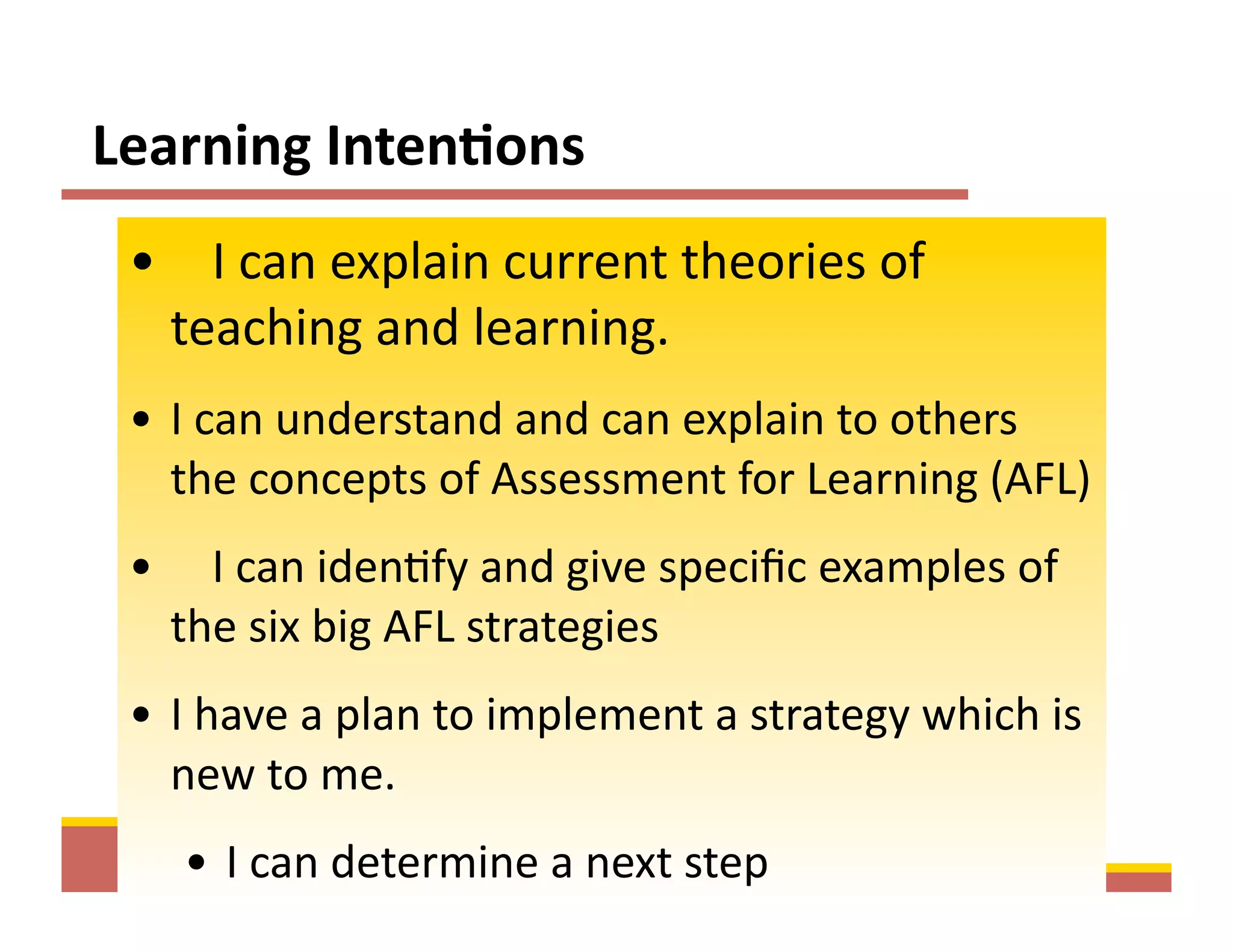
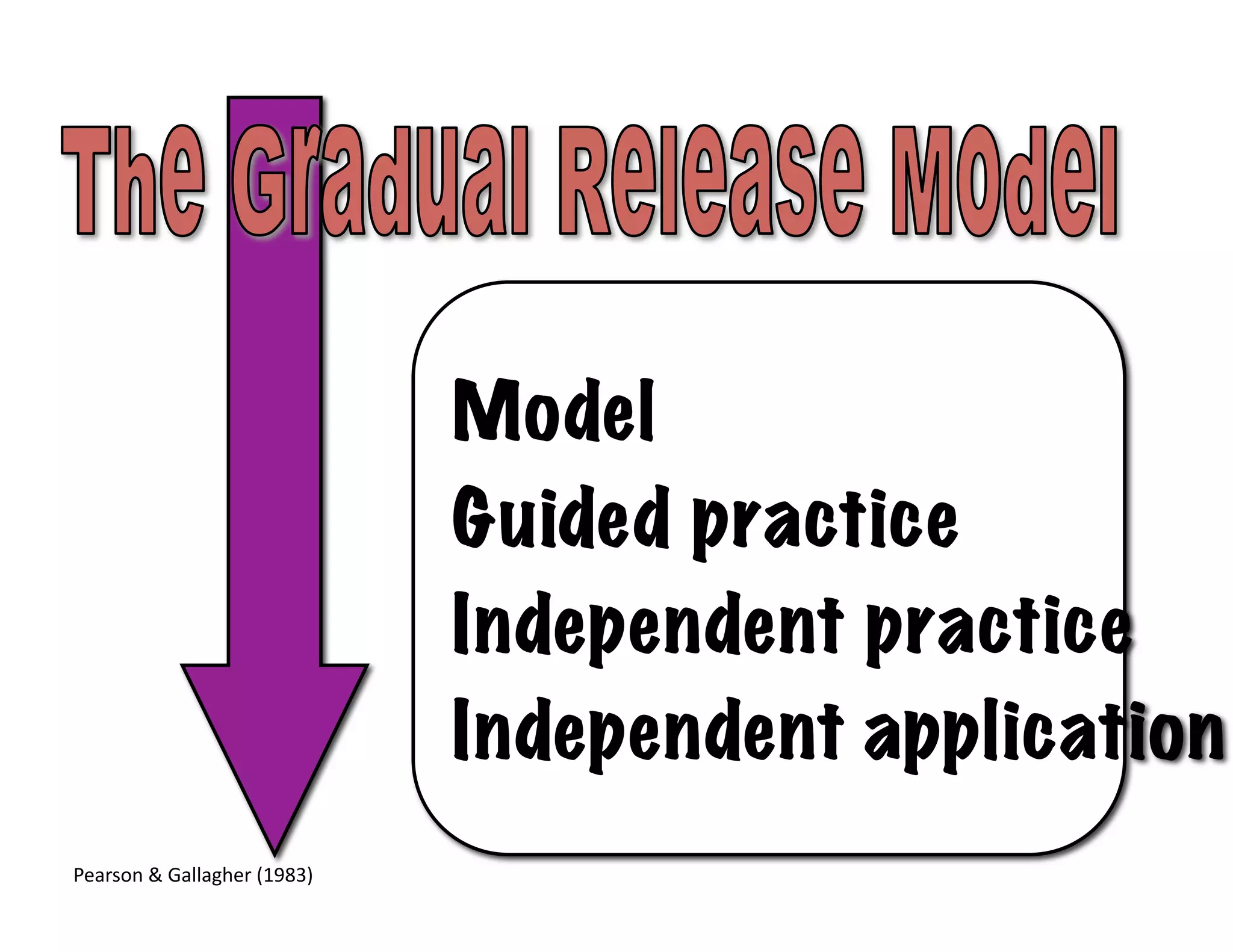
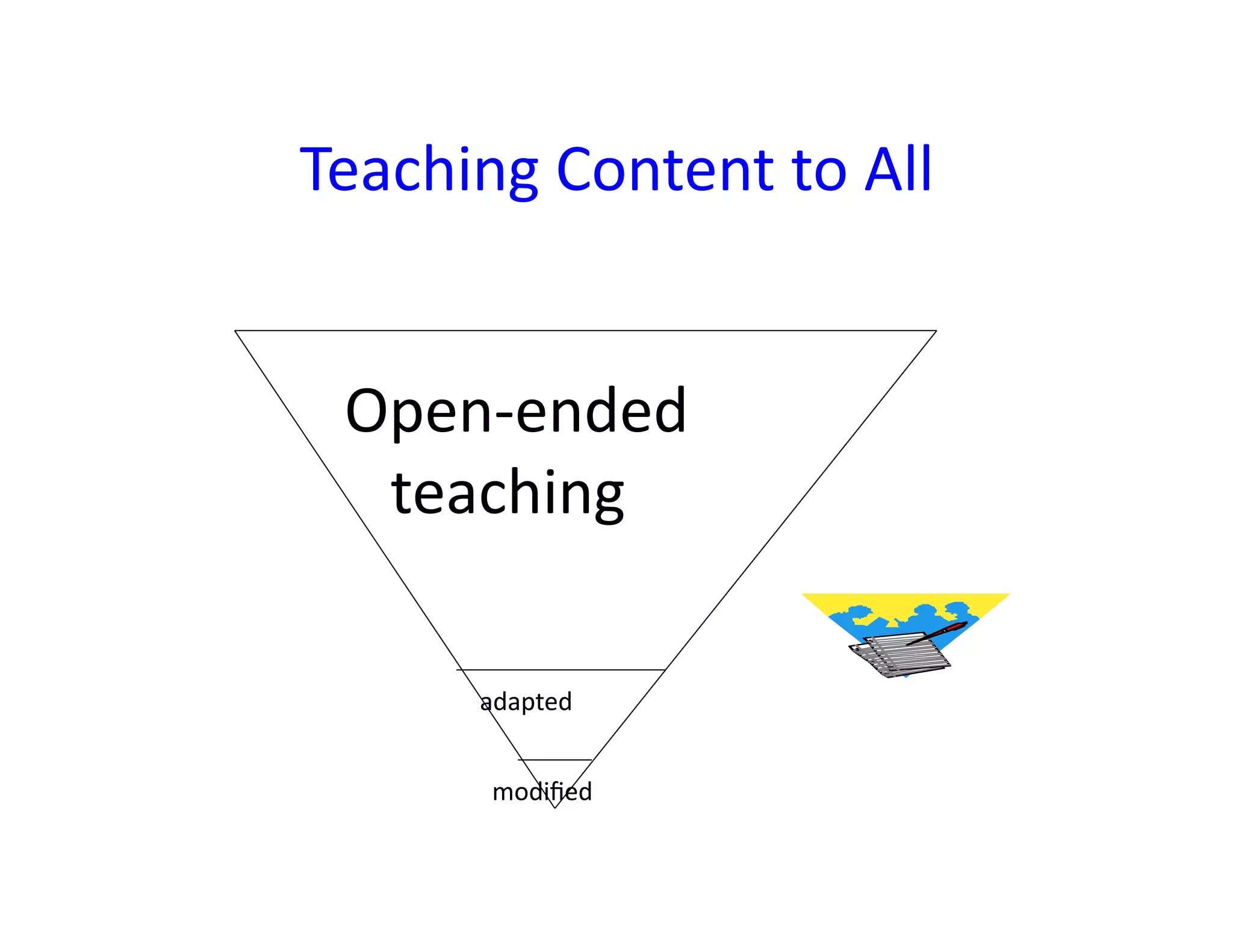
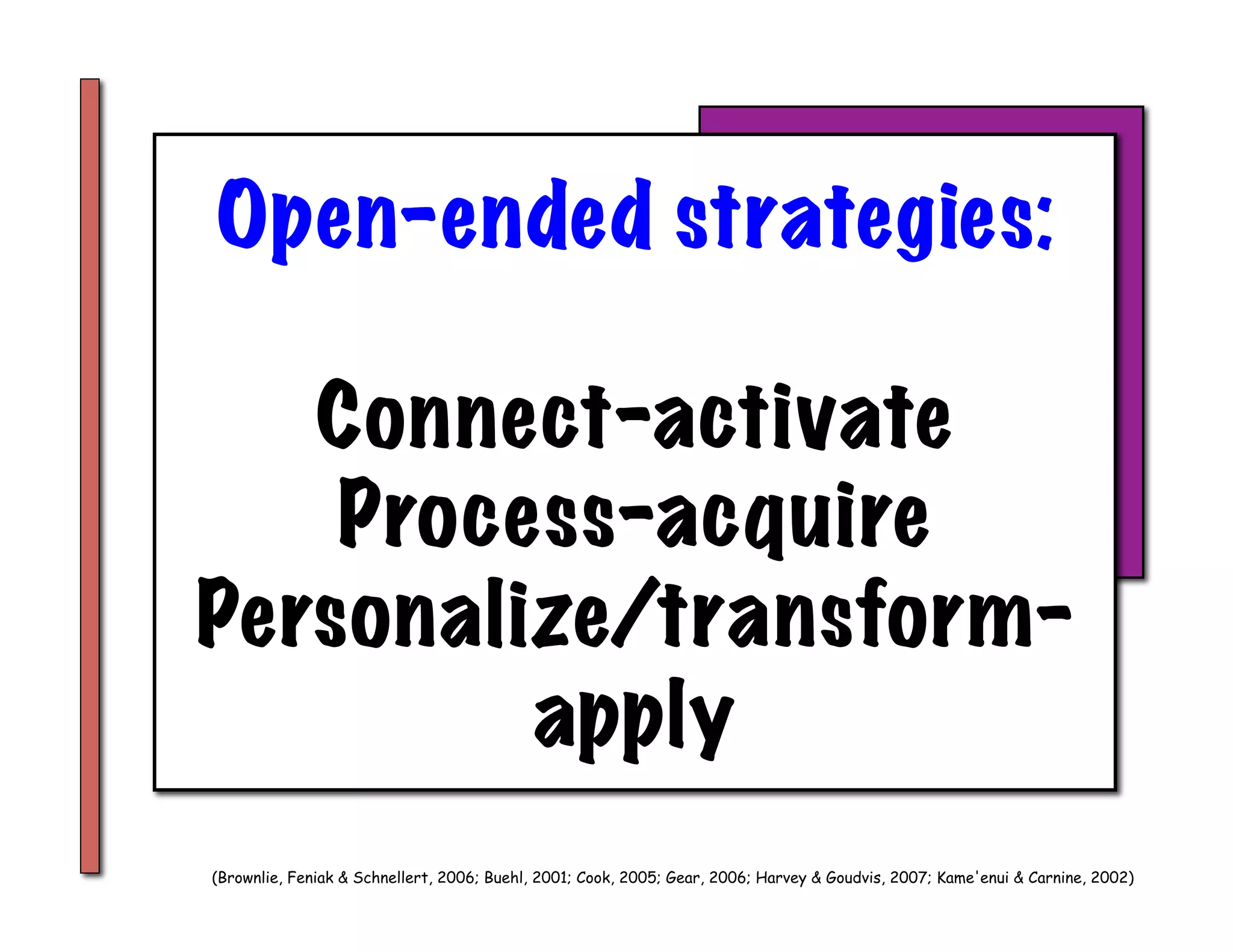
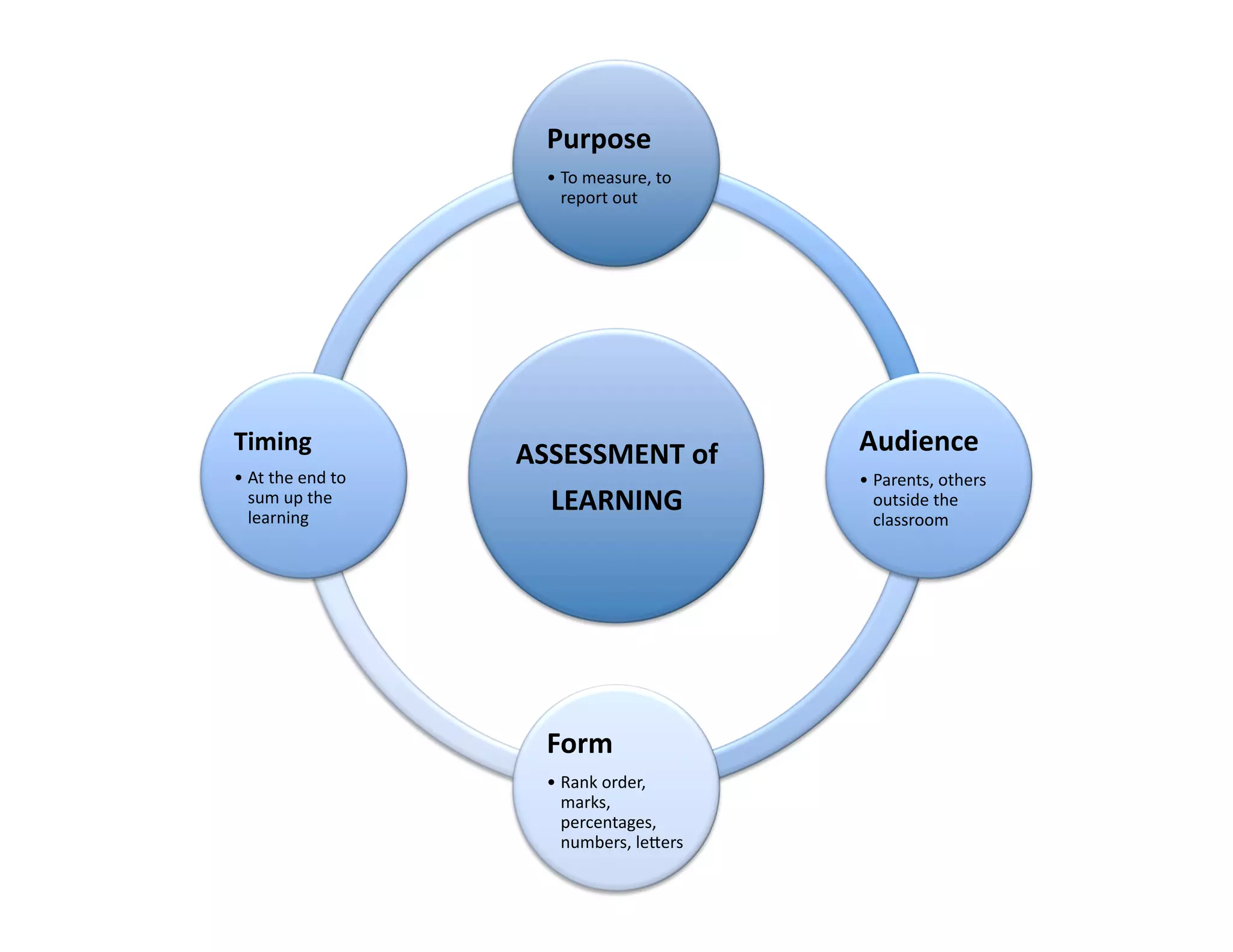
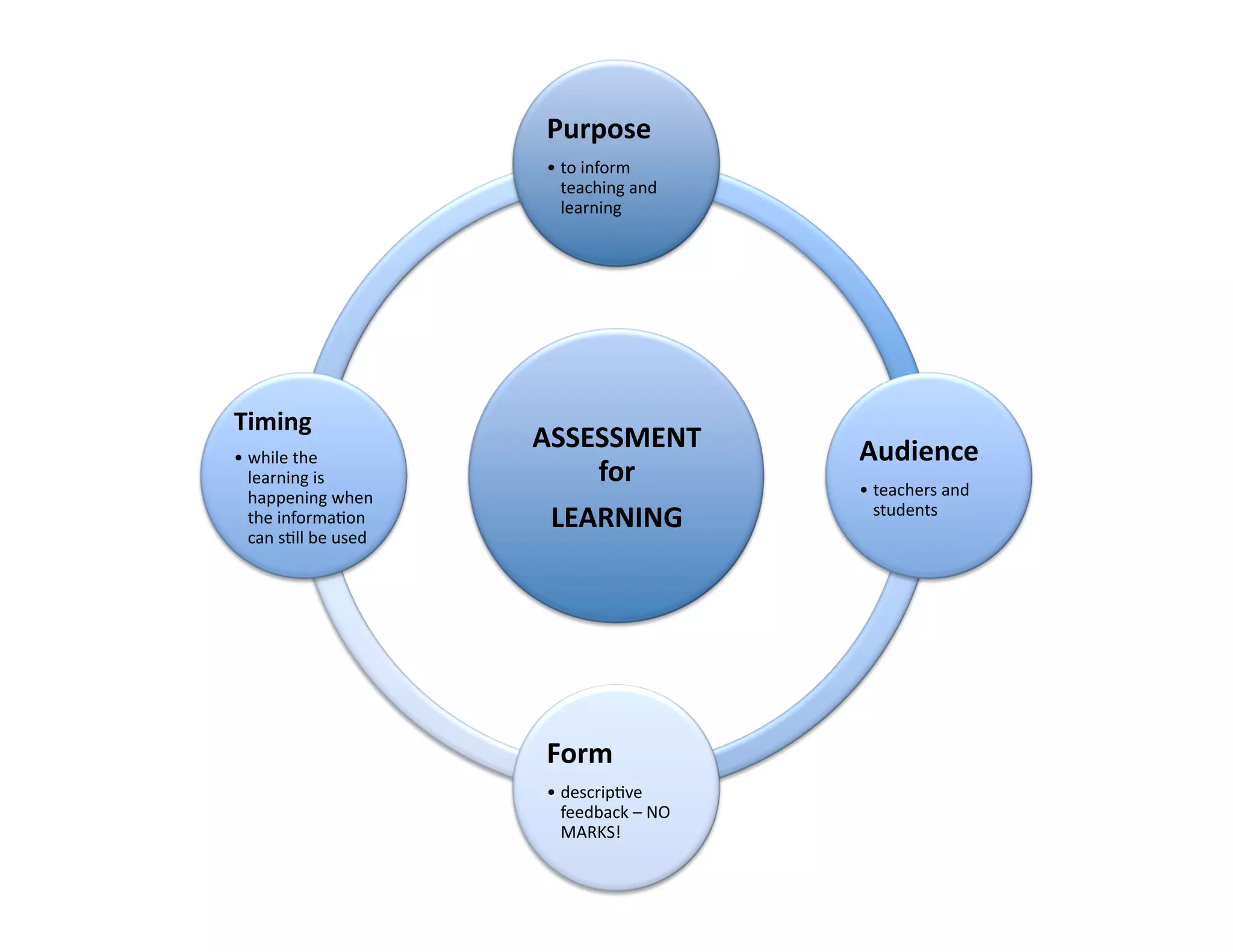
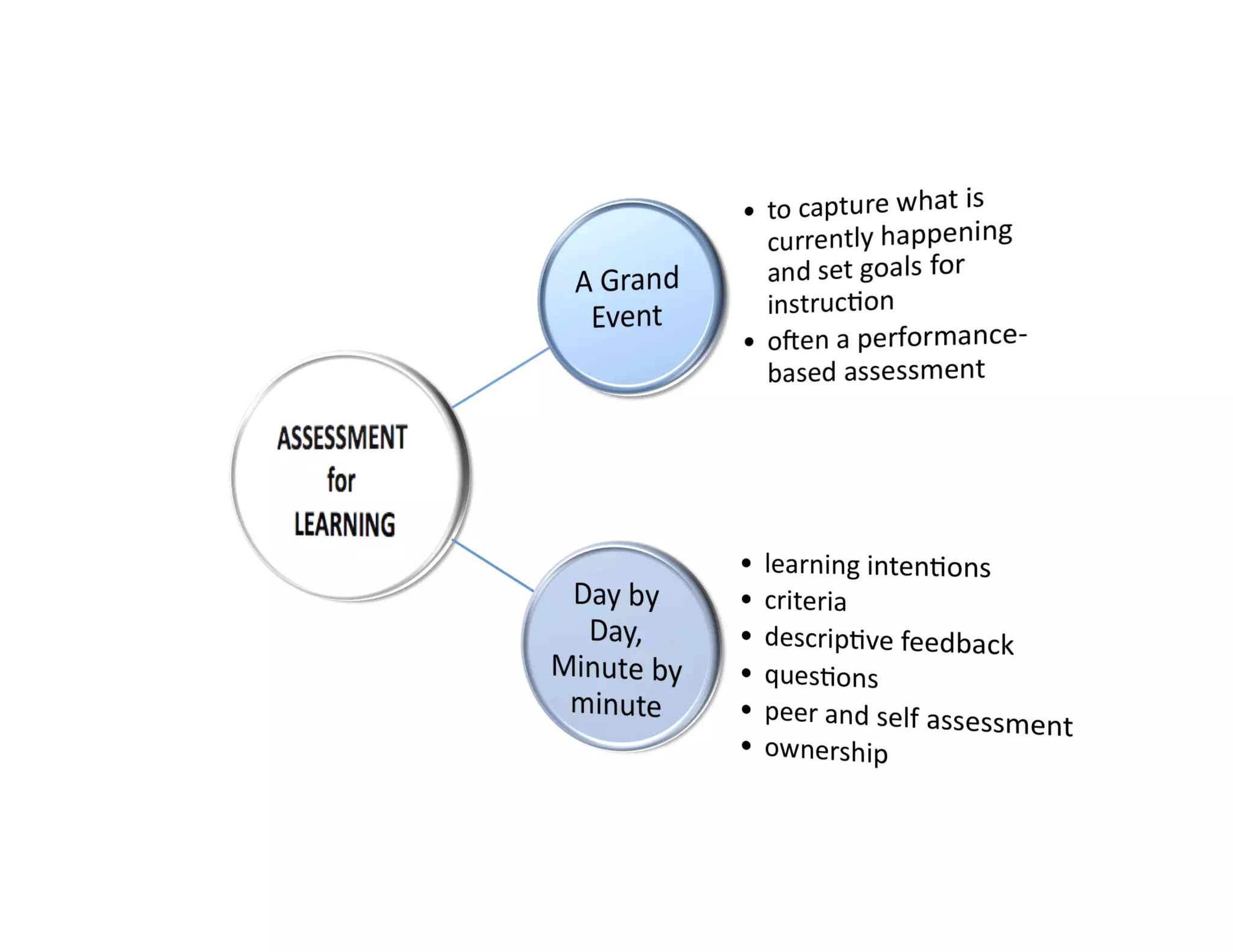
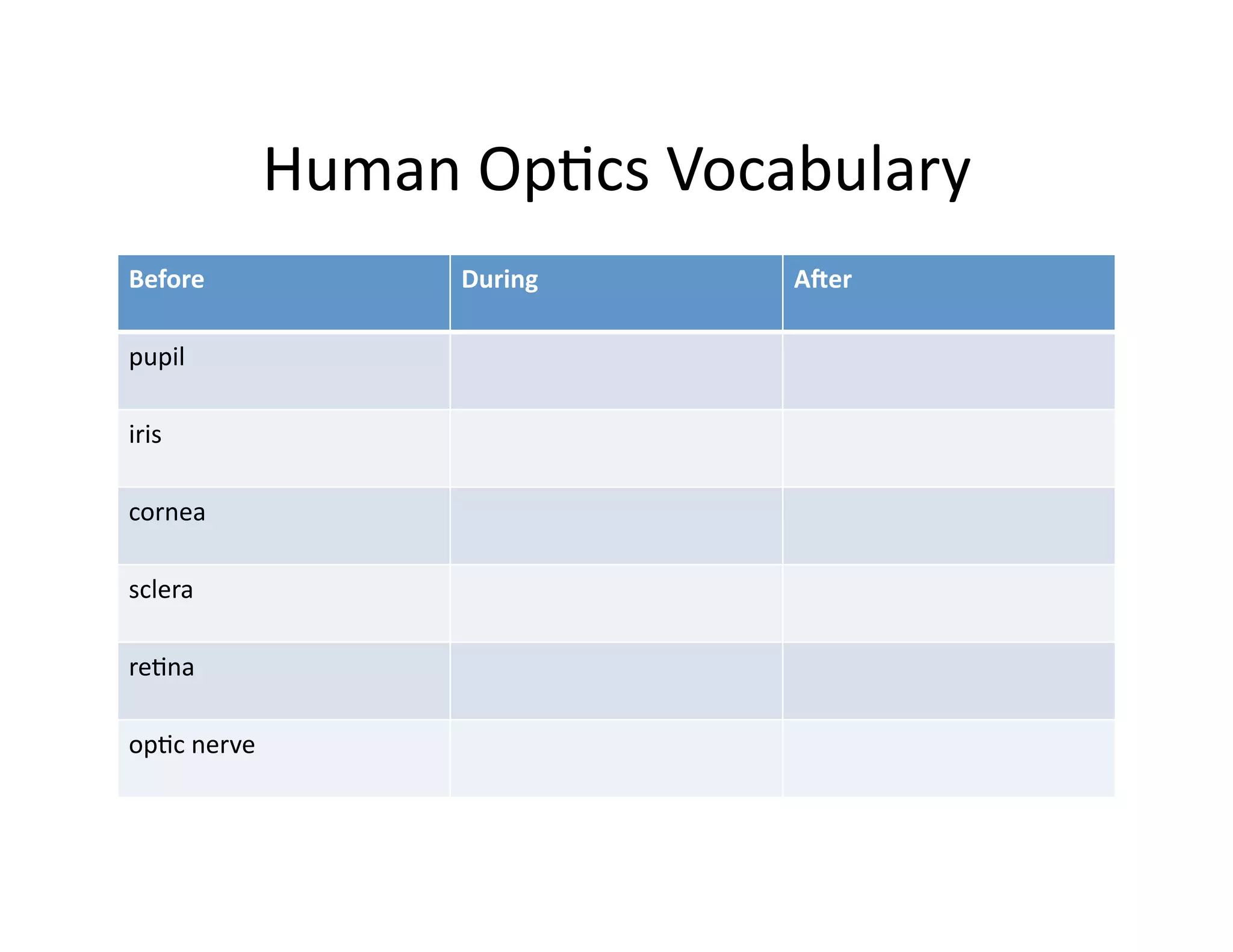
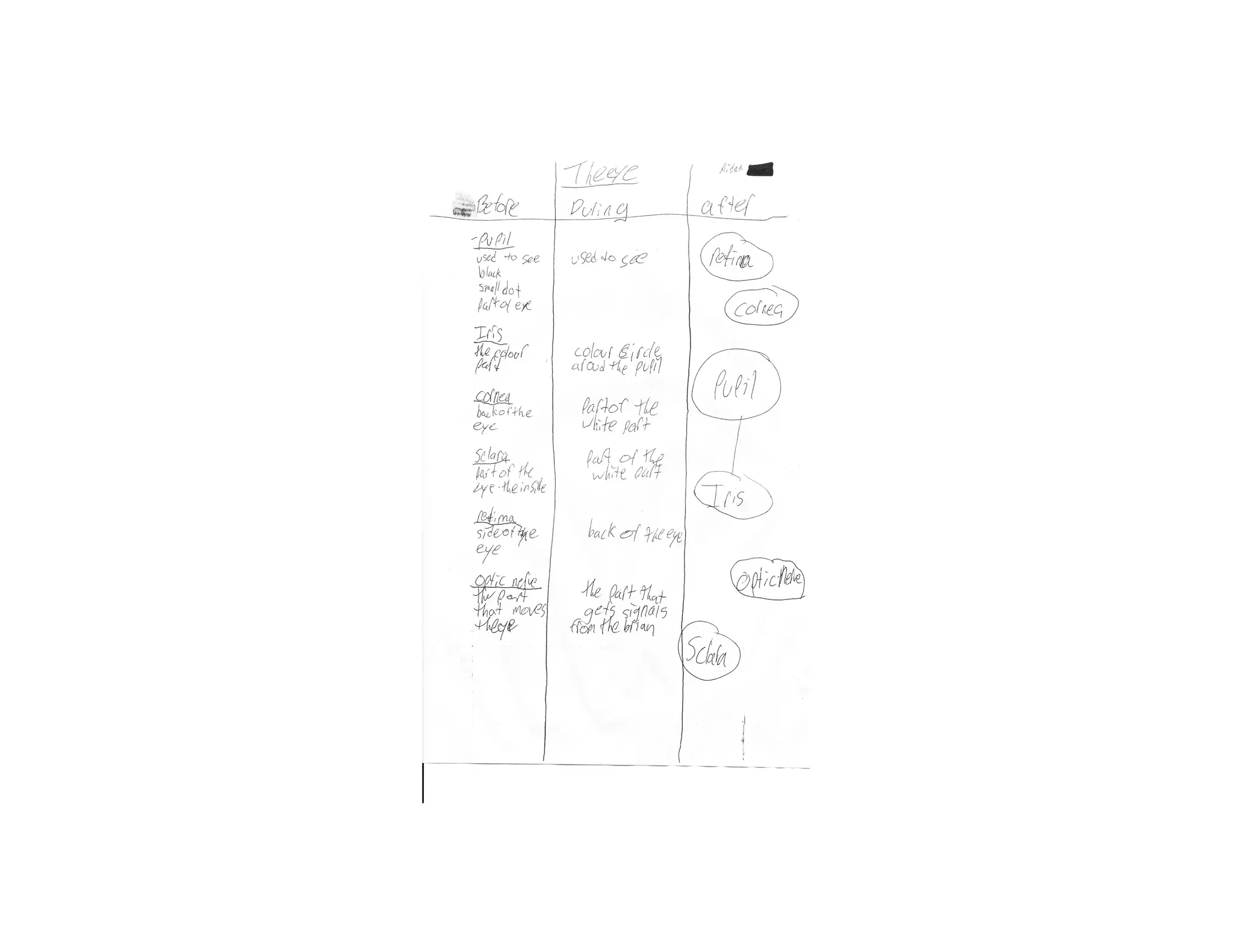
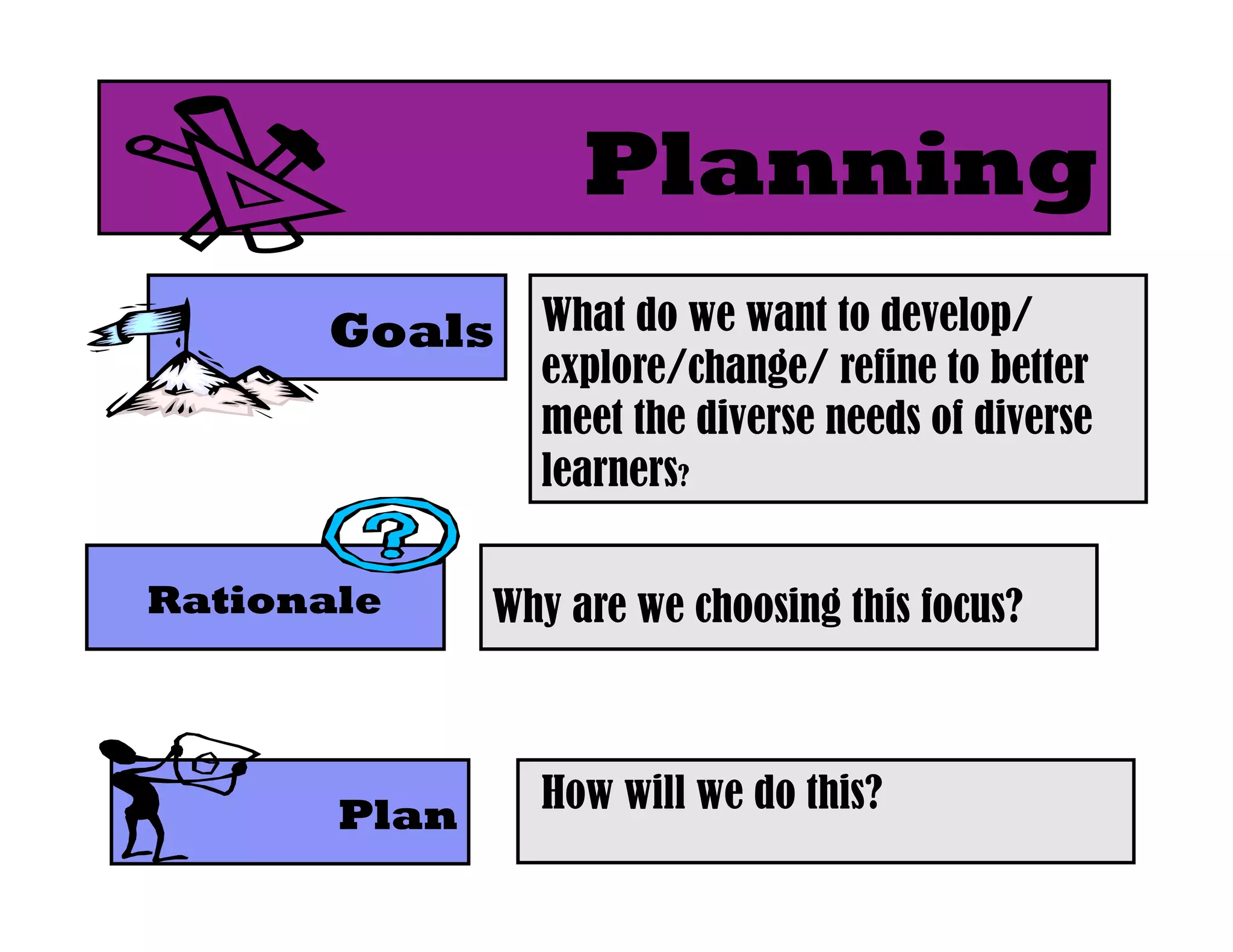
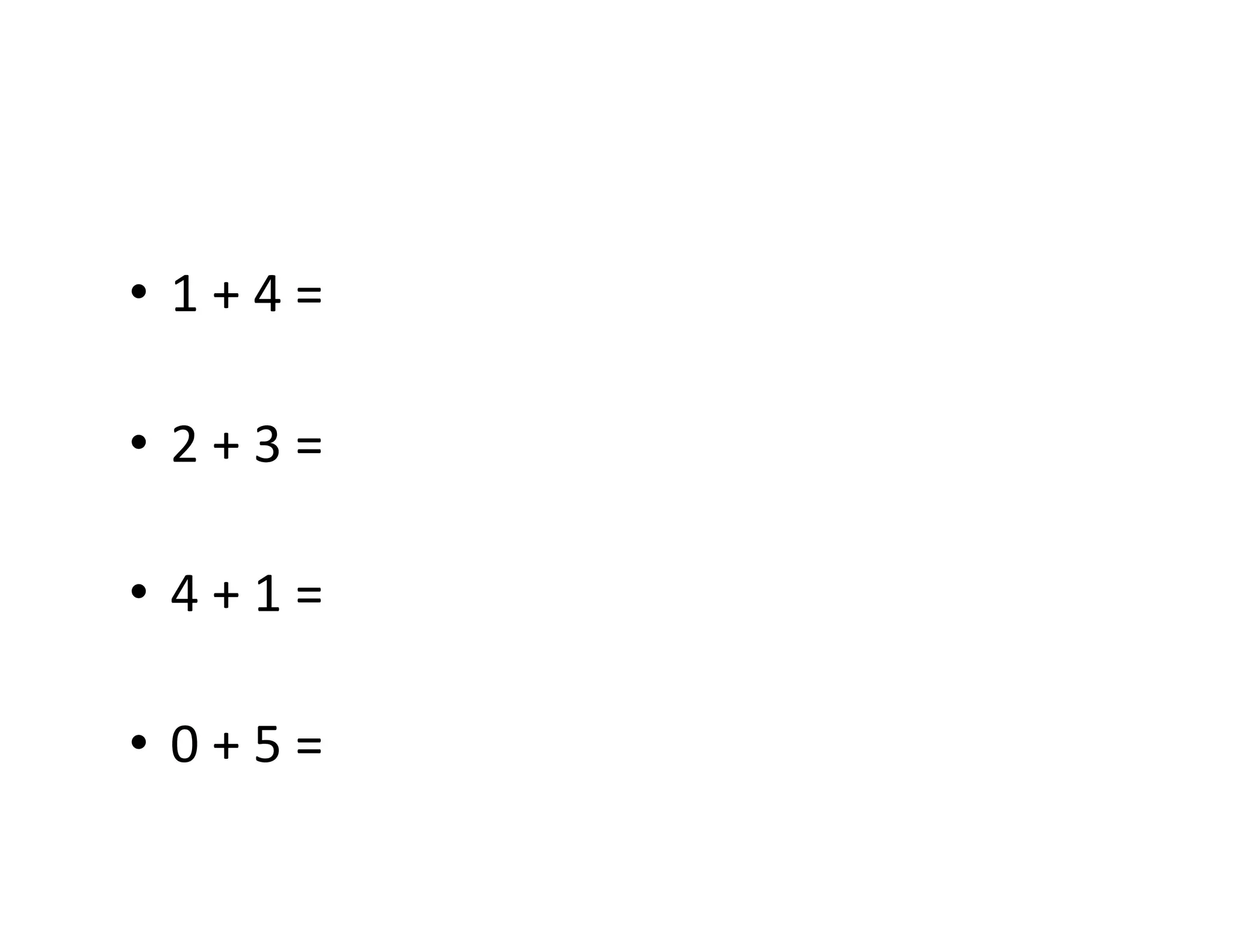The document summarizes a presentation given by Faye Brownlie on September 24, 2010 in Coquitlam about formative assessment and quality teaching in inclusive classrooms. The presentation covered current theories of teaching and learning, the concept of assessment for learning (AFL), examples of AFL strategies like learning intentions, descriptive feedback, questioning and student ownership of learning. Classroom examples of how to implement these strategies were also provided.