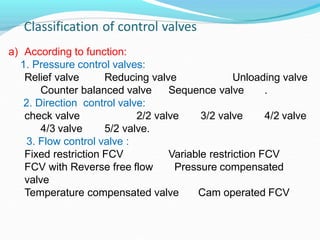
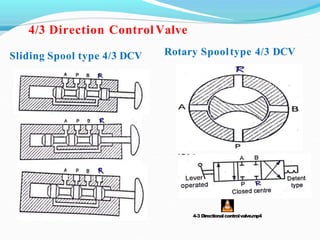
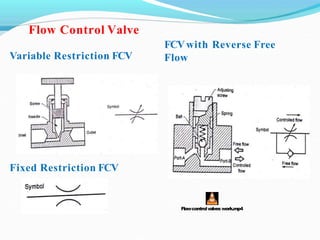
This document discusses different types of hydraulic valves and components. It covers pressure control valves like relief valves, reducing valves, and unloading valves. It also covers direction control valves like check valves, 3/2 valves, 4/2 valves, and 5/2 valves. Additionally, it discusses flow control valves, manual and pilot operated valves, poppet and spool valves, actuators, pipes and hoses, fittings, seals, accumulators, and pressure boosters.