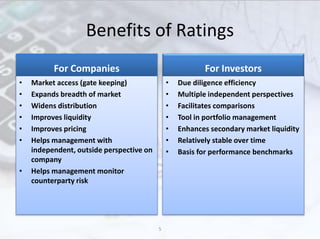
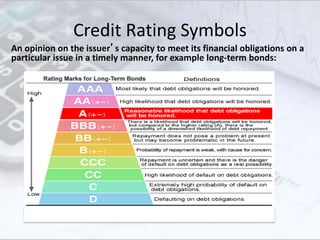
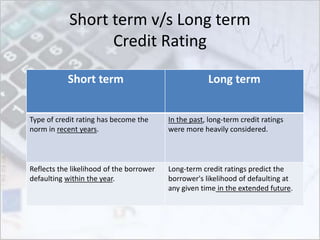
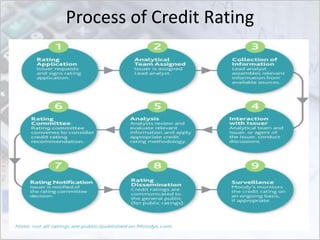
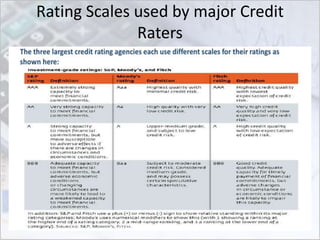
This document discusses credit ratings and the credit rating agencies. It provides information on what credit ratings are, their importance, benefits, factors that affect ratings, rating scales and methodologies. It also discusses the major global and Indian credit rating agencies like S&P, Moody's, Fitch, Crisil, CIBIL and CARE. It outlines the business models, market shares and rating scales of these prominent agencies. Finally, it notes the advantages and disadvantages of credit ratings.