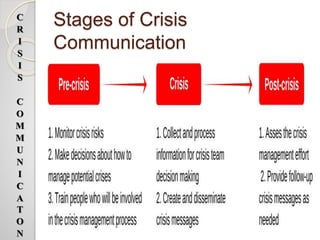
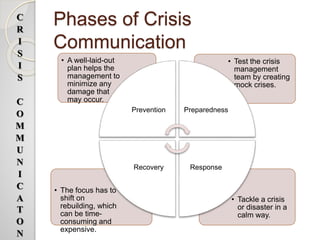
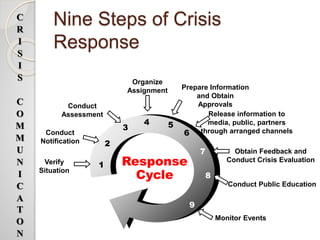
The document discusses crisis communication and provides information on various topics related to crisis management. It defines what constitutes a crisis and lists different types of organizational crises. It also outlines potential threats caused by crises, such as damage to public safety and financial and reputational losses for companies. Additionally, the document summarizes several crisis communication theories and models that provide guidance on how to respond to and manage crises effectively. It emphasizes the importance of understanding stakeholders' perspectives and selecting appropriate response strategies based on the specific crisis situation.