The document discusses various cost concepts and classifications including:
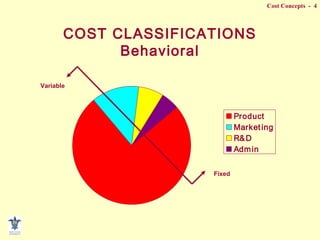
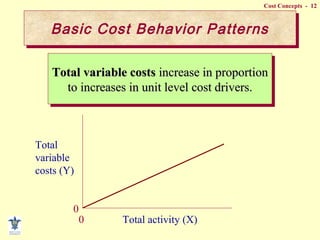
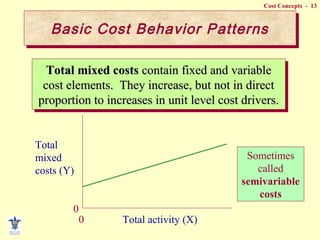
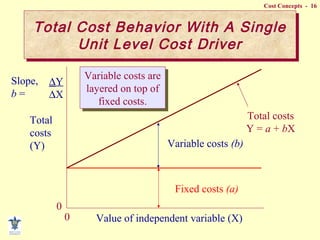
- Fixed vs variable vs mixed costs and how they behave differently with changes in activity.
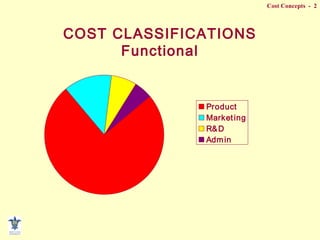
- Functional classifications like product, marketing, R&D costs.
- Behavioral classifications like committed vs discretionary fixed costs.
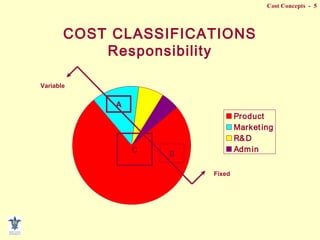
- Responsibility classifications that assign costs to cost centers like departments A, B, C.
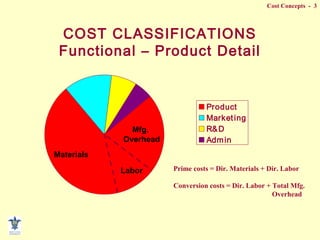
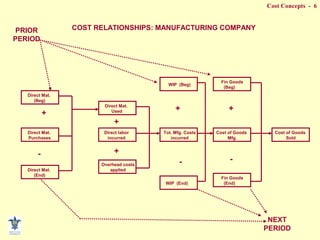
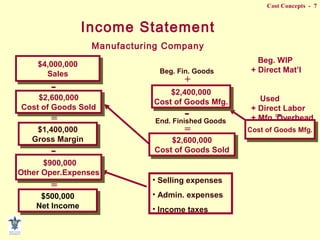
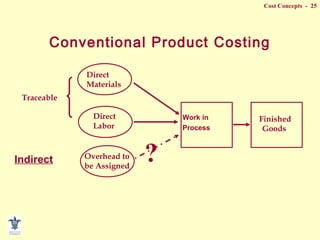
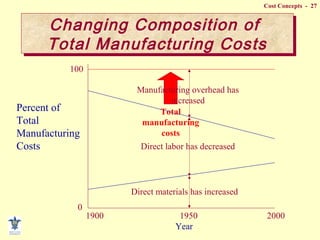
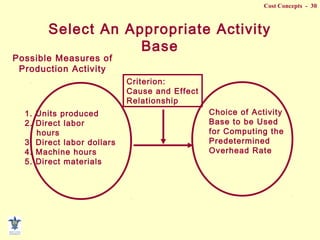
- Composition of manufacturing costs including direct materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead.
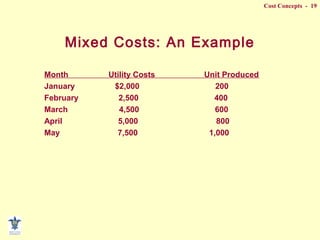
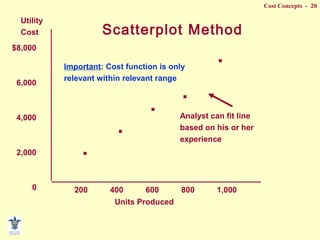
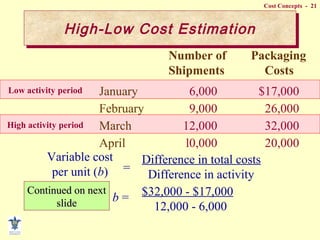
- Methods for separating mixed costs into fixed and variable components like scatterplot, high-low, and least squares.