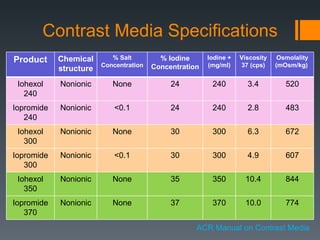
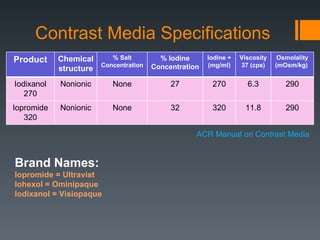
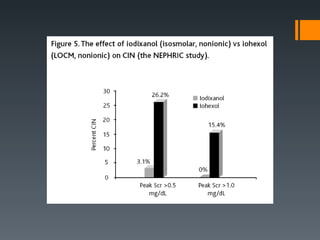
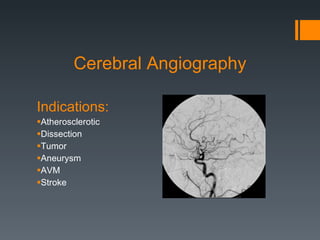
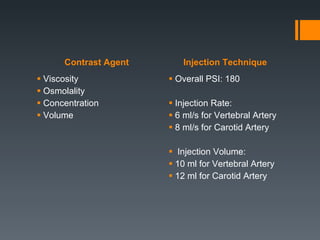
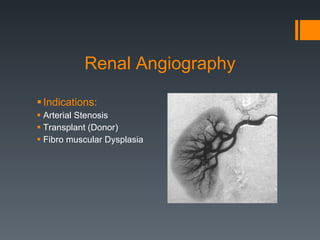
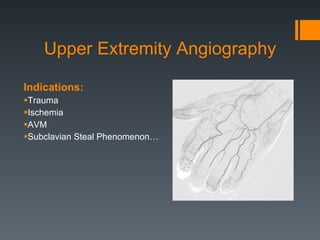
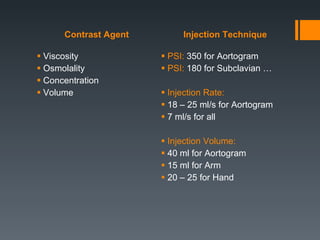
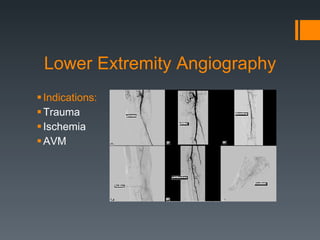
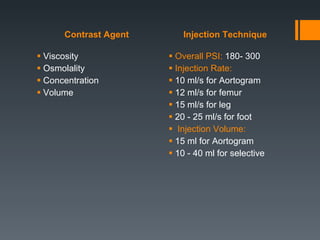
This document discusses contrast agents used in angiography and factors related to contrast-induced nephropathy (CIN). It notes that the route of contrast administration, volume administered, and properties of the specific contrast agent can influence CIN risk. Low-osmolar contrast agents are associated with less adverse effects than ionic agents. Hydration before and after the procedure can help reduce CIN incidence. Gadolinium may be considered as an alternative to iodinated contrast for patients at high risk of CIN.