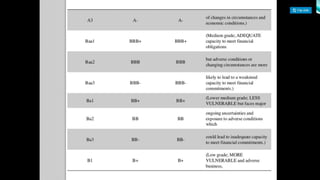
Credit ratings evaluate the creditworthiness of debtors like businesses and governments. They are determined by credit rating agencies based on their analysis of public and private information, not mathematical formulas. Credit ratings are used by bond investors to assess the likelihood that the issuer will repay its debt obligations. In India, credit rating agencies must register with SEBI and meet requirements regarding net worth, infrastructure, and experience. The major credit rating agencies in India are CRISIL, ICRA, CARE, and FITCH Ratings India. Credit ratings provide benefits to both investors and companies by improving transparency and access to funding.