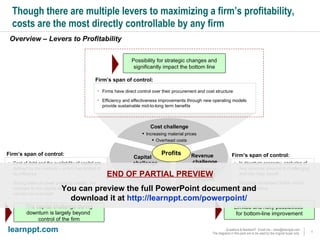
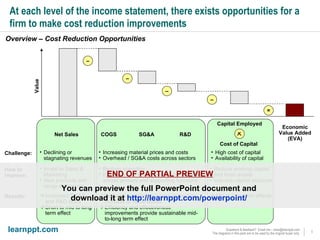
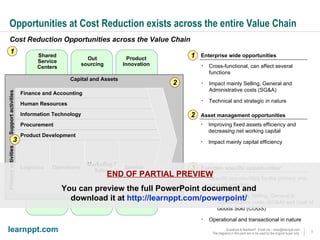
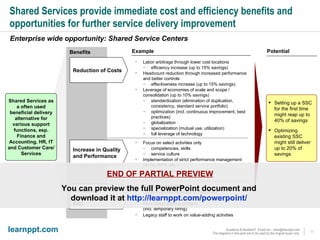
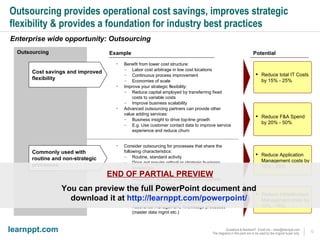
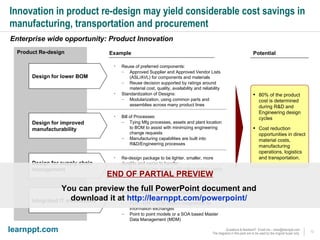
The document is a comprehensive cost reduction toolkit detailing over 45 initiatives categorized across enterprise-wide, asset management, and function-specific opportunities, aimed at improving profitability amidst economic challenges. It emphasizes the importance of managing costs through procurement efficiencies, outsourcing, and product innovation to navigate downturns effectively. The toolkit provides specific examples and potential savings associated with each initiative, alongside insights into managing overheads and capital challenges in today's economy.