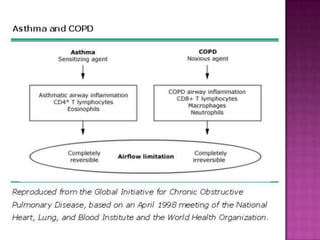
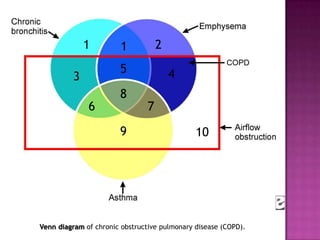
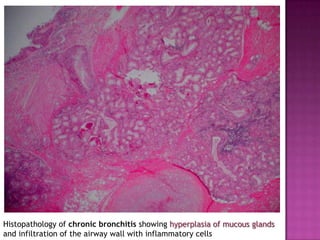
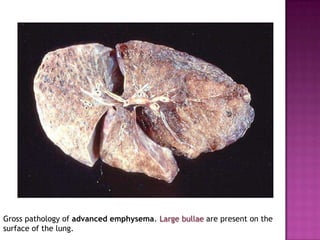
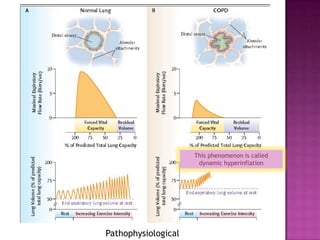
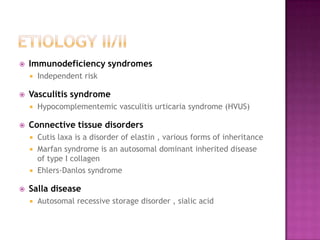
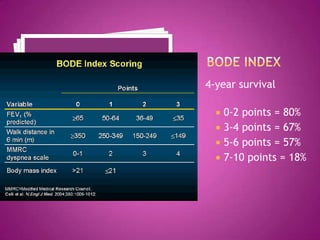
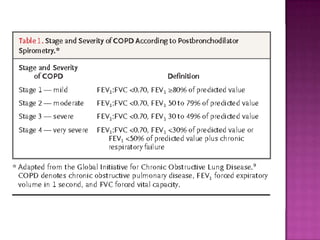
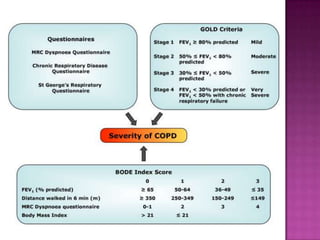
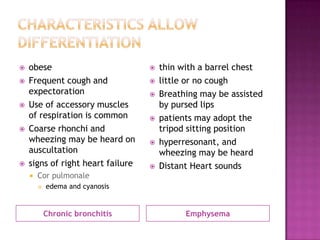
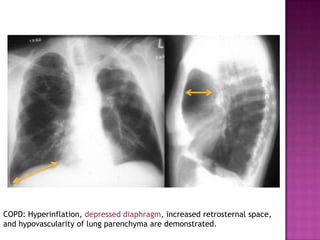
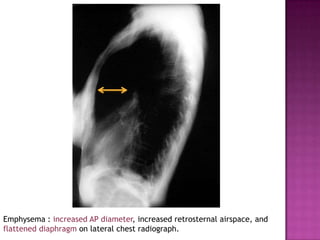
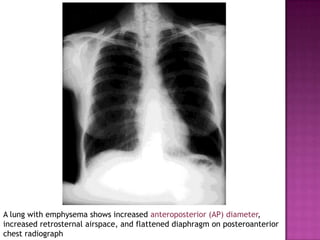
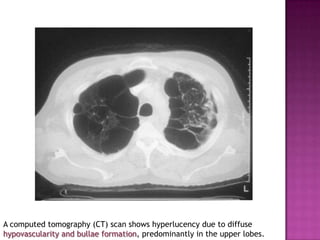
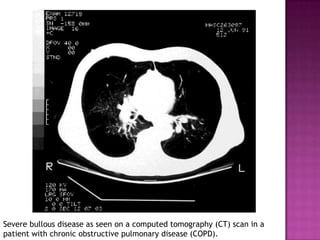
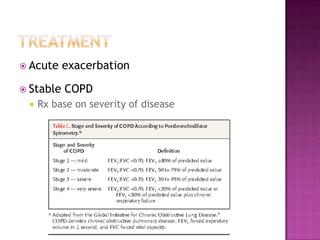
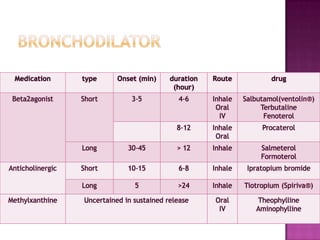
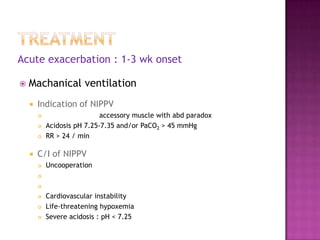
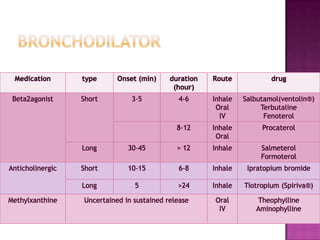
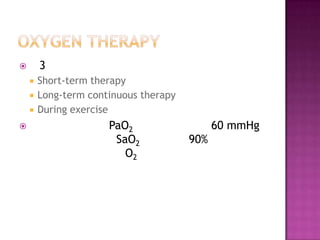
This document discusses chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). It defines COPD as a progressive lung disease characterized by airflow limitation that is not fully reversible. The main phenotypes of COPD are chronic bronchitis and emphysema. The document discusses the pathogenesis and risk factors of COPD, as well as the clinical presentation and complications. It provides details on diagnosing COPD through pulmonary function tests, blood tests, imaging and other evaluations. Treatment options are outlined for acute exacerbations and management of stable COPD based on disease severity. Management includes bronchodilators, corticosteroids, pulmonary rehabilitation, oxygen therapy and occasionally surgery.