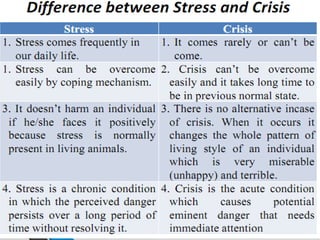
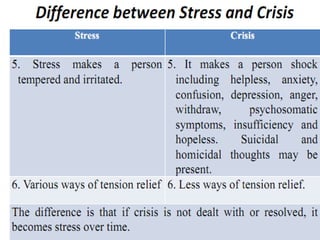
The document discusses crises as disturbances caused by stressful events, detailing their characteristics, causes, and various types such as financial, technological, and socio-cultural crises. It outlines crisis intervention principles and steps, emphasizing the importance of support and coping mechanisms to aid individuals during crises. Additionally, it highlights mobile crisis programs and community efforts to provide effective intervention and support.