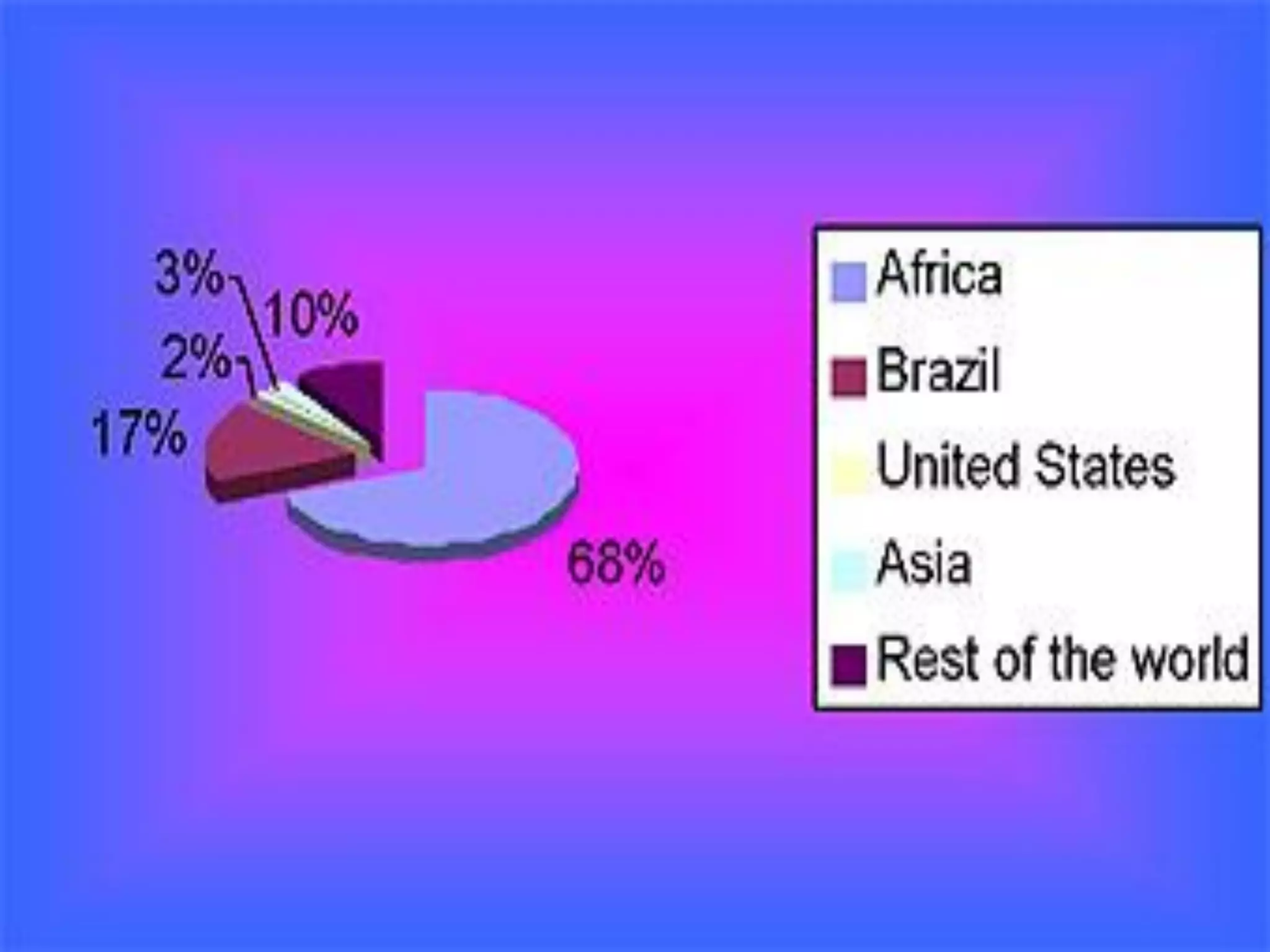
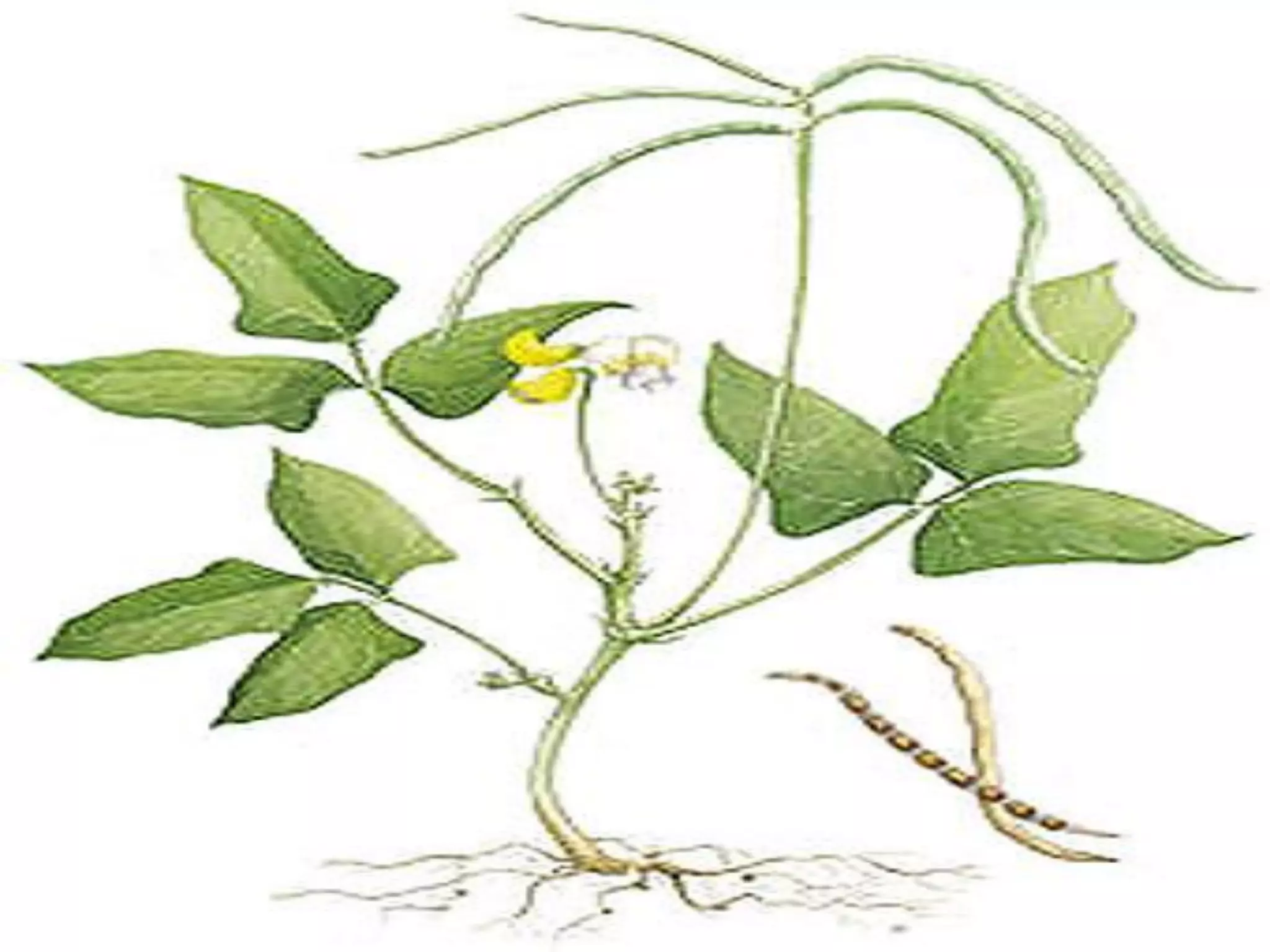
Cowpea is a warm-season legume originating from Africa. It is an important food crop grown in tropical and subtropical regions. Cowpea has a diploid chromosome number of 22 and is self-pollinated. Major varieties grown in India include KBC-2, IT-38956-1, and KM-5. Breeding objectives focus on increasing yield, resistance to diseases and insects, and developing dual-purpose varieties.