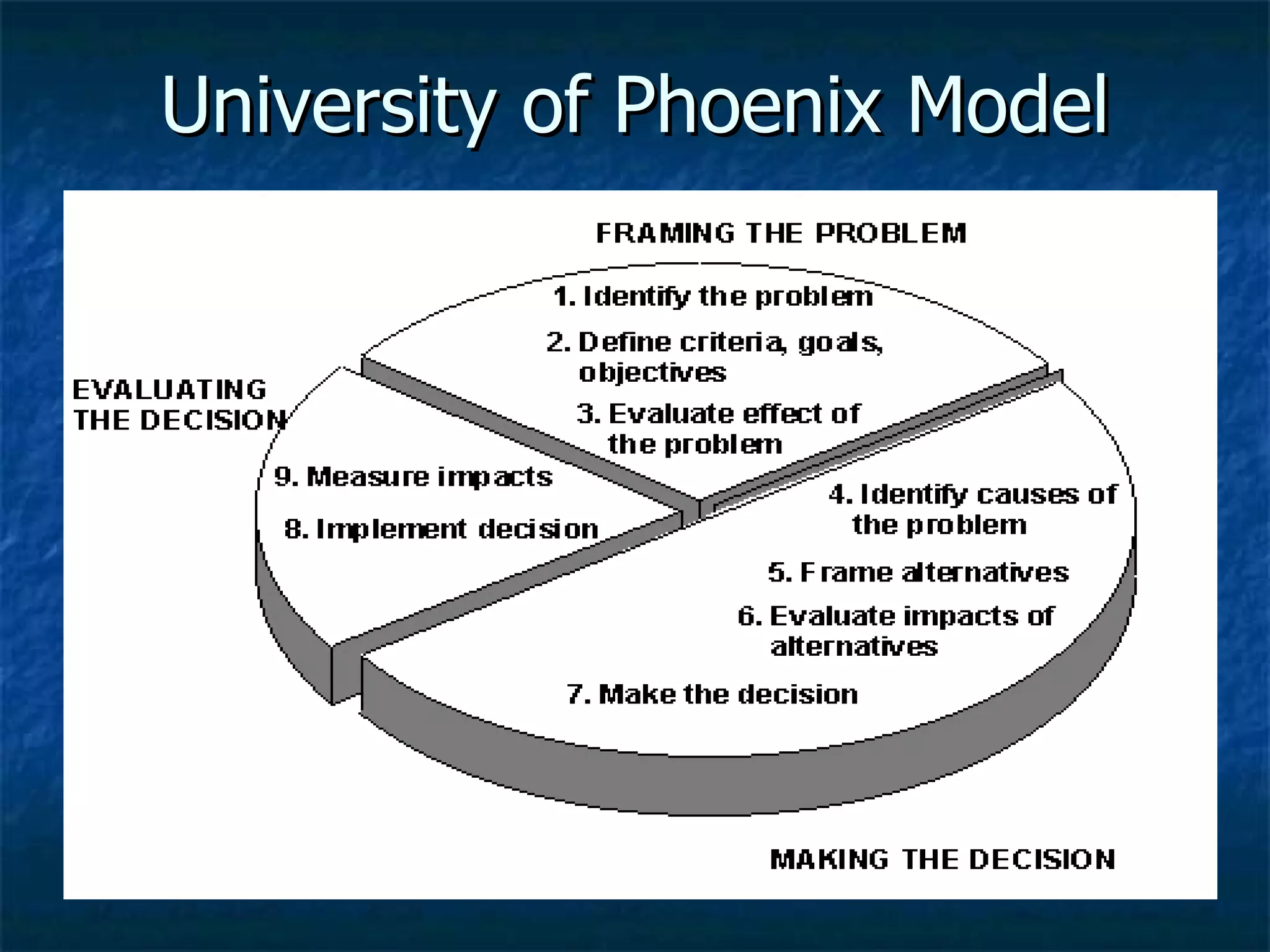
This document provides an overview of a course on critical thinking and decision making. It introduces course objectives, assignments, and key topics that will be covered such as critical thinking skills, decision making processes, identifying assumptions and biases, and overcoming barriers to effective thinking. The document outlines phases of critical thinking and questions students should ask themselves to evaluate arguments and make well-reasoned decisions.