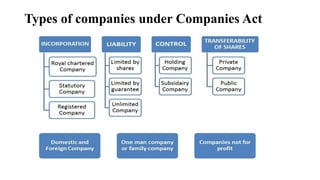
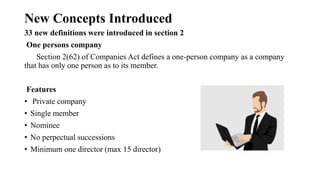
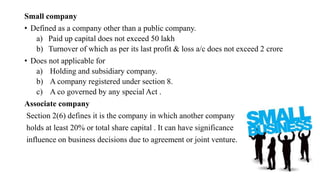
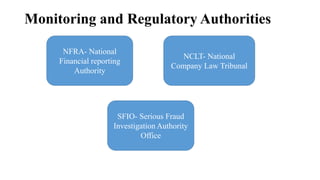
The Companies Act 1956 established the legal framework for company formation and management in India, comprising 658 sections and provisions for various types of companies and procedures for winding up. It was partially replaced by the Companies Act 2013, which introduced modern regulations, streamlined processes, and enhanced oversight, including provisions for corporate social responsibility and the establishment of the National Company Law Tribunal. The 2013 Act defined new types of companies and emphasized transparency, accountability, and corporate governance, significantly altering the landscape of company law in India.