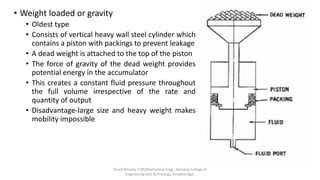
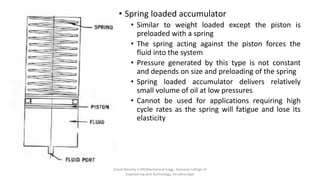
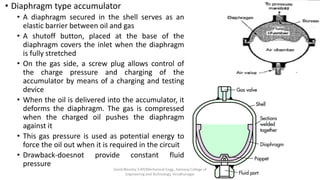
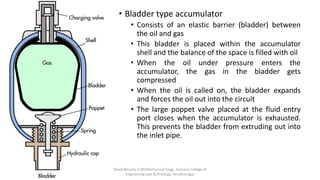
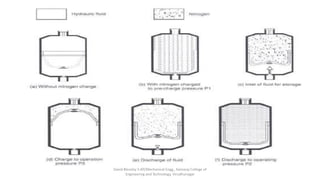
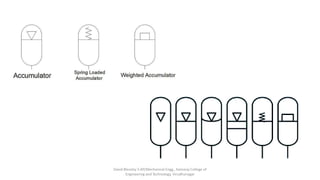
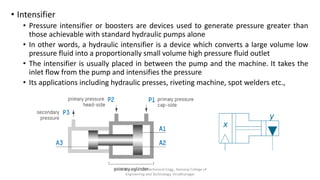
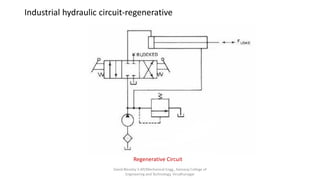
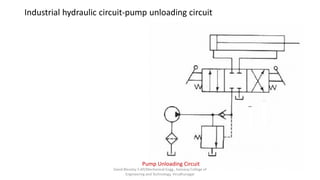
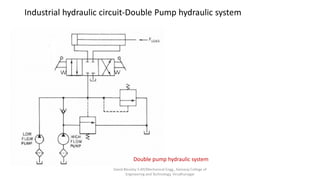
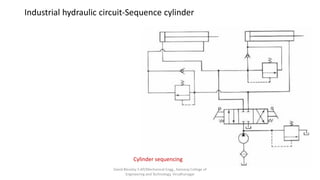
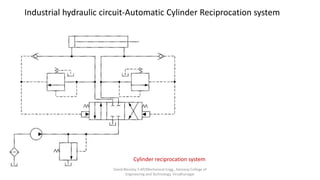
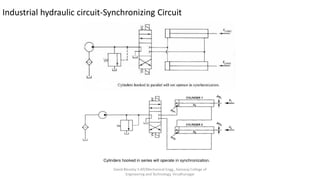
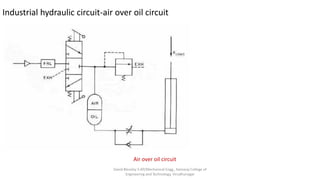
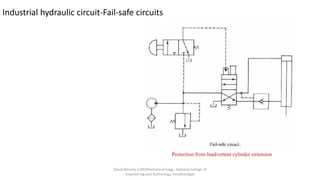
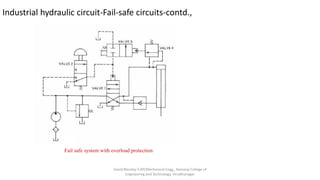
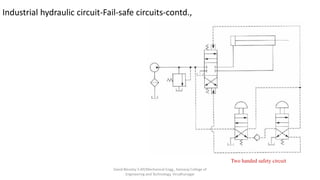
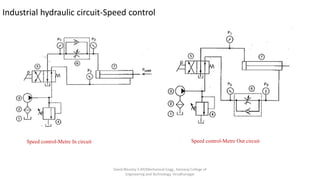
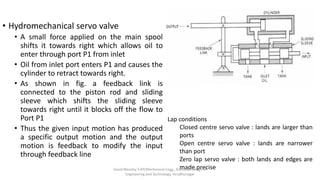
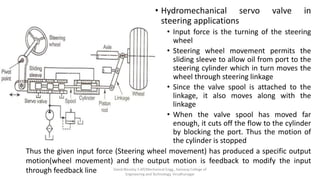
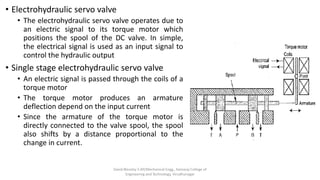
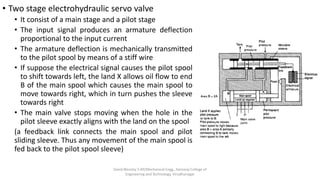
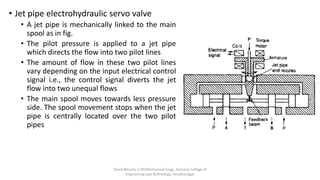
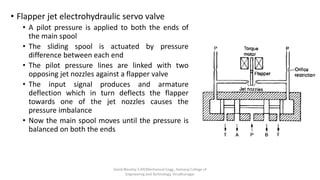
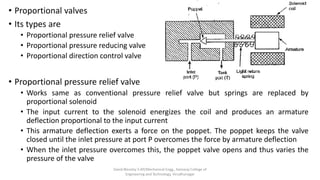
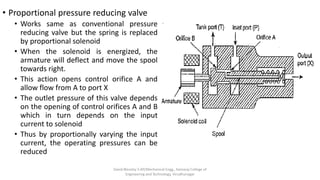
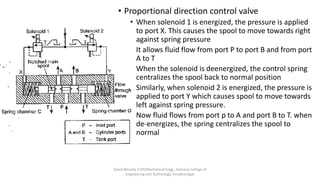
The document discusses various types of hydraulic accumulators and components. It describes weight loaded, spring loaded, and gas loaded accumulators. It also explains intensifiers, which convert low pressure fluid into high pressure fluid. Additionally, it discusses servo valves, proportional valves, and various industrial hydraulic circuits like regenerative circuits and pump unloading circuits.