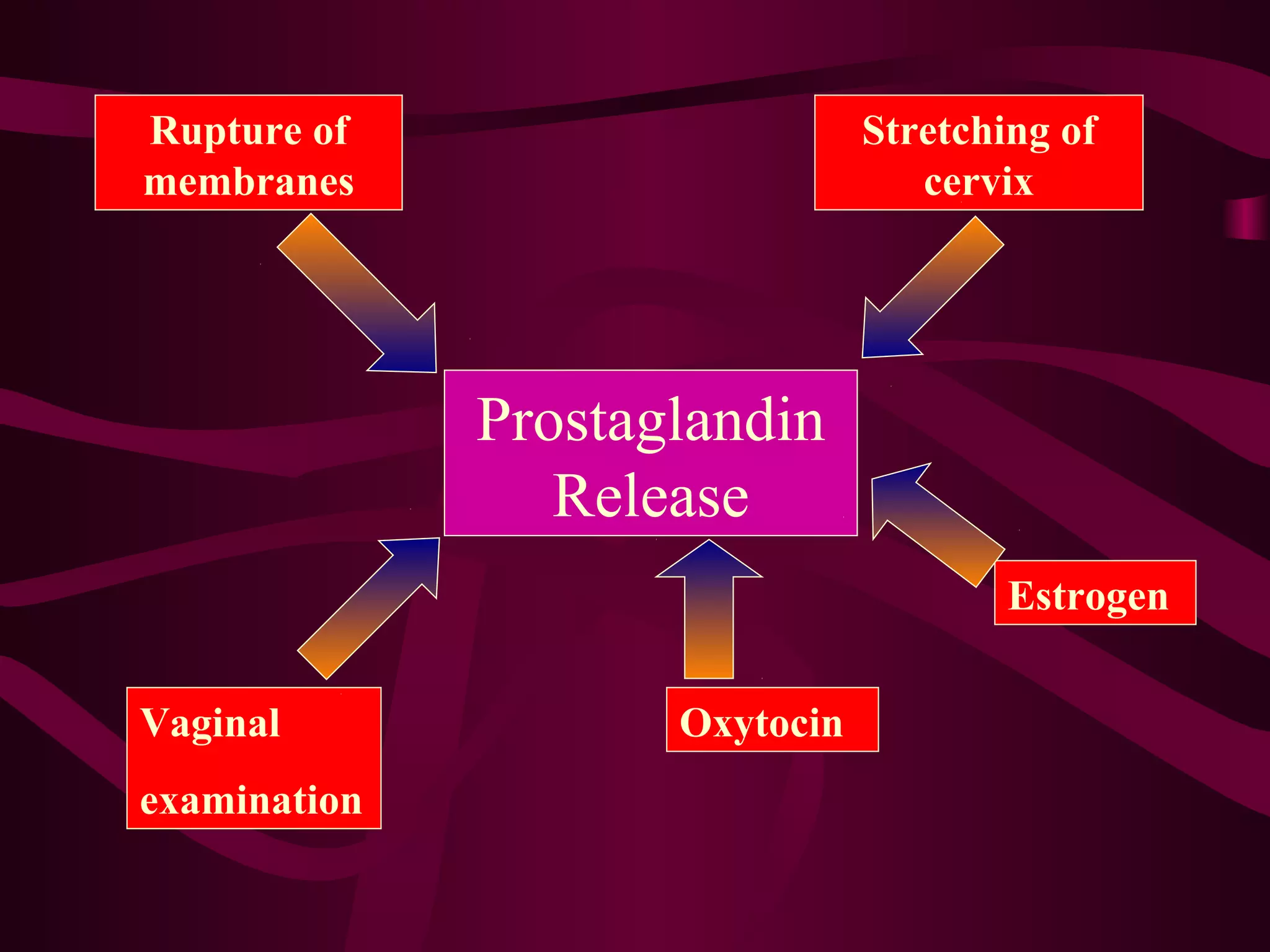
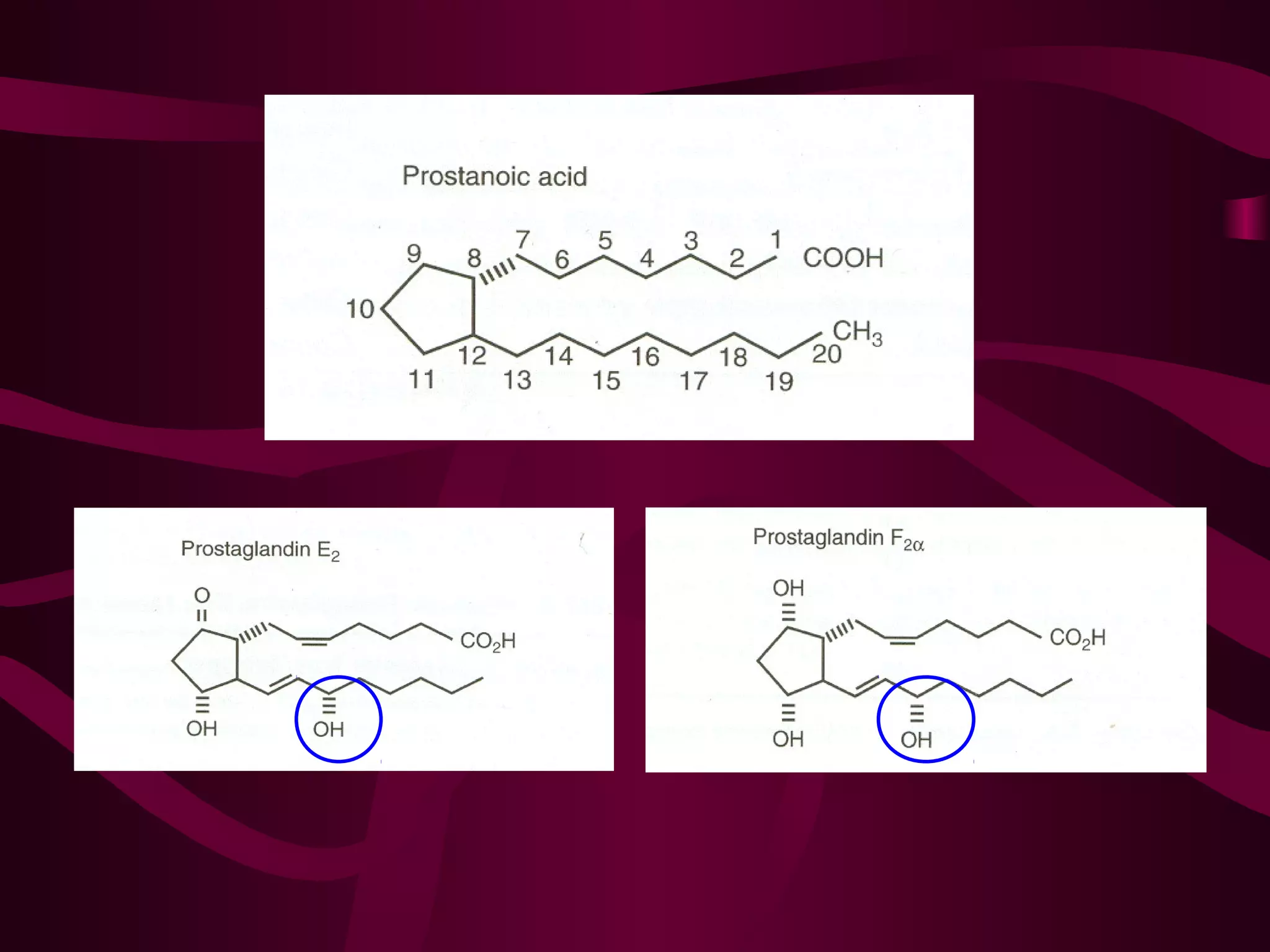
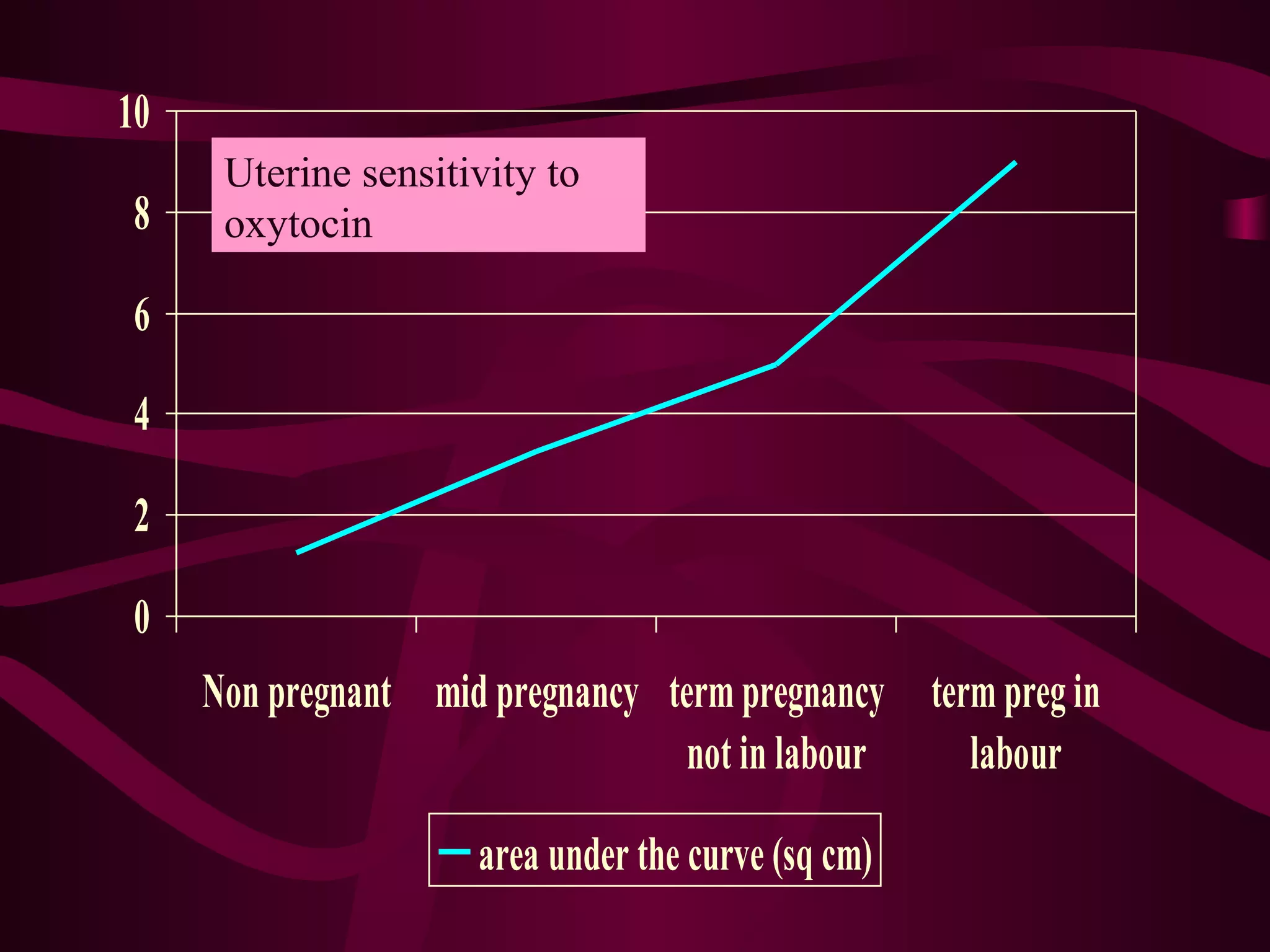
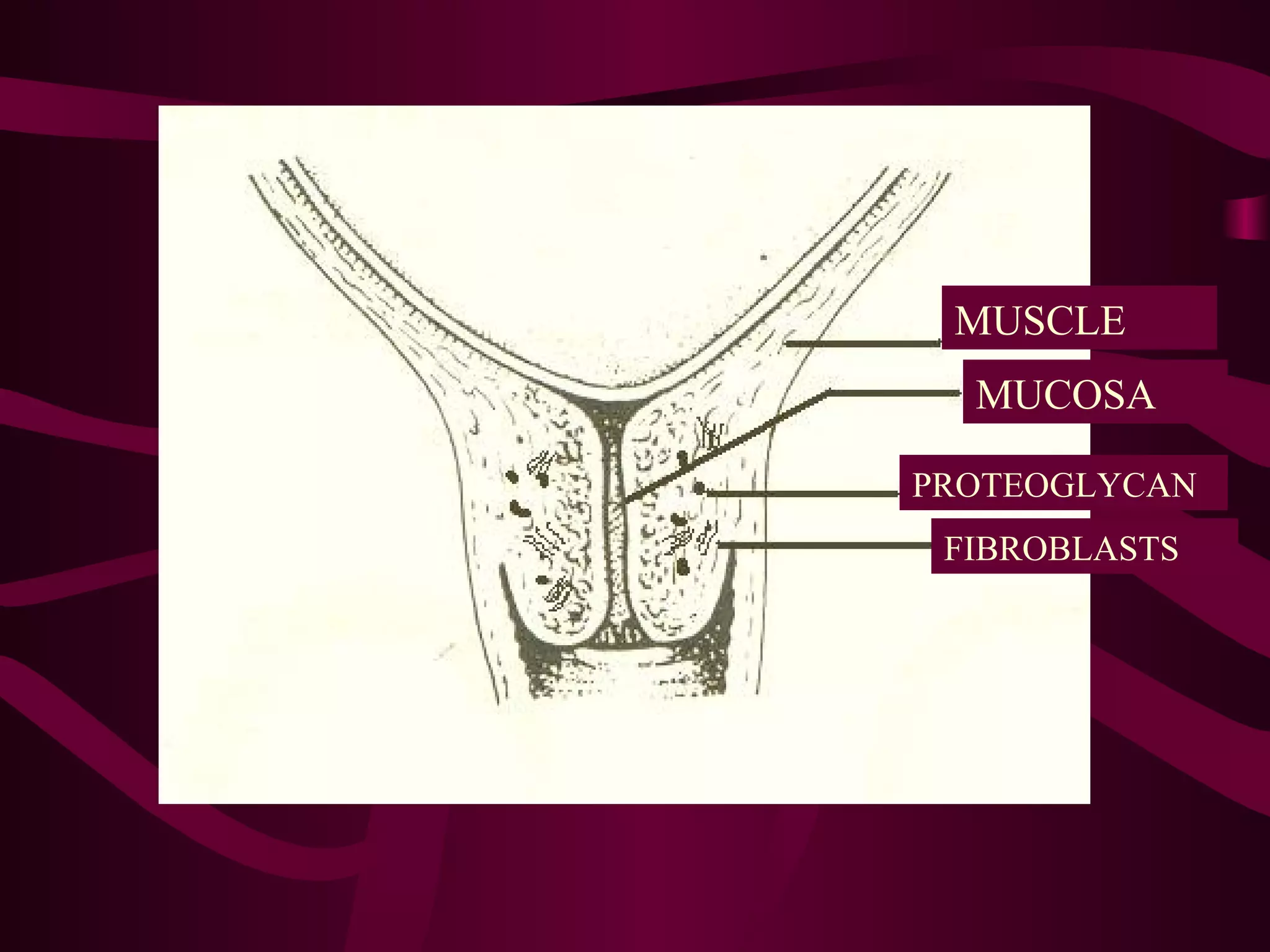
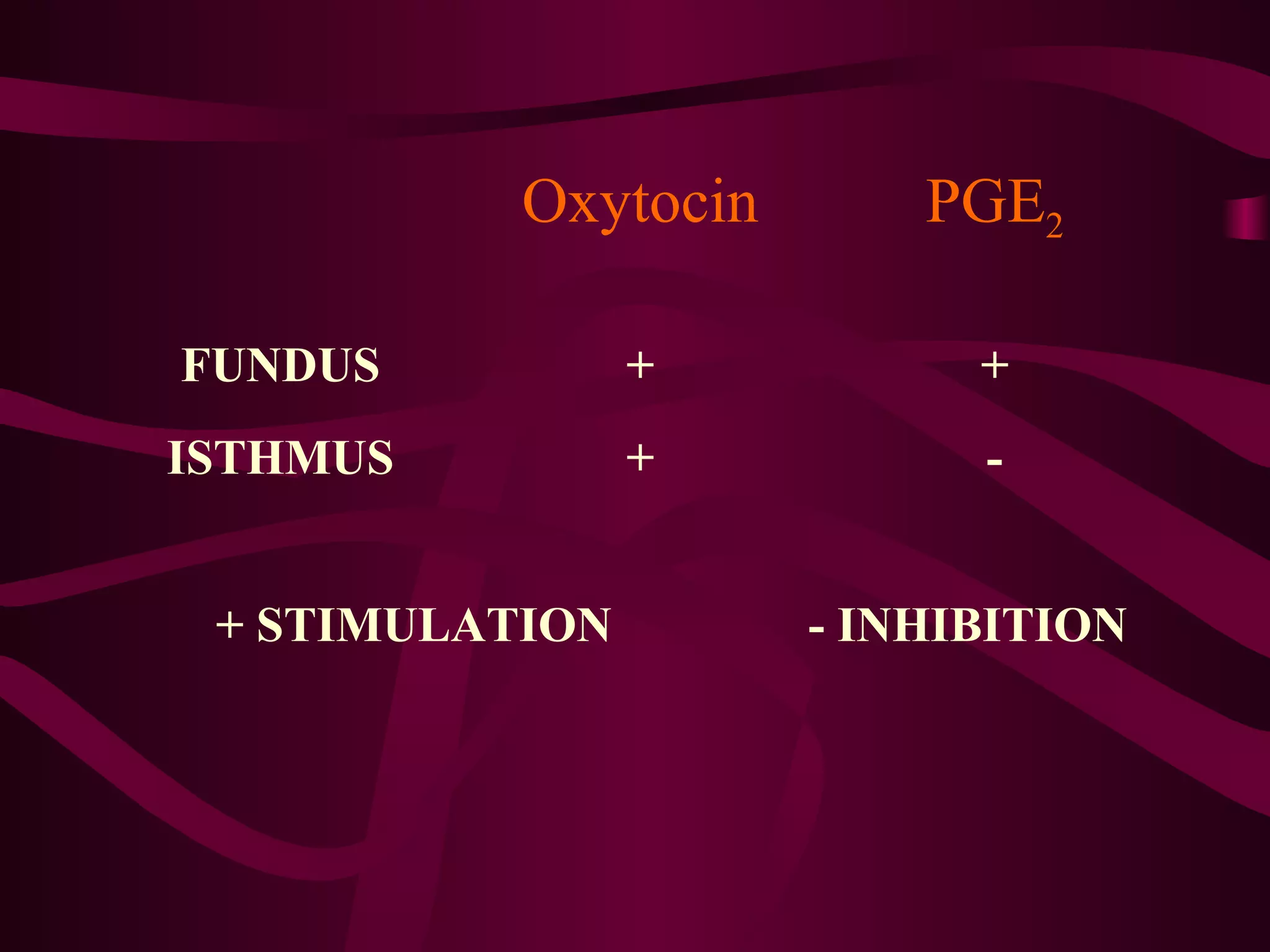
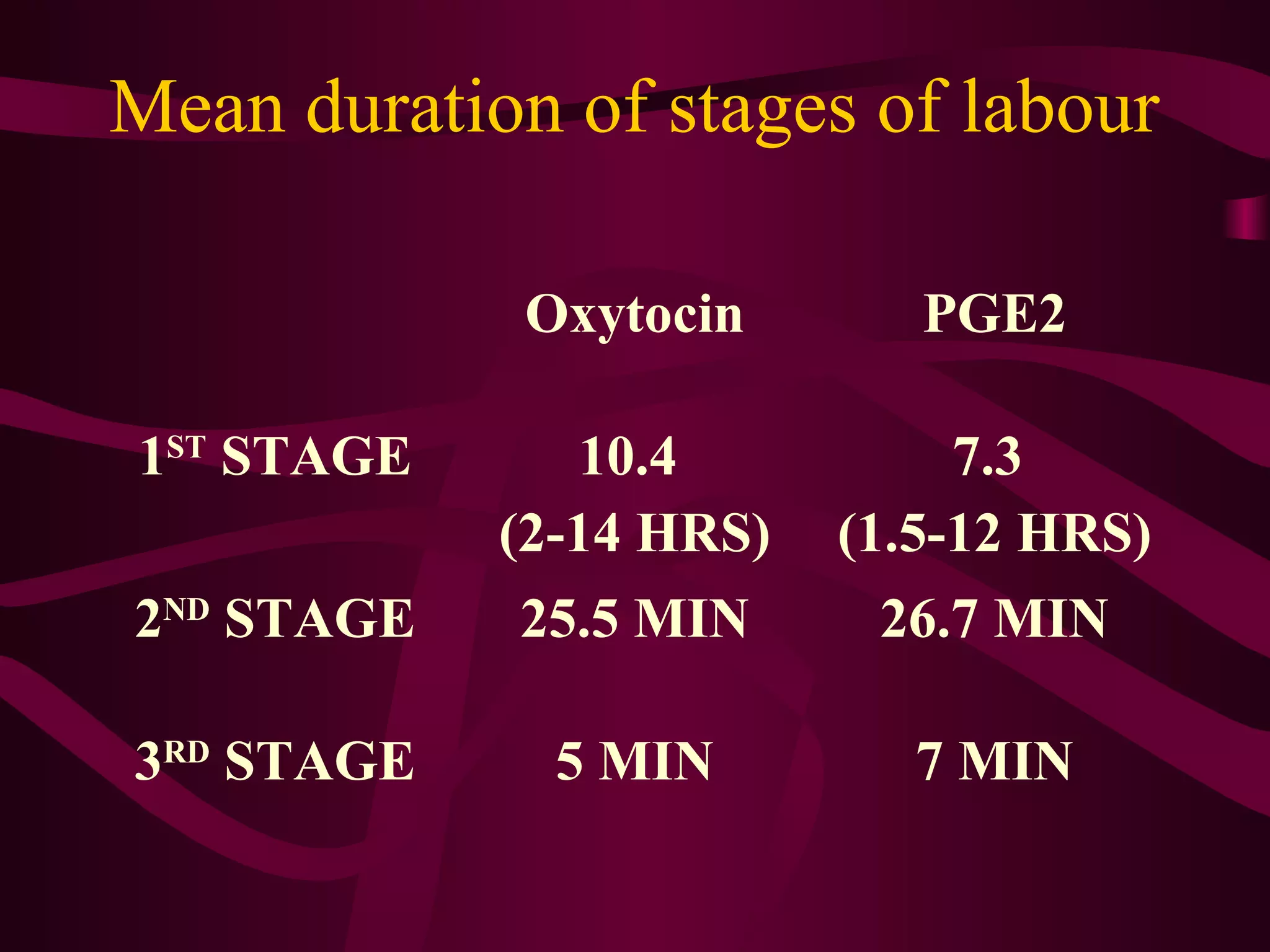
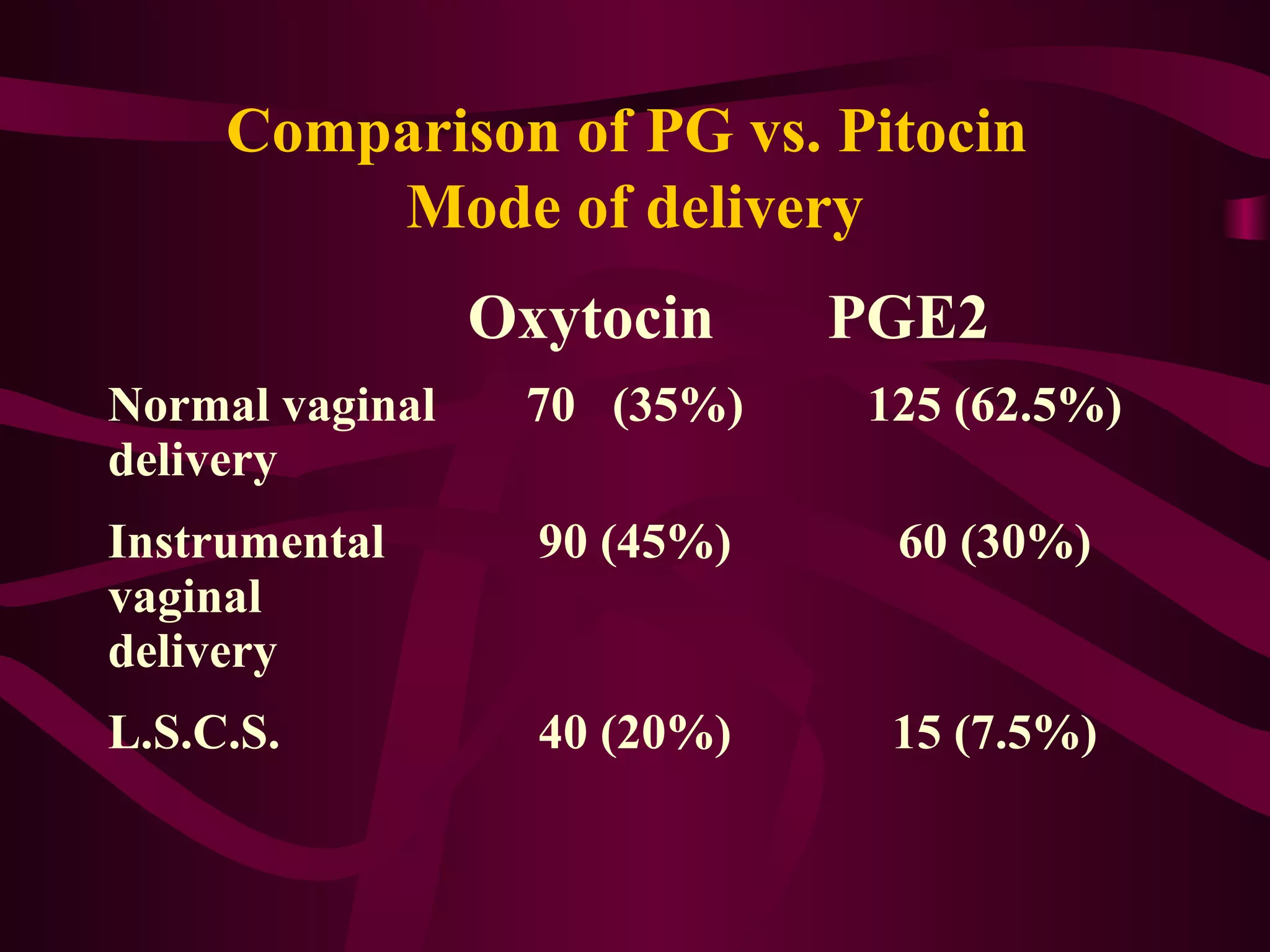
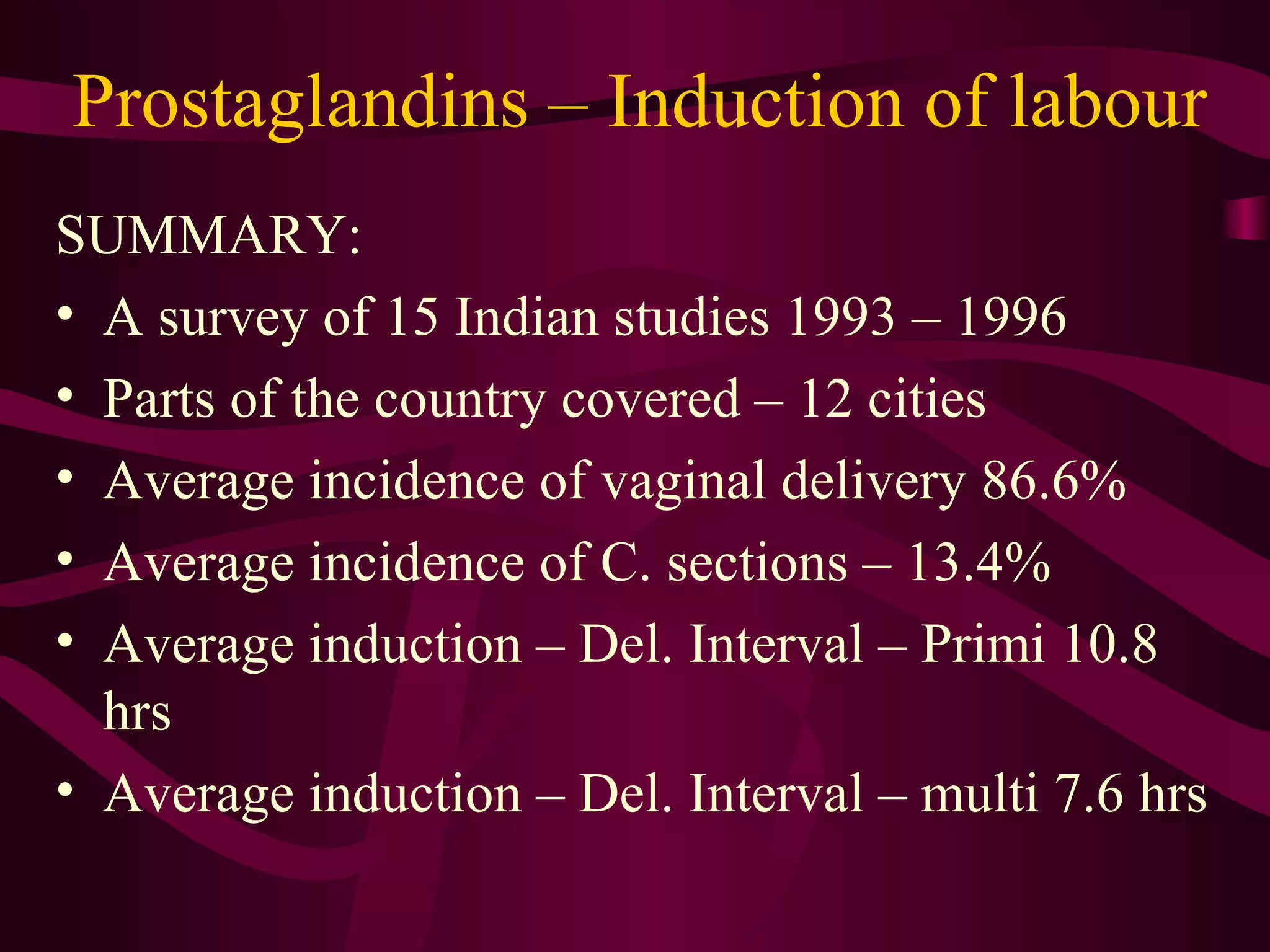
This document discusses the historical and clinical use of prostaglandins in obstetrics, specifically their role in inducing labor and cervical priming. It highlights the advancements in prostaglandin research, the efficacy of prostaglandin treatments compared to oxytocin, and various studies indicating their impact on delivery outcomes. The document also outlines the indications, contraindications, and formulations of prostaglandins used in labor induction, emphasizing their safety and effectiveness for both mothers and neonates.