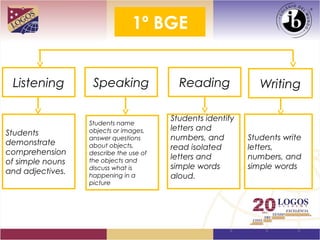
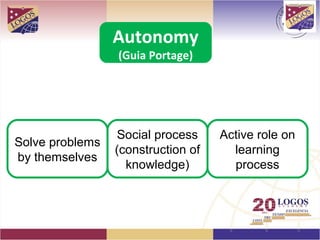
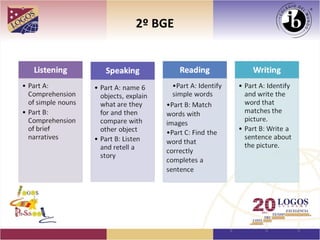
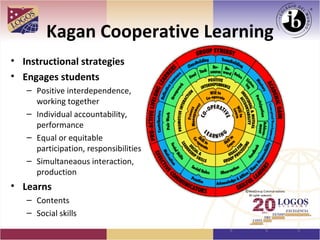
The document proposes a K-12 education plan focused on meeting student needs. It discusses analyzing learning needs, establishing learning objectives, identifying gaps, and determining how to help students progress from their starting point to the desired destination. It also covers adapting instructional plans, monitoring effectiveness, learning styles, comprehensive input/output, language acquisition vs learning, autonomy, integrated evaluation domains, minimum achievements, understanding by design, TESOL standards, cooperative learning, cognitive science, Finland's education success, and quality circles for staff training. The overall goal is to develop a plan to help students improve skills and meet learning goals through an effective instructional approach.