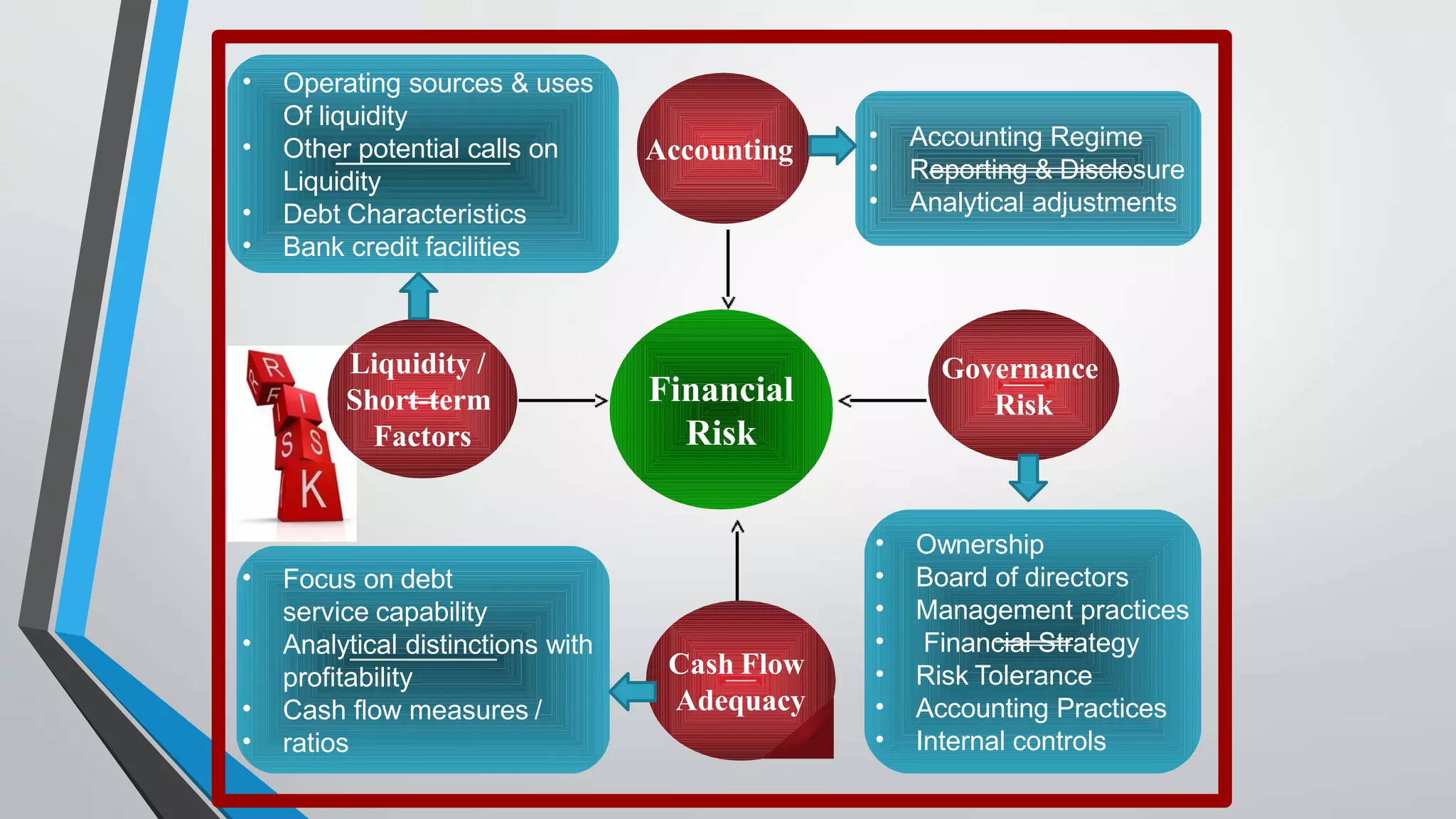
This document discusses credit rating methodologies. It defines credit ratings and explains that they are determined by credit rating agencies to evaluate a debtor's ability to repay debt. The top credit rating agencies are listed as Dun & Bradstreet, Moody's, Standard & Poor's, and Fitch Ratings. Credit rating methodologies involve business analysis of industry and company risks, financial analysis of accounting practices and cash flows, management evaluation, and fundamental analysis of liquidity, assets, profits, and taxes. The rating process involves agencies collecting information, analyzing it through a team, submitting recommendations to a rating committee, and continuously monitoring the rating.