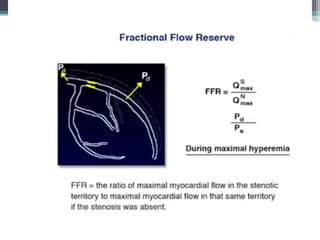
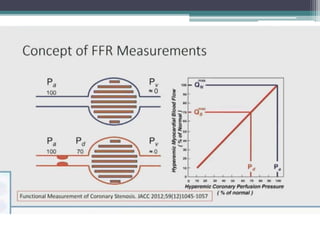
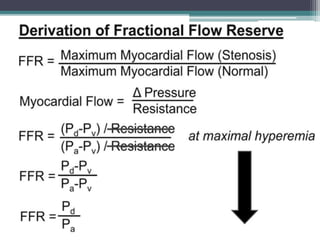
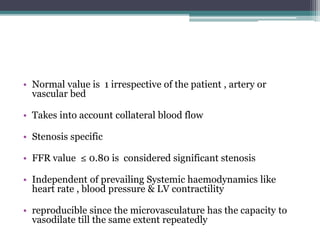
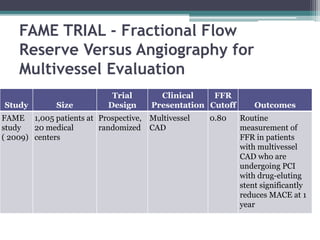
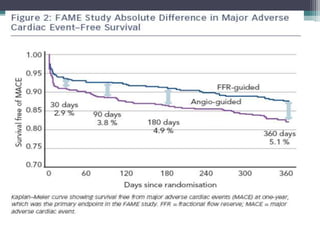
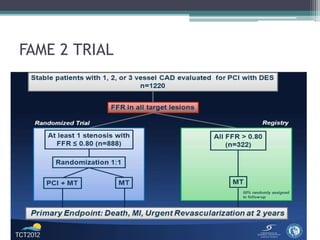
Fractional flow reserve (FFR) is a technique that evaluates the hemodynamic significance of coronary artery stenoses. It is defined as the ratio of maximal flow achievable in the stenotic coronary artery to the maximal flow achievable if the artery was normal. An FFR value ≤ 0.80 is considered hemodynamically significant. Several clinical trials including DEFER and FAME have found that FFR-guided revascularization reduces major adverse cardiac events compared to angiography-guided procedures alone by helping to identify which intermediate lesions are functionally significant. Guidelines recommend using FFR to guide revascularization decisions, especially for intermediate lesions, multivessel disease, and acute coronary syndromes.