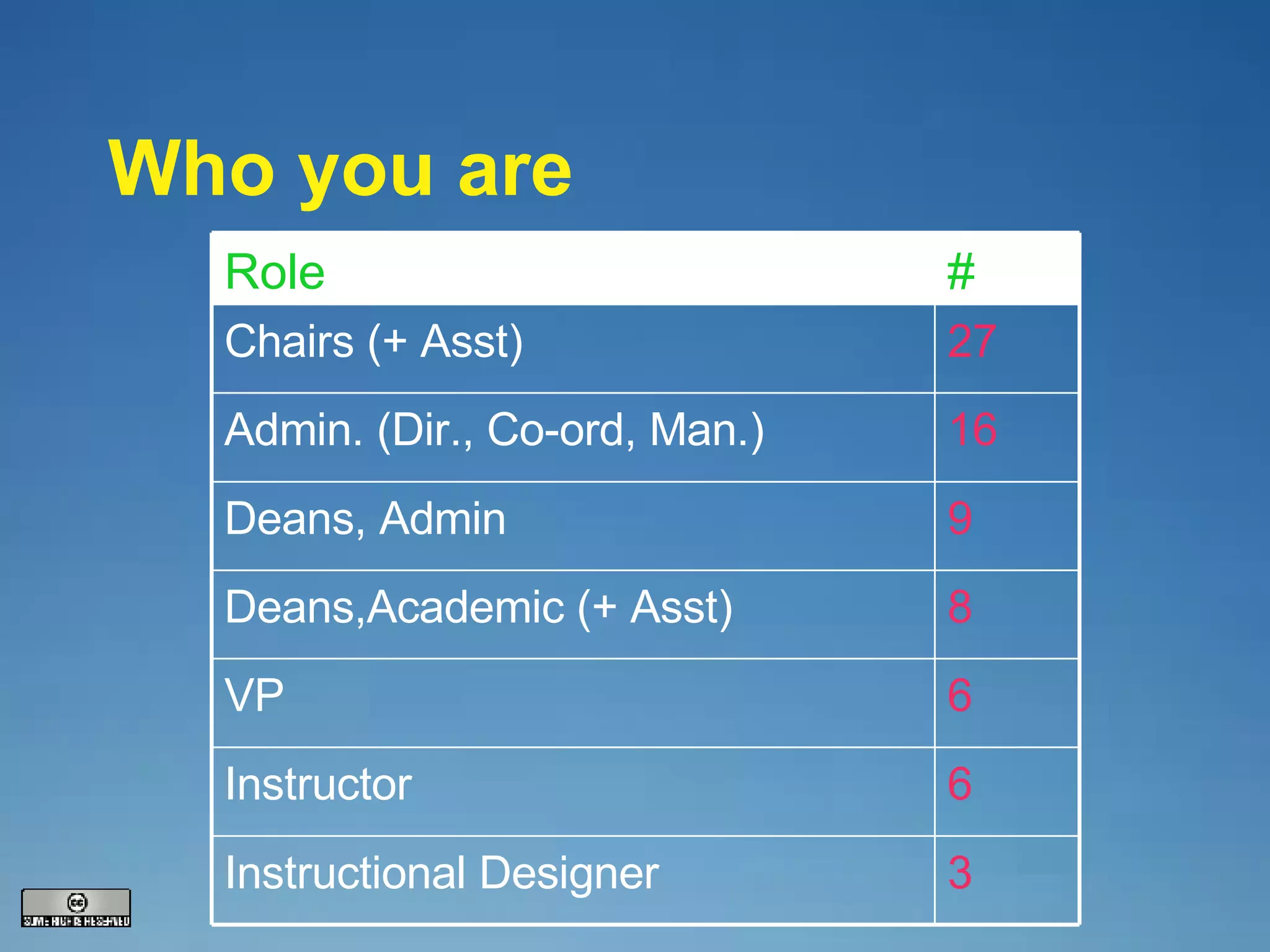
The document discusses the evolving landscape of teaching and learning with technology, highlighting issues such as accessibility, student preparedness, and the changing roles of faculty and students over the years. It emphasizes the importance of adapting course design and instructional methods to meet the needs of today's learners and addresses the challenges posed by technology and shifting educational paradigms. Additionally, it considers future trends in education, including collaborative models and innovative delivery mechanisms for courses.










































































![[email_address] Slides available from http://www.slideshare.net/ Search for Patricia McGee Other materials available from http://drpmcgee.googlepages.com/home](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/the-future-looks-digital-tccta958/75/The-Future-Looks-Digital-TCCTA-77-2048.jpg)
