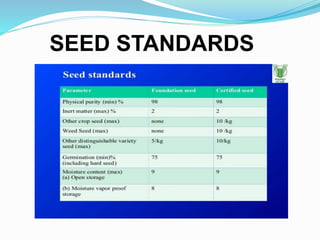
This document provides information on cowpea (Vigna unguiculata), including its scientific name, origin in Africa, common uses, production statistics in India, recommended growing conditions, cultivation practices from land preparation to harvesting, pests and diseases, and standards for seed production. Cowpea is grown widely in central and peninsular India, with a production of 4.8 lakh tonnes annually on 5800 hectares.