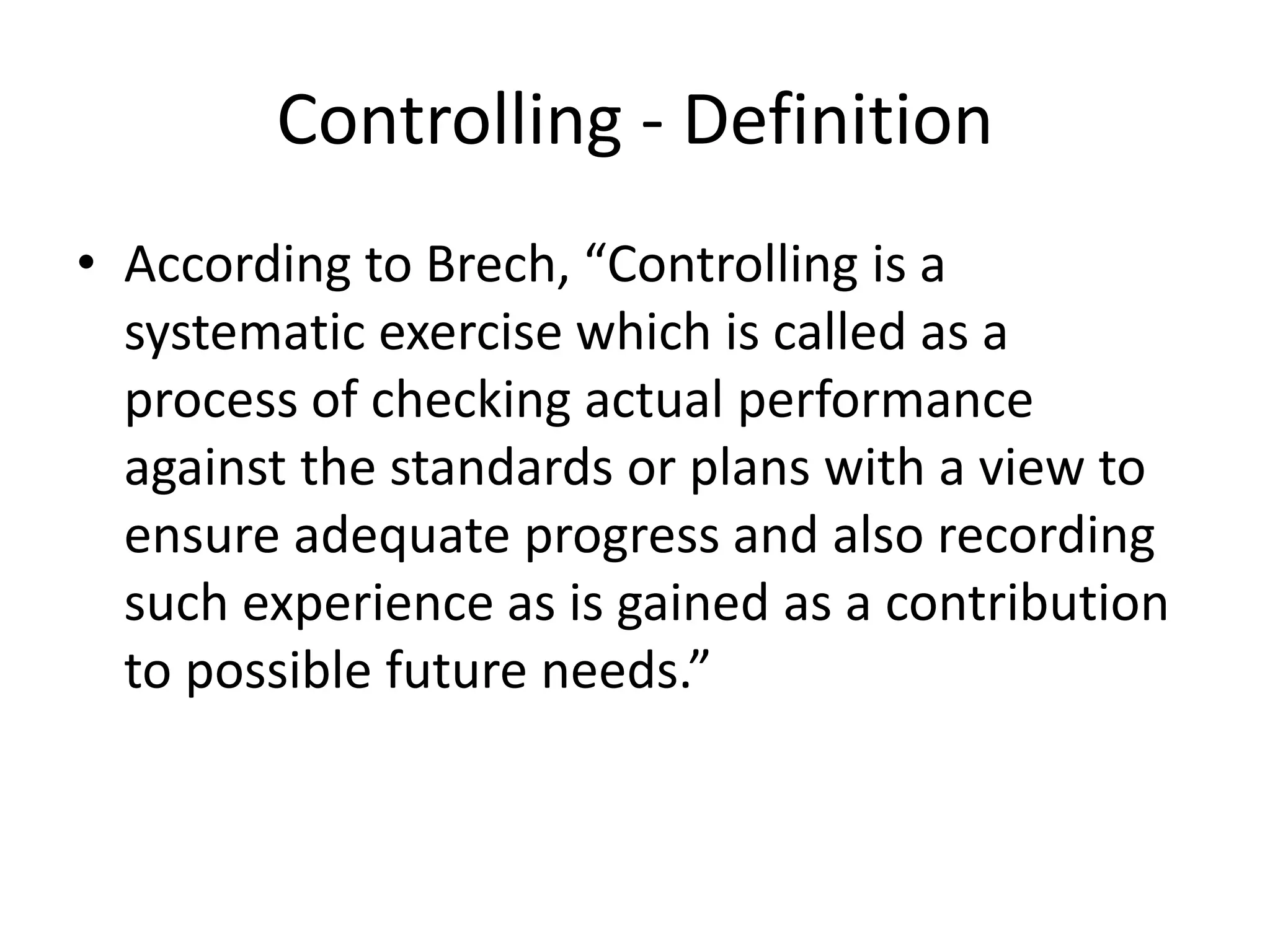
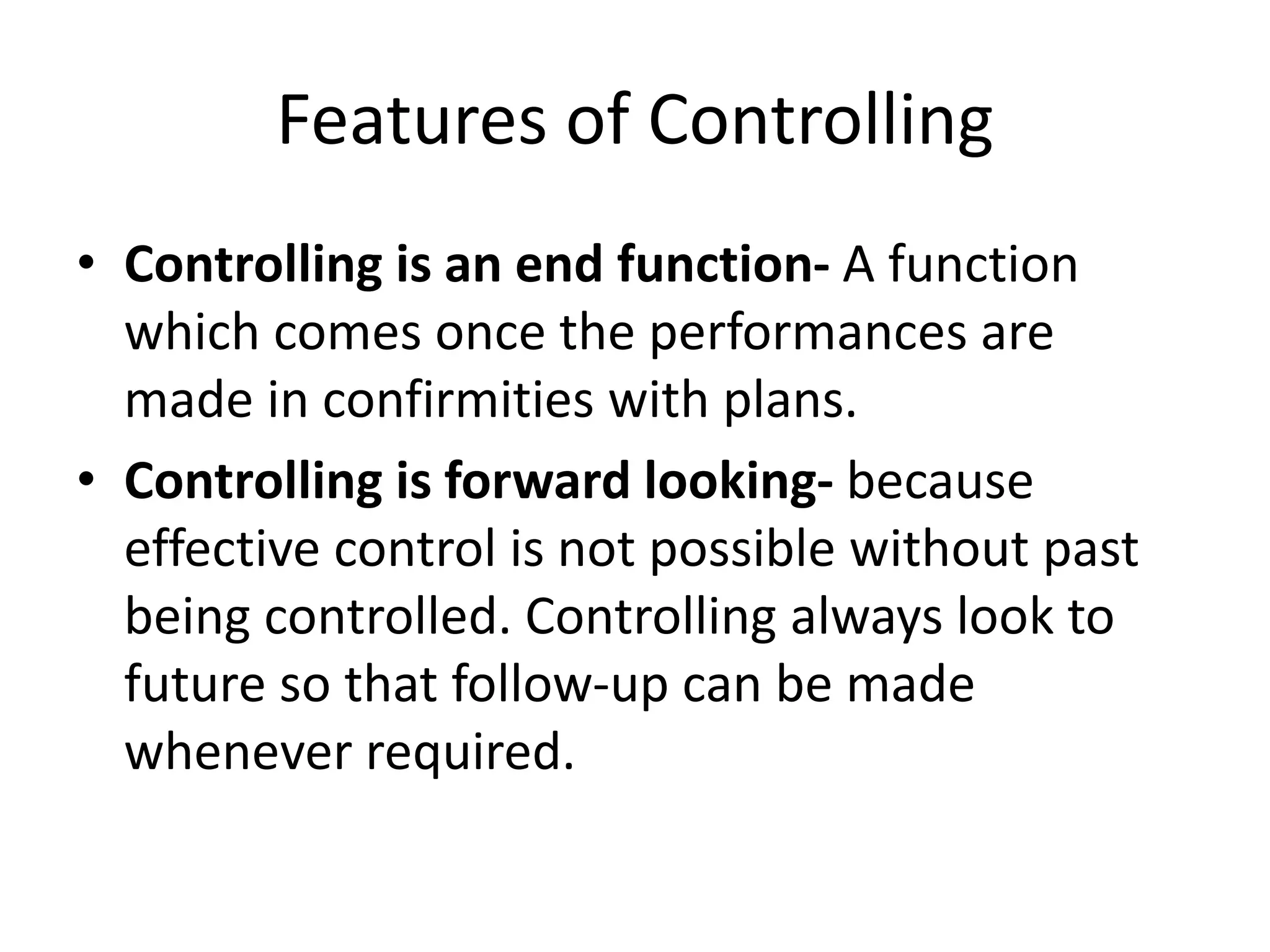
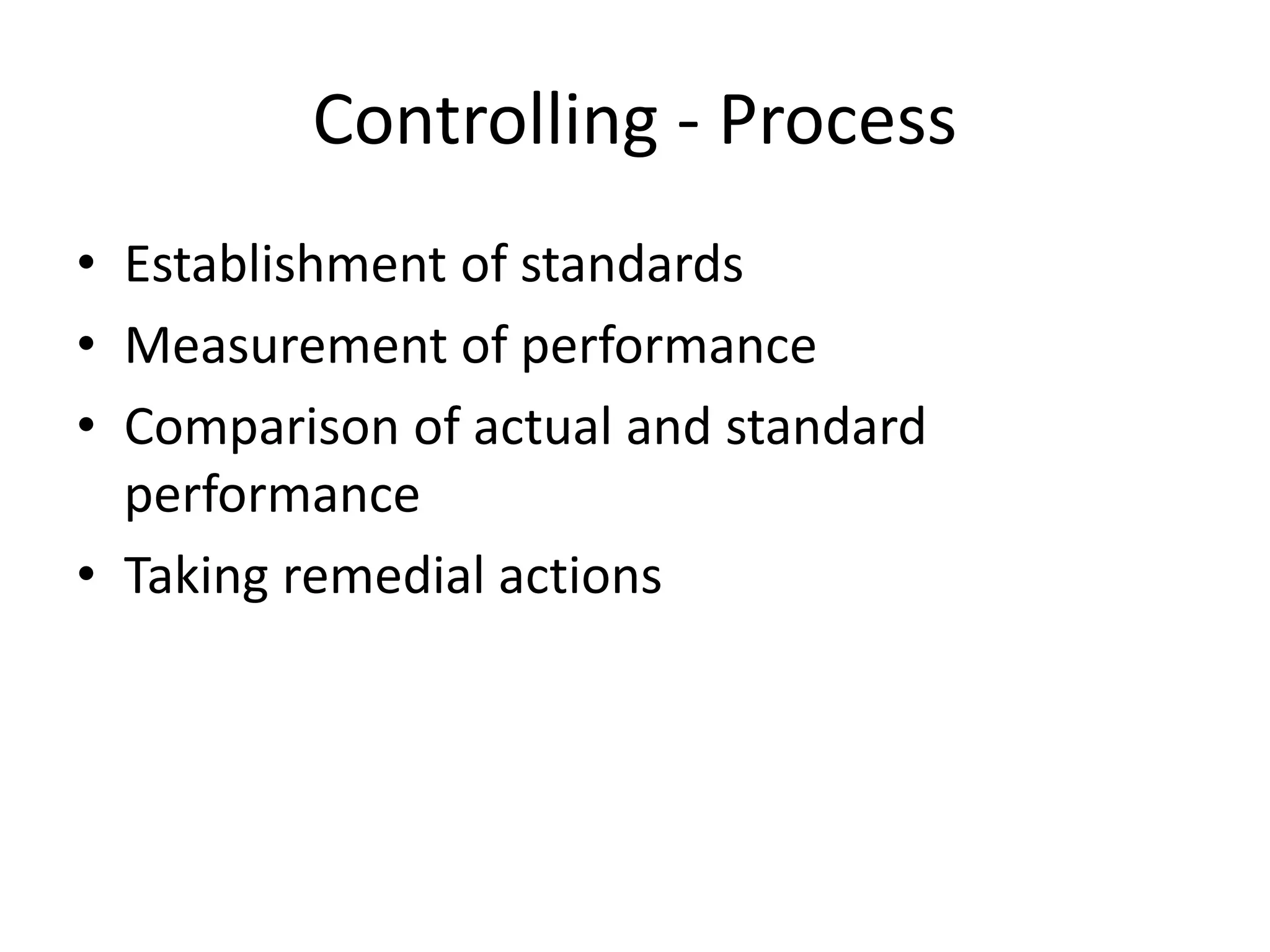
This document discusses controlling as a management function. It defines controlling as verifying that plans are followed and resources are efficiently used to achieve goals. Controlling measures deviations from standards and helps take corrective actions. The controlling process involves establishing standards, measuring performance, comparing actual and standard performance, and taking remedial actions. Traditional controlling techniques include personal observation, statistical data, break-even analysis, and budgetary control. Modern techniques include management information systems, PERT, CPM, and management audits. For controlling to be effective it must be accurate, timely, flexible, integrated, economically feasible, and enable corrective actions.